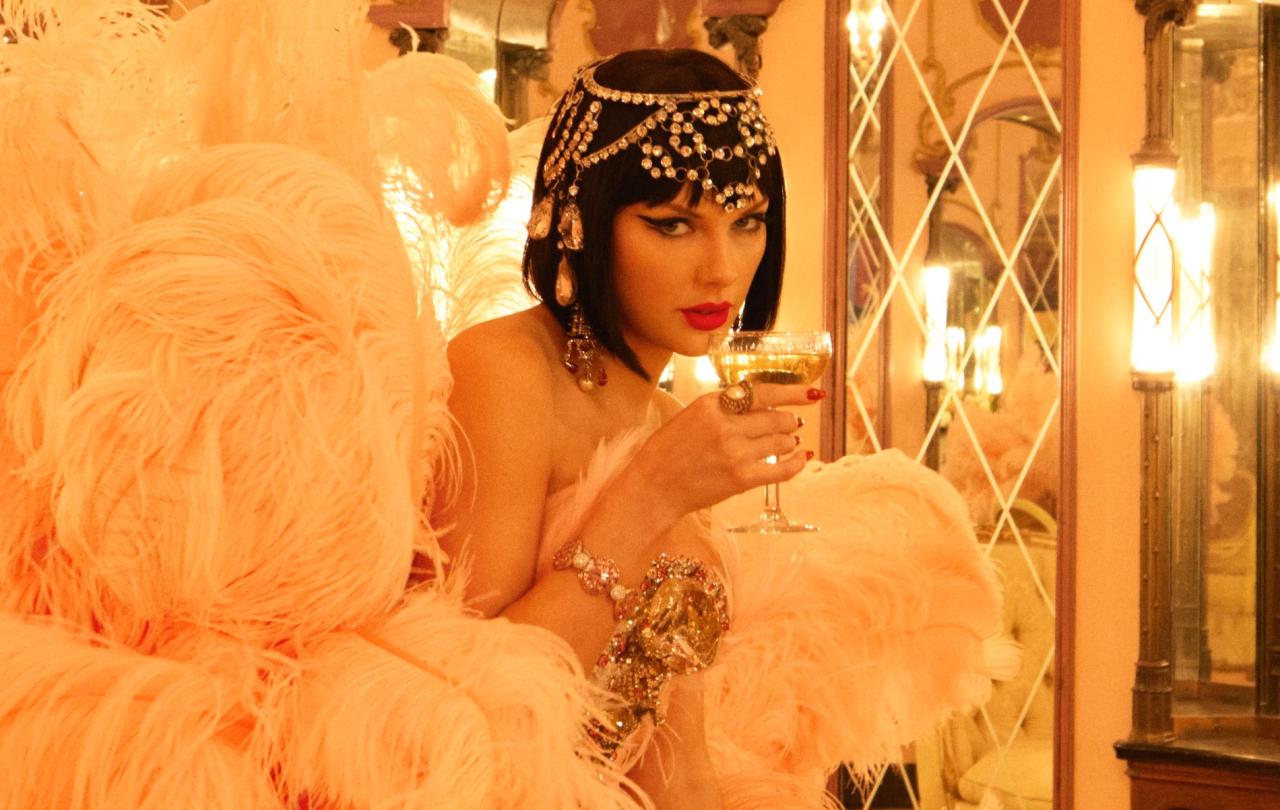
Taylor Swift released an album last week and, from what I can see, the world seems to hate it.
Life of a Showgirl was written and recorded while Taylor was on her two-year-long Era’s tour, hence the album’s title. She would fly to Sweden between tour dates to record with the infamous producers, Max Martin and Shellback. This matters. Why? Well, because this means that each song on this album has grown out of the soil of unfathomable success; record-breaking numbers and history-making impact, it’s not an exaggeration to say that the Era’s tour shifted the landscape of popular culture. Many critics have reflected on this context, citing ‘burnout’ and ‘frazzle’ as reasons why this album sits far below Taylor’s usual standard.
They implore Taylor to take a day off: put her feet up, recuperate, and re-gather her musical senses.
