Portrayals of mental health were revolutionised from the nineteenth century onwards. While previous generations had focused on the ostracism of those suffering mental illness, and the fear their condition aroused in others, modern artists began to focus on the dignity and humanity of sufferers. Four current London exhibitions show this move towards compassion.
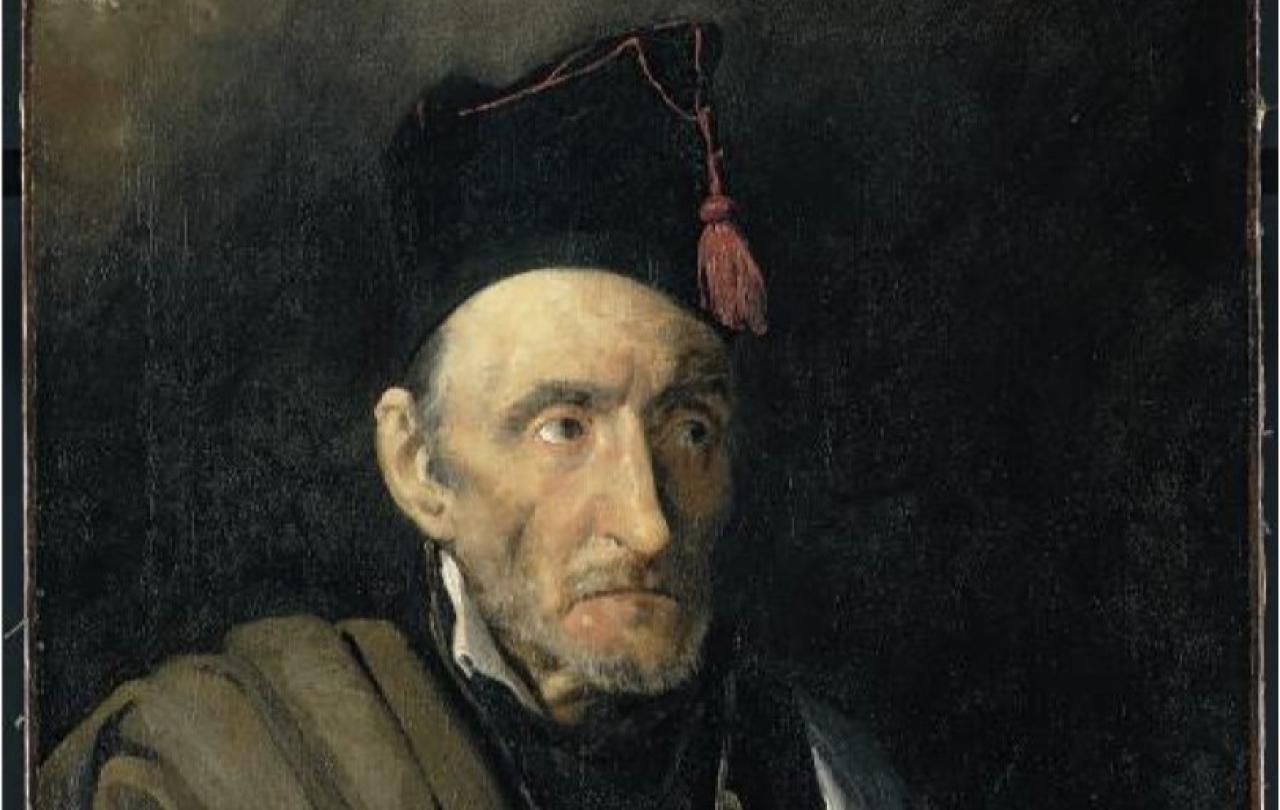
On display at the Courtauld’s Goya to Impressionism, Theodore Gericault’s A Man Suffering from Delusion of Military Rank, c.1819 -22, shows the artist’s sensitive response to ‘monomania’, the term coined in the early 1800s for people living with a single delusional obsession. It is thought this painting is part of a series of portraits on fixations including A Child Snatcher, A Kleptomaniac, A Woman Addicted to Gambling and A Woman Suffering from Obsessive Envy, the face of the last rendered in an unsettling green tinge.
