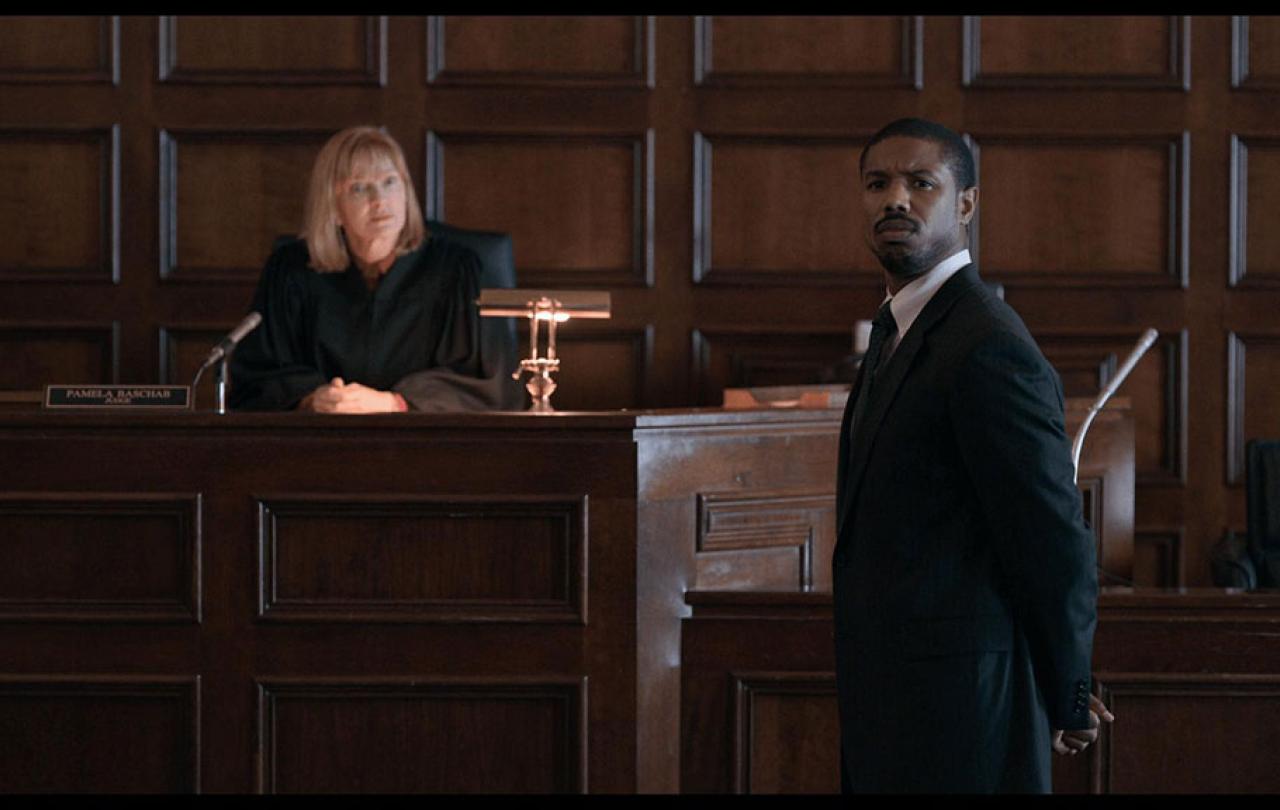
My friend Jo was killed by a lorry driver while she was cycling to work. She was thirty-four. The driver wasn’t paying attention. A couple of distracted minutes had tragic consequences. One life was lost; many others would never be the same again.
Months later, in court, the driver pled guilty to causing death by careless driving, and the judge warned him that he was facing time in prison. But between the verdict and the sentencing, Jo’s parents wrote to the judge asking him to show mercy.
So he did. The driver didn’t go to jail. He was spared the punishment that our legal system says he deserved. He admitted his guilt, and he didn’t ask for leniency or mercy or forgiveness, but Jo’s parents showed it anyway. They even made a point of going over to him to tell him clearly that they forgave him for taking their daughter’s life.
