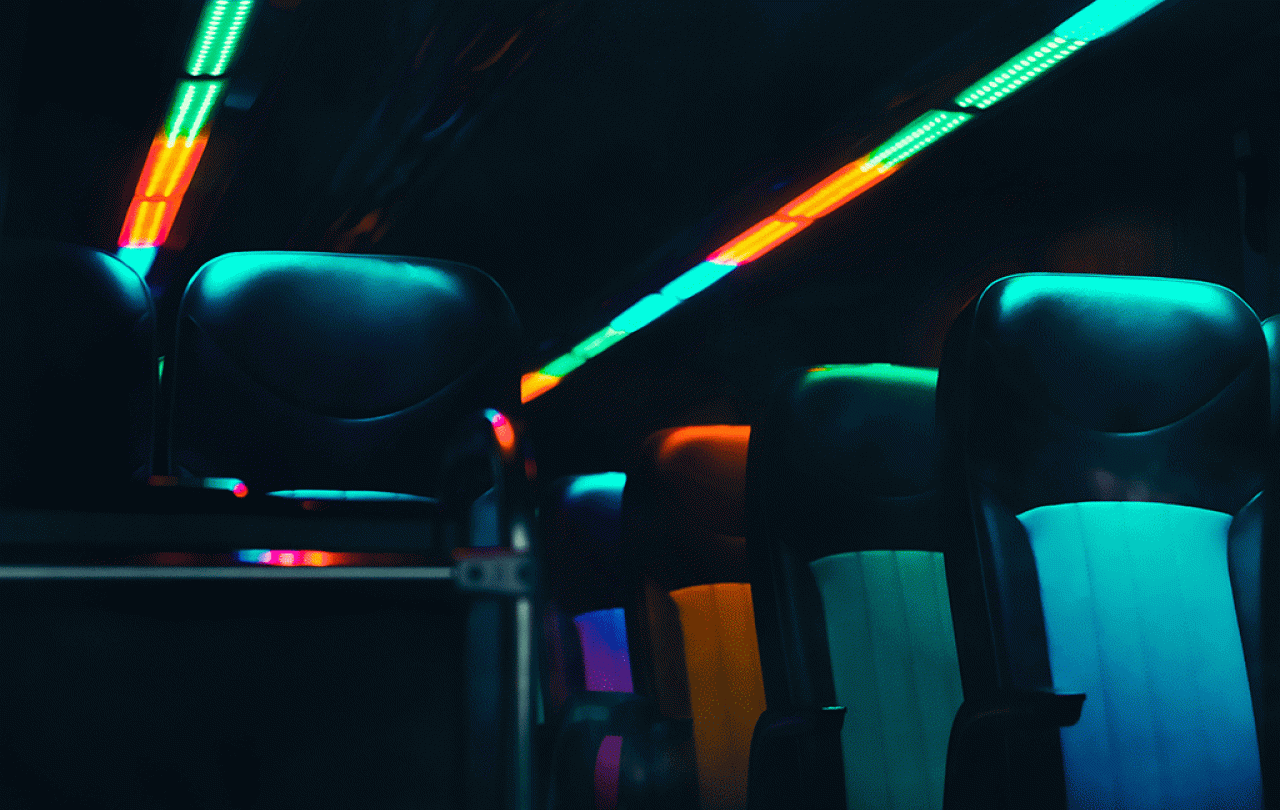
It is 1979. I am aged 23 and have been in great mental and emotional anguish and pain for years. I am on a pointless journey, on Greyhound busses, from the East coast of America to the West, and am presently sitting in a parked bus just outside a city in Arizona; the powerful engine idles as we wait for departure time, giving a gentle to-and-fro rocking motion to the bus. I have not eaten for days, am unspeakably tired of my life, and have made a written list of possible ways to end it.
But not on that list is one possibility I have not previously considered, but which is now before me. As I look out to my right, up into the Arizona desert hills, I realise that here is an option which perfectly fits with my desire, not so much to do away violently with myself, as simply to drift into a passive oblivion; I realise that I could simply rise from my seat right now, get off the bus, stumble off into the desert hills, lie down, and wait to die. I need not shoot or poison myself after all. I know I can do this, and fairly easily; to die will take time, but no matter. No-one knows where I am, no-one will know I am missing, no-one will come looking for me, and probably no-one will find me. It is suddenly an immensely attractive prospect, and I am seconds away from rising up from my seat...