Then there are the critics who seem to be directing blame toward Taylor’s obvious happiness. If you didn’t know, she’s engaged to American footballer, Travis Kelce – and they, as a couple, are sickly sweet. Honestly, they’re defiantly mushy. They’re cheesy to the point of protest. They’re just happy – and, apparently, therein lies the problem. I’ve heard more than one critic quote Oscar Wilde in their takedown of Swift’s latest offering:
‘In this world there are only two tragedies: one is not getting what one wants, and the other is getting it’.
This album, they say, is proof that Taylor Swift is victim to the latter kind of tragedy. She’s got everything one could ever want, and the world seems pretty agreed that her music is suffering because of it. We like to keep our artists tortured, thank you.
For the record, I don’t hate the album. But I don’t love it either. I resonate with The Guardian’s Alexis Petridis who writes that it simply ‘floats in one ear and out the other’. There’s nothing to hate about it, which, I guess, also means there’s very little to love about it. I’m not outraged, nor am I enamoured – and I say that gingerly, because I fear that’s the worst review of all.
So, in some ways I’m agreeing with the general consensus – Life of a Showgirl is not Taylor Swift’s best work. I don’t, however, think that her success, nor her happiness, are quite to blame for it. I think those are slightly lazy critiques, they’re shallow scapegoats.
I think, rather, the problem with this album is that Taylor has made herself the biggest thing within it.
When introducing the album on Instagram, she thanked her collaborators for helping her to ‘paint this self-portrait’ – the strange thing is that this ‘self-portrait’ feels considerably less honest or authentic than her previous, more conceptual, albums.
I’ve spent a couple of days wondering why this is and have come up with two theories.
Firstly, we tend to be far more honest to and about ourselves when we’re able to kid ourselves into thinking that it’s not actually our own selves that we’re talking about. For example, I think of Billie Eilish’s Grammy and Academy Award-winning song – What Was I Made For? – which she wrote to accompany Greta Gerwig’s Barbie movie. In an interview, Billie explained how writing a song about a Barbie somehow allowed her the space and freedom to create the most honest, raw, and revealing song she’d ever written.
We’re self-preserving creatures, you see.
If we’re knowingly speaking of, writing about, painting or in any way presenting ourselves - our ego gets in the way, preferring us to offer the world a shiny, carefully constructed façade.
Taylor, in intentionally painting a ‘self-portrait’, has unknowingly offered us less than herself.
And, now for my second theory. Every good self-portrait is actually about something bigger than its subject; they are able to point toward something more universal than the individual reflected. I think of Frida Kahlo’s self-portraits, the way she used her hair to communicate societal expectations, or how she framed herself with wildlife, or the time she painted a necklace of thorns around her own neck – leaving an uncomfortable feeling in the pit of the beholder’s stomach as they think about the nature of pain and liberty. She painted herself, endlessly. Kahlo pointed to herself in order to point through herself – she was never the subject that she was most interested in, she was never the biggest thing in her own self-portrait.
Like I say, the problem with Taylor Swift’s okay-ish album is simply that she is the biggest thing within it. The key ingredient it’s lacking is awe; it leaves nothing to marvel at.
And that’s rare for Taylor.
I’ve often written that she is a Romantic in every sense of the word; concerned with the feelings and experiences that are powerful enough to knock us off our feet: big feelings, big thoughts, big truths, big questions, big mysteries, big language. These things have always been baked into her lyrics.
This album, in comparison, feels small. It doesn’t transcend Taylor Swift’s feelings about – well, Taylor Swift. She hasn’t quite managed to point through herself, she is the sole subject of her own self-portrait.
And therein lies its OK-ness.
Honestly? Therein lies all of our OK-ness. Taylor Swift may be anomalous in many things, but not in this - the presence of ego means that we’re all prone to self-portrait-ise ourselves. Left unchecked we are (or at least, we can be), what Charles Taylor calls, ‘buffered selves’; thinking of ourselves as the maker and subject of all meaning, shielded from awe and wonder.
But the best art will never flow from those who think themselves the biggest and deepest subject. Because, quite simply, we’re not.
Support Seen & Unseen
Since Spring 2023, our readers have enjoyed over 1,500 articles. All for free.
This is made possible through the generosity of our amazing community of supporters.
If you enjoy Seen & Unseen, would you consider making a gift towards our work?
Do so by joining Behind The Seen. Alongside other benefits, you’ll receive an extra fortnightly email from me sharing my reading and reflections on the ideas that are shaping our times.
Graham Tomlin
Editor-in-Chief