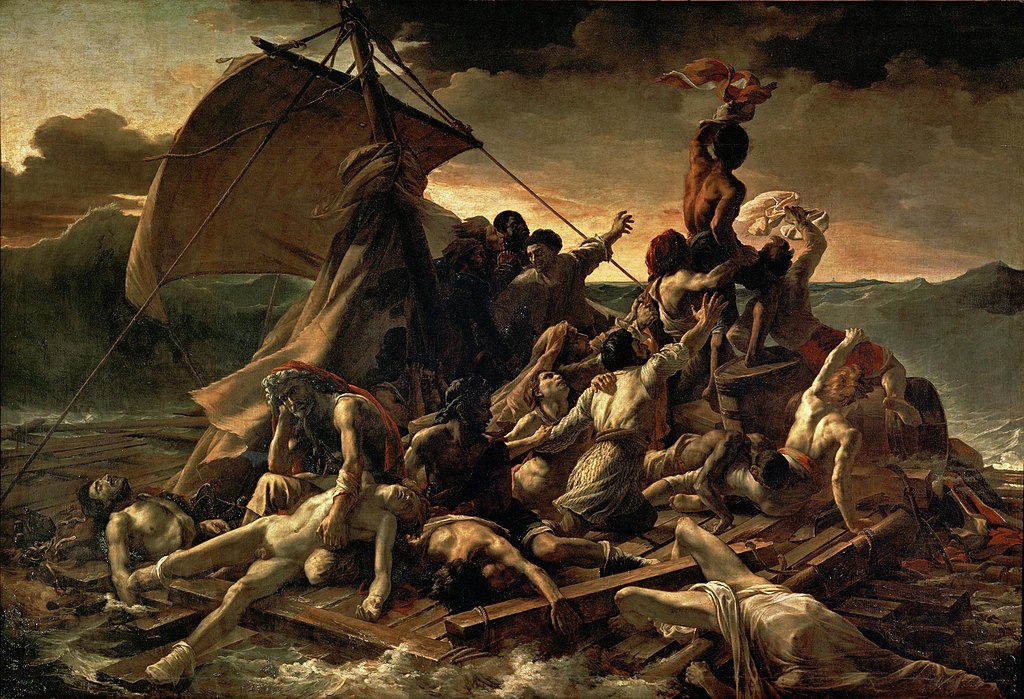
The circumstances surrounding the painting of the series remain mysterious. The timing coincides with Romantic painter Gericault completing his most famous work, the monumental The Raft of the Medusa, 1818-19, depicting 15 survivors of a shipwreck, who had been adrift on a makeshift raft, originally containing 147 passengers, from the French frigate Meduse. Gericault’s preparation for the canvas included visiting morgues to check on the colour of decomposing flesh and building a model of the doomed raft. His difficulties in completing the huge work, over 23 feet long, and the possibility some of his close family may have suffered from mental illness, have supported the belief Gericault painted A Man Suffering from Delusion of Military Rank, and related portraits for personal reasons, possibly out of gratitude to the physician who cared for his family. But there is now doubt if Dr Etienne-Jean Georget commissioned the painting, and whether he was chief physician at Saltpetriere asylum in Paris.
Even if a biographical motivation for the series falls down, and there is no way of knowing if the subjects of the portraits were individuals living with mental health conditions, these portraits remain unique in early nineteenth century painting. People deemed at the very margins of society are portrayed in the same manner as the most powerful, in half-length portraits emphasising their dignity and humanity, over their social estrangement and health challenges.
The Raft of the Medusa, Louvre, Paris.

Van Gogh’s mutilation of his own ear is interwoven into his biography and his art. In The Ward in the Hospital at Arles and The Courtyard of the Hospital at Arles, both 1889, the artist depicted the interior and exterior of the institution where nuns cared for him, during his mental health crisis. The paintings’ significance to his recovery is shown by Van Gogh taking them with him when he moved to another psychiatric facility 25 kilometres away at Saint-Remy-de-Provence.
