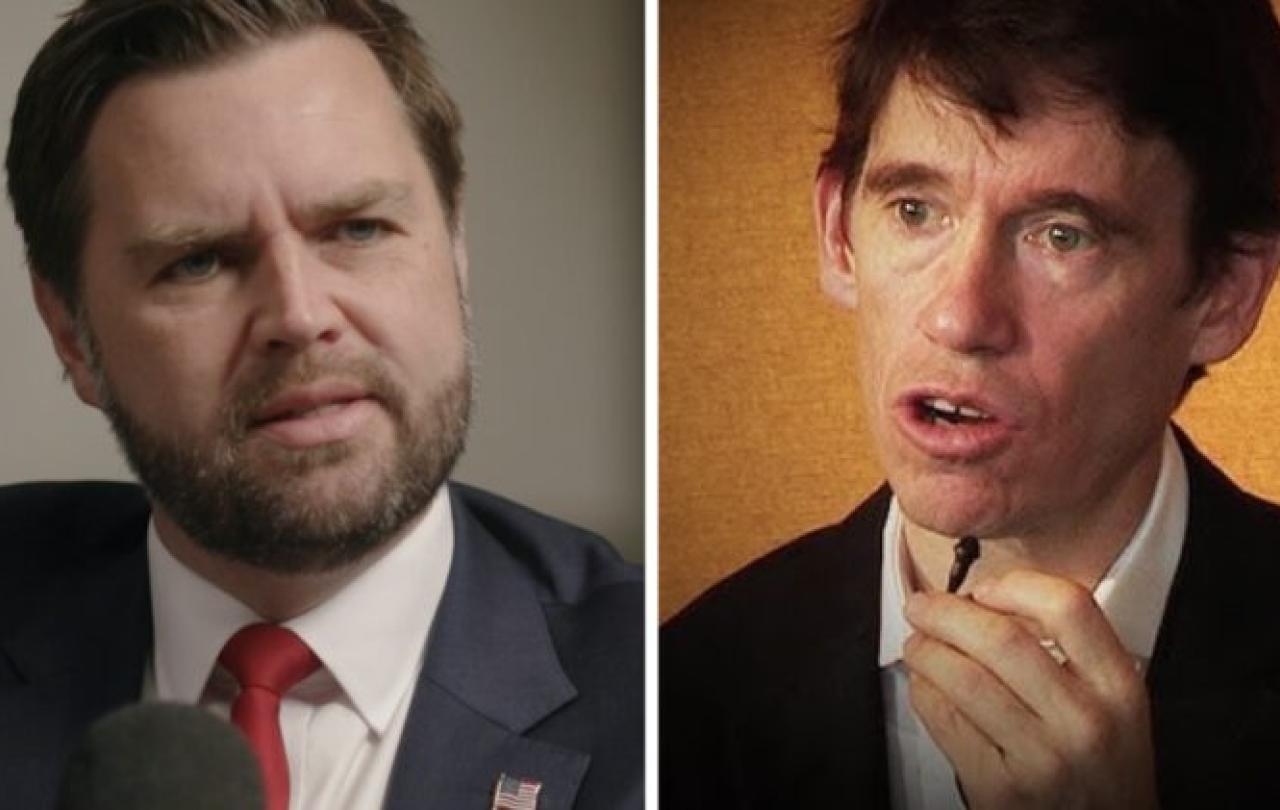
Everyone seems to be leaving it these days, but be that as it may, the other day something quite extraordinary happened over on Elon Musk’s X.
In case you didn’t see it, the Vice President of the United States of America and a Yale Professor, who is also a co-host of the biggest politics podcast in the UK, found themselves arguing about an abstruse aspect of Augustinian theology. Before we get on to the theology itself, just pause for a moment to think how remarkable that is. For decades we have been told that religion is on the way out. The secularisation thesis claimed that the more wealthy and sophisticated societies become, the less religious they will be. Religion, we were assured, is a part of humanity’s infancy, and now we're grown up, we don't need that kind of nonsense any longer. Religious language and ideas would fade from the popular mind as quickly as the church numbers decline, and we’ll all be better off for it.
And yet here we have something straight out of the middle ages - politicians and public thinkers arguing the toss about the interpretation of one of the greatest of the early Fathers of the church. Yes, church numbers continue to fall. Yet we cannot rid ourselves of religion and theology as vital sources for thinking about our life together. God may have been shown the door. But he continues to haunt the building.
