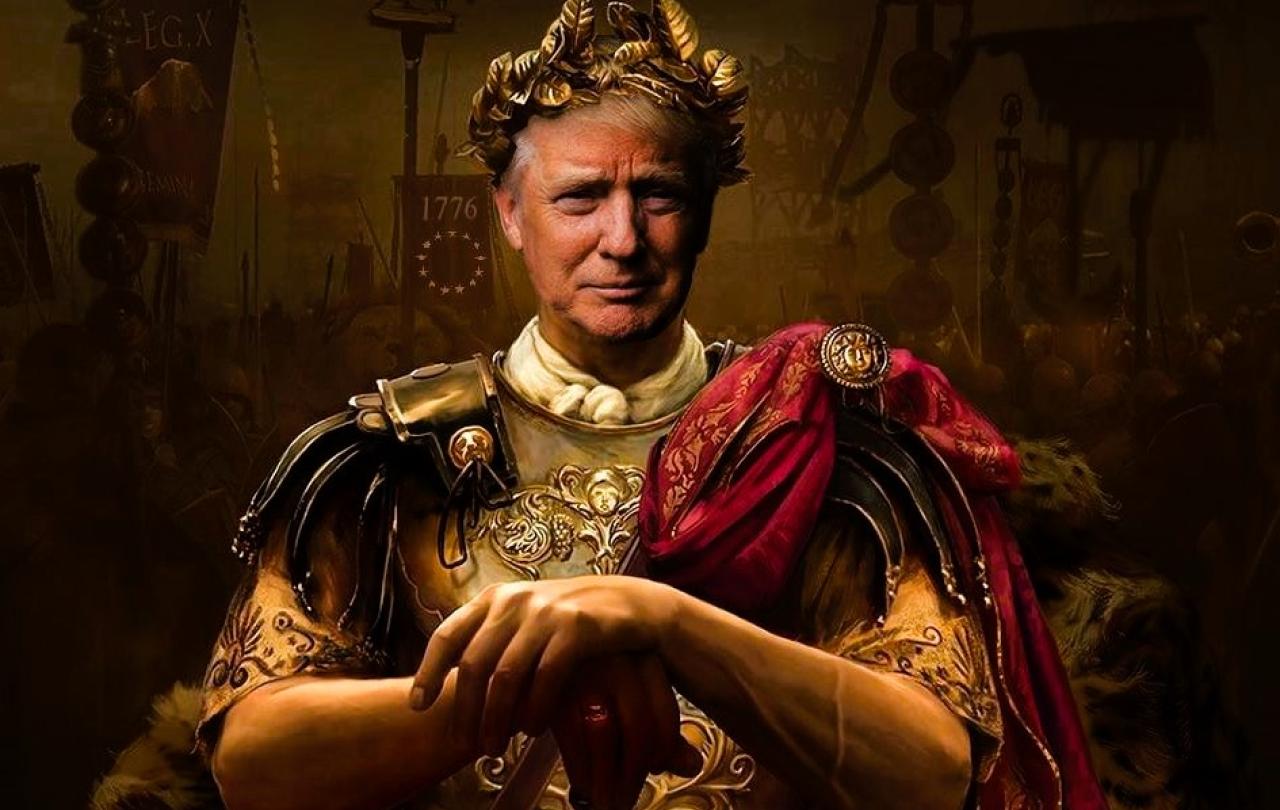
After years of polarised politics, nepotism from previous rulers and disputed claims to power, an unpredictable and egotistical leader believes that God had saved him to make the nation great again. He is acclaimed as the most powerful leader in the world and instantly surprises everyone by issuing a raft of disruptive new measures to radically change the way society functions and announces that he is going to target anti-Christian bias in society.
Sounds familiar?
No, it’s not Donald Trump. It is the fourth century ruler of the Roman empire – Constantine the Great. And the parallels are striking.
Constantine, the son of a Roman general and a Balkan barmaid, was the first Christian Roman emperor. Before then, all emperors were pagans, worshipping the Greek and Roman gods. In the early 300s AD, the emperor Diocletian launched a period of intense persecution of Christians, aimed at suppressing their subversive influence. After it died down, and after years of political infighting within the empire, Constantine marched on the capital and defeated his enemy Maxentius at the battle of the Milvian Bridge outside Rome. Just before the battle, Constantine had a dream in which he saw a sign of something that looked like a cross in the sky, with the tagline “in this sign, conquer”. From that time onwards, he believed that God had chosen him for this direct purpose – to bring peace to the empire by conquering its enemies, internal and external, under the banner of Christianity.
After his accession Constantine, like Trump, introduced new economic policies to reverse rampant inflation, restructured government, and strengthened military capacity to deter the empire’s enemies. He also started to give privileges to the until-now persecuted Christians. Paganism, the ‘official’ religion of the empire was increasingly relegated to second place. Churches were granted land on which to build new edifices, and gatherings of Christian leaders became commonplace, some of which he presided over, such as the Council of Nicaea which took place in 325 AD, 1,700 years ago this year. Christian priests were excused from public duties to give themselves to their prayers. Crucifixion was abolished as a form of execution. Sunday became a weekly holiday, pagan practices were outlawed in public.