Blue is the dominant colour of The Ward, permeating the walls, the beamed ceiling, the crucifix and the door underneath it, and several patients. wear dark blue clothing, including the two nursing Sisters at the centre of the scene, whose Order of St Augustine black and white habits, have been realised in darkest blue. Van Gogh described the long ward as ‘the room of those suffering from fever’, most probably referring to patients with mental illness. The painting was reworked during the artist’s admittance at Saint-Remy-de-Provence, with the symbolic empty chair used in other works to represent him and his housemate Paul Gauguin added to the foreground, together figures gathered around a stove. The return to the painting was prompted by reading Dostoevsky’s The House of the Dead, a fictionalised account of the author’s spell in a Siberian prison, and the book’s characters may have provided the inspiration for the huddled men.
The Courtyard of the Hospital at Arles captures the grace of the hospital’s Renaissance building, by depicting the inner courtyard from the vantage point of the first-floor gallery. From this aerial angled viewpoint, the garden’s bright flora, radiating from a central pond, spreads out in all directions. Van Gogh’s description of the scene to his sister Willemien, hints at their Bible reading, clergy childhood: ‘It is therefore a painting full of flowers and springtime greenery. Three dark and sad tree trunks however run through it like snakes…’
Van Gogh’s images of healing were from memory rather than life, and document his own mental health recovery:
‘I can assure you that a few days in hospital were very interesting and one perhaps learns how to live from the sick.’
The Ward, Vincent van Gogh, Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons.

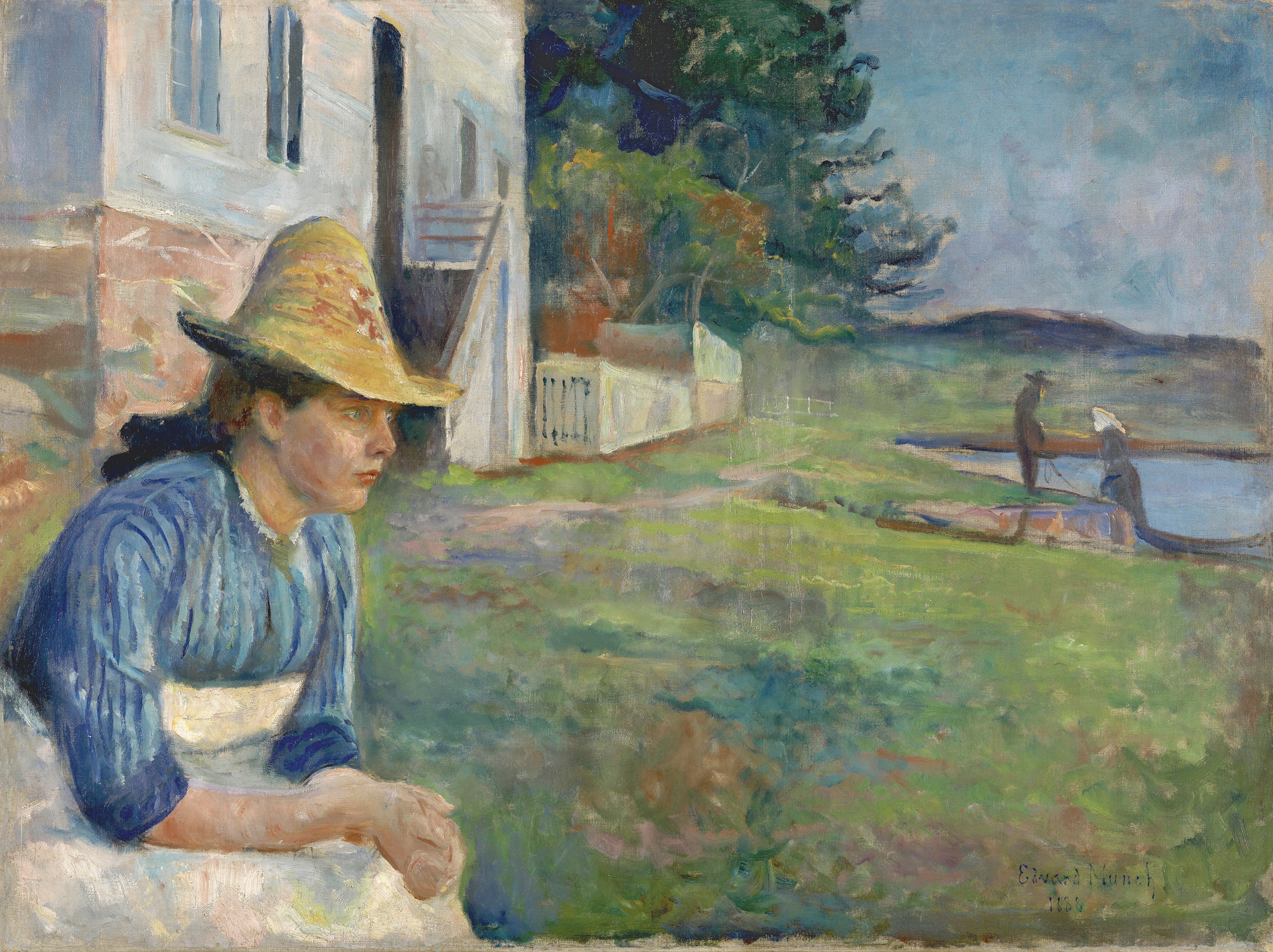
Edvard Munch's Portraits, Evening 1888, shows the artist’s sister Laura, who had been hospitalised for mental illness, on and off, since adolescence. Although Laura is lost in her own world, staring fixedly ahead against a coastal landscape, the affection of the artist for the subject is palpable. Fashionably dressed in straw hat and summer dress, Laura’s dignity anchors the composition. Munch documented his own breakdown after alcohol poisoning in a portrait of Daniel Jacobson. His full-length portrayal of the doctor, arms akimbo, drew the reaction: ‘just look at the picture he has painted of me, it’s stark raving mad.’ Munch’s fascination with the doctor-patient relationship is evident in Lucien Dedichen and Jappe Nilssen, 1925-6, where Dedichen’s looming, purple presence, overshadows the diminutive, seated patient.