Now JD Vance and Rory Stewart are both serious Christians, the former having converted to Roman Catholicism, the latter a baptised and recently confirmed Anglican. Sharing a common faith, of course, doesn't mean they will agree upon everything - and they don't. The argument emerged from an interview in which JD Vance claimed that there was a Christian ‘order of love’ by which your first calling was to love your family, then your neighbour, then your immediate community, then your fellow citizens and then the rest of the world. The ‘far left’, he claimed, had inverted that, by putting the love of the stranger above the love of our immediate neighbour.
Rory Stewart responded by saying it was ‘a bizarre take on John 15:12-13 - less Christian and more pagan / tribal.’ And in the usual social (or unsocial) media fashion, others weighed in on both sides of the argument, some pointing out quite rightly that it related to Augustine's teaching on the ‘ordo amoris’ – the order of love.
JD Vance may have done his theological research via Google, but it’s hard to criticise him for that. Vice Presidents have a day job after all, and at least he tried - it’s hard to imagine his boss quoting the ordo amoris anytime soon. And he has a point.
Jesus does say that the second great commandment after loving God is to love our neighbour – literally the person ‘nigh’ - right next to you. Yet who is my neighbour? It’s complicated. The parable of the Good Samaritan seems to suggest that your neighbour may well be a person who you happen to find in great need, yet awkwardly, may belong to the entirely opposite tribe to you. For the Democrat, it might be a hated Trump-voting gun-toting Republican. For the arch-Conservative, it might be the blue-haired, nose-ringed woke activist in the local café. Jesus also suggests at times that love for spouses, parents, brothers or sisters might come second to the call to love his friends: “Who is my mother, and who are my brothers?’ Pointing to his disciples, he said, ‘Here are my mother and my brothers!”
Loving my family teaches me to love my friends. Loving my friends teaches me to love my neighbours. Loving my neighbours teaches me how to love the stranger.
St Augustine, in the City of God (Book 15, if you’re interested) does talk about the importance of the right ordering of our loves. Yet he doesn’t delve much into love of family, community, nation and so on. His point is about directing our loves and desires at the right things. He mainly wants to tell us (something both Vance and Stewart both seem to have missed) that the primary object of human love ought to be not your family, your neighbour, or the immigrant applying for asylum - but God. And as we learn to love God, we learn a different kind of love than the kind we are used to.
The problem comes when we think of love as like a kind of cake. There are only so many slices of cake and you have to be careful who you give them out to because sooner or later they will run out. In this way of thinking, love is a limited commodity where you have to be sparing who you love, because there isn't enough to go round.
Yet divine love is a bit more like fire. When you take a light from a candle and light another candle with it, the first candle is not diminished, but continues to burn brightly. Fire can be passed on from one place to another and spread widely because it's not finite in the way that a cake is.
Augustine's understanding of love is that if this kind of divine love has grasped your heart, then love becomes something that you are rather than something that you do. There can never be a conflict between loving God and your neighbour or even your neighbour and your enemy, because divine love extends to whoever it comes into contact with, like fire warming everything with which it comes in contact. This kind of love, unlike ours, is not drawn out by the attractiveness of the beloved, but it just loves anyway. Which is why it is capable of loving the enemy as much as the friend.
They may have missed the key point, but I tend to think both JD Vance and Rory Stewart have much to learn from each other. Our love does begin with those closest to us. It is entirely natural to love our family, friends and those we encounter every day. Yet to suggest that somehow this is an alternative to the love of the stranger is a mistake.
Of course, loving your family and friends may sound easy. But it doesn't take much to realise it's not always that straightforward. Families and marriages are not always a bed of roses. Loving a difficult spouse or an errant child teaches you to keep on loving that person, even when they (or you) are acting badly, precisely because you have a stronger bond than just the attraction you initially had for them. This kind of experience begins to teach you this different kind of love. Loving our family and friends is therefore a kind of tutorial in divine love, the kind that spreads like fire. Practising the art of love on those closest to us helps us learn the skills of loving others. Loving my family teaches me to love my friends. Loving my friends teaches me to love my neighbours. Loving my neighbours teaches me how to love the stranger. And loving the stranger might even help me learn to love my enemy.
The Danish Christian philosopher Søren Kierkegaard once wrote:
“The task is not to find something loveable, but to find whatever has been given to you or chosen by you, loveable, and to be able to continue finding them loveable, no matter how they change.”
If this brief internet spat directs us towards this kind of love, then it will have been a good argument, not a bad one.
Join with us - Behind the Seen
Seen & Unseen is free for everyone and is made possible through the generosity of our amazing community of supporters.
If you’re enjoying Seen & Unseen, would you consider making a gift towards our work?
Alongside other benefits (book discounts etc.), you’ll receive an extra fortnightly email from me sharing what I’m reading and my reflections on the ideas that are shaping our times.
Graham Tomlin
Editor-in-Chief