Historians have debated Constantine’s motivation for years. Was he a genuine Christian, wanting to advance the faith by giving the church a good run at converting the empire? Was he a boon for the church in releasing it from the burden of persecution? Certainly, at the time, many Christians were delighted, enjoying their new privileges and access to the imperial court like wide-eyed pastors invited to the White House. Eusebius, the great historian of the early church wrote: “in every city the victorious emperor published decrees full of humanity and laws that gave proof of munificence and true piety. All tyranny had been purged away.” It could be the voice of a Southern Baptist.
Yet on the other hand, Constantine was irascible, unpredictable and vindictive. He had his second wife, three brothers-in-law, his eldest son and his father-in-law executed.
His vanity extended to renaming the old city of Byzantium, newly made the capital of the empire after himself – Constantinople. Was he cynically using the growing cultural force of Christianity to bring unity to a divided and fragmenting empire? Some historians suggest that in doing so, he fatally changed the nature of Christianity. Constantine was exactly the kind of military messiah that first century Jews had expected, yet one totally different from the crucified rabbi from Nazareth.
Which was it? It's hard to tell. He certainly promoted the Christian faith and gave it new freedoms. Yet, although he presided over the Council of Nicaea, with its famous decree that Christ shared the same nature (‘consubstantial’ was the technical term) as God the Father, there is little mention of Jesus in Constantine’s religion. He sometimes seems to have thought of himself as the Saviour of the Church rather than Christ, with the watershed of history not in the first century with the victory over sin and death in the Resurrection of Jesus, but in the fourth century with his own victory over Maxentius.
For some historians, the Christian church was originally a counter-cultural movement, offering a radical new vision of life, favouring the poor over the rich, the weak over the powerful, centred on the crucified Jesus. After Constantine, Christianity became centred on a majestic ruler of the heavens and the earth. Christ the Pantokrator, the image of Christ in glory found in Orthodox churches around the world replaced images of Christ on the cross. This was, they suggest, not Constantine being formed into the image of Christ, but Christ being conformed to the image of Constantine.
Christians might be glad of the opportunities that a Trumpian world might offer. But they need to be careful in what they wish for
The similarities with Donald Trump will be obvious, even if different readers will vary on how they see the extent of the likeness. They both favoured Christianity even though their own personal faith is hard to pin down. They can both be ruthless and vindictive towards those that cross them. They are not afraid to tear up the rule book and adopt new policies that shake up the established order.
So, what might the story of Constantine have to tell us as we consider the second coming of Donald Trump?
Many Christians rejoiced at Trump’s re-election. At his inauguration, Franklin Graham, like Eusebius many centuries before, pronounced that God had ‘raised up’ the new President. Trump himself claimed that God had saved him through the assassination attempt last year to Make America Great Again. Others see it as a disaster, offering a ruler of dubious character who looks nothing like Jesus.
Constantine was, on balance, a mixed blessing for the church. His rule did enable the church to thrive. It gave it a position within society that made possible a network of churches, parishes, dioceses that helped its message spread far and wide. It was no doubt easier to be, and to become a Christian under Constantine than under his anti-Christian predecessors. Yet at the same time, he subtly changed the shape of Christianity and made the Church the faith of the powerful, even though Christianity has always flourished more among the poor and struggling who know they need help.
The Church under Trump might be glad of laws and cultural moves that make it easier to practice and promote their faith. Yet the danger of allowing Trump rather than Jesus to determine the Church's vision of leadership and lordship, remains. In subsequent years, while making the most of the opportunities that a newly Christianised empire gave, the church also needed figures like Ambrose, the fourth century Bishop of Milan who was willing to ban the emperor Theodosius from church when he committed crimes in the name of the empire. It also needed the radical Christianity of the desert fathers and mothers who withdrew to remote places to pray and live a radically alternative lifestyle from the increasingly soft and easy Christianity of city life. As Paul Kingsnorth recently reminded us, “the monks built the West, just as surely as the soldiers did, and they built the more enduring part.”
Christians might be glad of the opportunities that a Trumpian world might offer. But they need to be careful in what they wish for. Followers of the crucified rabbi from Nazareth need to be wary of hitching their wagon to any one political ruler. There is only one messiah after all.
Join with us - Behind the Seen
Seen & Unseen is free for everyone and is made possible through the generosity of our amazing community of supporters.
If you’re enjoying Seen & Unseen, would you consider making a gift towards our work?
Alongside other benefits (book discounts etc.), you’ll receive an extra fortnightly email from me sharing what I’m reading and my reflections on the ideas that are shaping our times.
Graham Tomlin
Editor-in-Chief