There is one thing, one thing only, that makes me hesitate; it is what other people would call ‘a religious belief’, but to me it is simply a truth.
It is this; I am absolutely sure that there is a God. And suddenly there is something grimly, darkly humorous even, in what I thus believe will follow my death; I will find myself, not in peaceful oblivion, but in the presence of God. I will, as they say, ‘meet my Maker’. And what then will I say to God? I will say: “Apologies: I could not go on, there was no other way out for me”. But what, I reason, if God were then to say: “You are wrong. There was a way forward. Look: you could have stayed on the bus, and had you done so, let me show you how your earthly future would have panned out…” And I will listen, and I will watch, as the film rolls on, showing me an alternative future. But of course, by then it would be too late…
And suddenly, sitting on that bus, in a moment of cold clarity, I realise, with a kind of desolate logic, how I am caught. In a very real sense, my belief in God my Creator means that I am not in fact ‘free’ to dispose of myself; more, that what I refer to so glibly as ‘myself’ is not in fact MY self. The bus ticket in my pocket may be ‘my’ ticket, my rucksack ‘my’ rucksack, but my life is not after all my possession, mine to dispose of; it is a loan, a gift, from a Giver, to Whom I am responsible, answerable…
I remain in my seat. The bus continues its gentle rocking motion a while longer. The driver gives his familiar 1970s Greyhound driver’s recitation, the various admonitions and prohibitions I have heard so many times as I have crossed America, I could give the speech myself (ending with the words ‘and no marijuana’, which always raises a smile) – and the bus pulls out onto the freeway. I look back over my shoulder at the desert hills as they recede, and feel I am leaving more than the desert hills behind; I am still in deep pain, but know I have left a possibility behind me, for good. Months later I will reflect on this moment and realise with a smile that the name of the city where I had put death behind me by not rising was Phoenix.
And so my journey has continued – on, in due time, to a return to England, to a measure of healing, to getting ordained as an Anglican priest, to thirty-four years of Church ministry, to marriage to a very remarkable woman, to fatherhood of two children - and, at some future moment, to my own death: all in God’s time.
How shoddy, shrunken and lonely, is our much vaunted and trumpeted vision of the autonomous individual.
The word ‘God’ was probably used very little, if at all, in the MPs debate on assisted suicide - and this debate has really been about assisted suicide, not ‘assisted dying’, given that people will be given drugs to self-administer. Even the Christian MPs who spoke, did not mention God, as they knew what could be said, and what could not, in order for them to be heard at all. The public arguments for, and against, the legalisation of assisted suicide have almost without exception had to be premised on one agreed assumption, apparently the only one now permissible in a post-Christian, liberal humanist, agnostic/atheist society: the assumption that my life is mine. The arguments used for assisted suicide resolve down to: “It is my life: I should be allowed to decide when to end it”. Most of the arguments used against resolve down to: “Yes, of course, granted, agreed, it is your life: but there may be unintended consequences for others in allowing you to end it, others may feel obliged to end their lives”, etc. At no point could anyone say, as I so passionately would claim: “No, it is not your life to dispose of”; there is now, it seems, no public place for the apostle Paul’s blunt statement in his letter to the Church in Corinth: ‘You are not your own.’
Yet this is now one of the most fundamental beliefs of ‘my’ life: and I have found it to be totally liberating and beautiful. I think of those glorious sculptures on the outer walls of Chartres Cathedral, including the representation of the creation of Adam, presented as emerging from the very mind of God. I think of the glory of man and woman made in God’s image as stewards of creation. I think of the extraordinary wonder of the Incarnation, of God embodied in Christ. I think of the sufferings of Christ on the cross; and I think, yes, of course I think, of the sufferings of my fellow men and women and children, and of my own sufferings, and of the call to me to shoulder the burden, both of living, and of dying, in God’s time.
And, alas, I think I also see something of how shrivelled, how wizened in comparison, how shoddy, shrunken and lonely, is our much vaunted and trumpeted vision of the autonomous individual – “my life, my rights, my body, my choice” - in the dominant contemporary Western mindset, eating away steadily like a corrosive acid any wider conception of community and the social institutions that enshrine it, and any sense of a deeper accountability to God.
Where will the current assisted suicide decision ultimately lead? What is the destination? It is difficult to predict, but the signs from other countries who have gone down this road are not good.
But what do I know? Do I have answers to all the questions around assisted suicide? I confess I do not. But one thing has become clearer to me: I am on a very different journey from the one my nation is travelling now.