The court case was covered by national and local media, with one newspaper summing up what had happened with the headline: ‘Death driver shown mercy.’
It made national news because mercy of this magnitude is rare in society today. In fact, mercy of any magnitude is scarce. We live in an increasingly polarised world, where our desire for justice eclipses the beauty of mercy because we cannot see how both could exist at the same time. We want justice, and rightly so. We want people to pay for harm they have caused and we especially cannot abide it when the obviously guilty use their power, wealth or status to get them off the hook.
Extending mercy seems to us to come at the expense of justice. If we forgive, somehow that seems to deny the damage caused.
But cancel culture is rapidly turning our society into a place where anyone with a remotely public profile needs to live in fear of saying or doing anything wrong. We increasingly err on the side of cynicism when someone says they are sorry. We dismiss apologies, even when accompanied with tears and distress, as a stunt or ‘too little too late’ or more to do with being caught than with the original offence. We have become predisposed to assume the worst.
We start by recognising that justice in its purest form, at its best, is inherently merciful because it wants repentance more than it wants retribution.
I wonder if we have strayed beyond the necessary and right fight for justice into an insatiable appetite for vengeance, which leads us to a place where there is no space for contrition. If guilt is irredeemable, punishment must be permanent and absolute.
We argue that mercy is not deserved. And we are right. But it never is. If it were deserved, it wouldn’t be mercy. The very definition of mercy is that it is undeserved – to receive mercy is to receive kindness, compassion and forgiveness that you have no right to, no claim on, no reasonable grounds to expect.
But a bigger problem with our desire for justice over mercy is that we are not consistent. I know that my default is to want justice when I am wronged, but mercy when I am in the wrong. Who among us has not made a mistake or hurt someone else but then defended our actions by claiming mitigating circumstances or good motives? We want to be forgiven. Even when we know we have done wrong, we do not want to be punished.
I’m self-centred in my approach to mercy and justice. I am also way more lenient when those I love get things wrong than I am when someone hurts someone close to me. I assume that those dear to me had the best intentions, and those I don’t know or don’t like had the worst. My friends meant well; my enemies meant harm.
The Bible presents God as both merciful and just. It repeatedly affirms his concern for victims of injustice and reminds anyone who claims to know him that, if they really do, pleading the cause of the vulnerable and marginalised will be an inevitable (even required) outworking of that. It says that getting justice for the oppressed is more important to God than religious rituals such as fasting from food. In fact, it calls caring for the afflicted and distressed “true religion”.
But at the same time, Jesus told the religious people around him – the justice-warriors of his day who looked out for the slightest misdemeanour in others so they could call them out on it – that they needed to learn that God prefers mercy to sacrifice. Indeed, there is no example in the Bible of anyone pleading for mercy and God denying them. Even the most wicked and cruel abusers of power, if they humbled themselves and cried out to God for mercy, were shown it.
And it is not just God who exercises both justice and mercy. He says that he wants ordinary human beings to act justly and love mercy. In Christianity, justice and mercy are not pitted against each other; they are woven together as time and time again we are invited to live a better way by valuing and practicing both. Jesus criticised the religious leaders of his day for following all sorts of detailed and pedantic rules while neglecting what he called “the weightier matters of justice, mercy and faithfulness” and ultimately he died on the cross in the most astonishing act of faithfulness to bring perfect justice and limitless mercy.
But how do we mere mortals do both? We start by recognising that justice in its purest form, at its best, is inherently merciful because it wants repentance more than it wants retribution. Without repentance, there can be no reconciliation or restoration. A society that rules out redemption – that says no apology or atonement can ever be enough – will soon become a harsh and hopeless place. Biblical justice always leaves space for mercy. So must we.
‘Natalie Williams' Tis Mercy All: The Power of Mercy in a Polarised World is published by SPCK.