Portrait, Evening. Museo Nacional Thyssen-Bornemisza, Madrid.

Mental health and delusion form the wellspring of Grayson Perry’s Delusion’s of Grandeur. The artist responds to the Wallace’s flamboyant rococo collection in the persona of Shirley Smith, a character believing she is the rightful heir of the Wallace Collection. Eighteenth century style ceramics are decorated with outline figures resembling the Simpsons. Perry creates a family tree for Shirley from the Wallace’s miniatures, A Tree in the Landscape where every member has a condition from the American psychiatric guide Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders.
Grayson Perry, Untitled Drawing, Courtesy the artist and Victoria Miro.

In Alison Watt: From Light at Pitzhanger Manor, the artist’s still lifes of roses, fabrics and death masks responds to the collection of Regency architect Sir John Soane, and the ever-present fragility and complexity of human life and psychological flourishing. “With a rose it is impossible not to be aware of human intervention. Roses are bred, altered outside of nature and given names. In the history of painting the rose can be read as a symbol of beauty, innocence and transience, but also of decline and decay, echoing Soane’s preoccupation with themes of death and memorialisaton.”
With the scientific and medical advances of the nineteenth century, life in all its psychological complexity, could supplant death as artists’ inexhaustible fount of inspiration.
Le Ciel, Alison Watt.
Find out more.
-
Goya to Impressionism. Masterpieces from the Oskar Reinhart Collection, Courtauld Gallery.
-
Edvard Munch Portraits, National Portrait Gallery.
-
Grayson Perry Delusions of Grandeur, Wallace Collection.
-
Alison Watt From Light, Pitzhanger Manor.
Celebrate our 2nd birthday!
Since Spring 2023, our readers have enjoyed over 1,000 articles. All for free.
This is made possible through the generosity of our amazing community of supporters.
If you enjoy Seen & Unseen, would you consider making a gift towards our work?
Do so by joining Behind The Seen. Alongside other benefits, you’ll receive an extra fortnightly email from me sharing my reading and reflections on the ideas that are shaping our times.
Graham Tomlin
Editor-in-Chief





