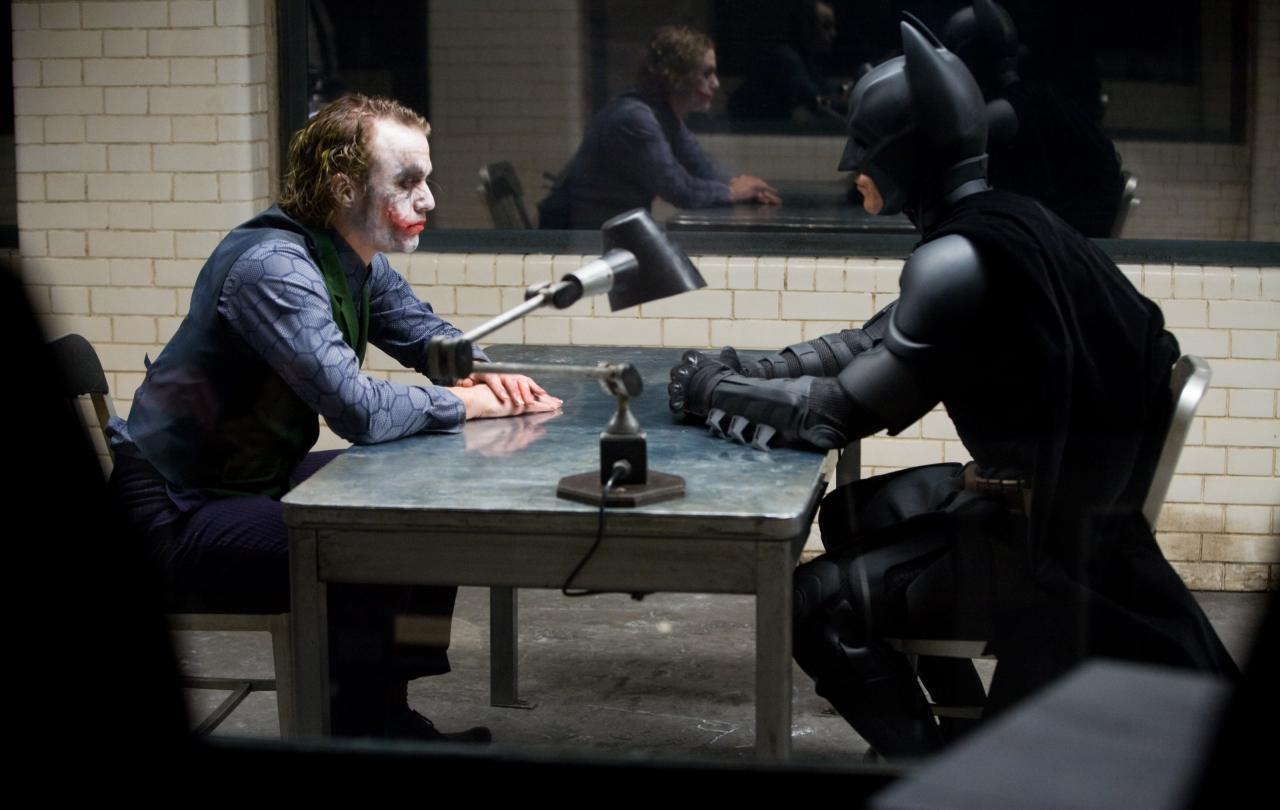
Christopher Nolan’s groundbreaking film The Dark Knight (2008), the second installment of his Batman trilogy, was a summer blockbuster that changed the superhero genre forever. Nolan’s gritty, realistic depiction of the Caped Crusader, played by a stoical Christian Bale, pushed back against the then nascent resurgence of comic-book cinema. Nolan resisted flashy computer-generated fight scenes and digitized superpowers in favor of psychological thrills intensified by cinematic restraint. The film’s combined financial and critical success empowered Nolan to become the preeminent big-budget auteur of Hollywood, going on to make such mind-benders as Inception (2010) and Interstellar (2014) and resurrecting the summer movie-going craze with the psychological biopic Oppenheimer (2023).
The Dark Knight changed the way the superhero genre was perceived not only because of its realism and cinematic skill, but also—perhaps principally—because of the late Heath Ledger’s performance as the Joker, Batman’s premier antagonist and the main villain of the film. Ledger’s Joker was mythologized even before the film’s release, as the actor’s untimely death from a drug overdose in January 2008 was almost immediately credited by the media to the intensity of having inhabited the Joker’s personality. Of more lasting importance, Ledger’s Joker in many ways marked the first serious consideration of moral and political nihilism for a large audience. The villain put on the page by Nolan and brought to life by Ledger (in a posthumously Academy Award-winning performance) was at turns disturbing in its philosophical coherence and alluring in the authenticity with which the Joker lived his principles. Batman was the unambiguous “good guy,” but the Joker captivated the audience’s imagination. I can remember being a high schooler the year after the film’s release, and at every sporting event or dance party there were dozens of Joker faces in the crowd, with the signature white makeup and lipsticked smile. Never before had insanity been so attractive. For those of us raised in the suburban optimism of the 1990s, this was the first time that nihilism had become cool.
In the wake of recent surges in political nihilism, though, ranging from online incel culture to a flurry of successful and attempted political assassinations to the January 6 capitol riots, it is perhaps worth revisiting the ideas considered by The Dark Knight nearly two decades after its release. Ours is a disaffected age, marked by despair at institutional incompetence and corruption on the one hand and a desire for a radical overhaul of justice on the other. As is often remarked, the predominant demographic of contemporary performative nihilism is millennial and Gen Z men, many of whom would have been old enough to see The Dark Knight in theaters but young enough to be profoundly impressionable to its ideas. It is not unreasonable to believe that the film acted as a foundational, if perhaps unconscious, philosophical education for whole generations coming of age in a cynical environment. Revisiting The Dark Knight today thus offers a potential lens on the sociopolitical challenges we face and the available philosophical and theological responses to them.
Part of the Joker’s appeal comes from the audience’s upfront endorsement of extrajudicial justice. No one enjoys a superhero flick unless they are willing to suspend the state’s monopoly on righteous violence, at least for the duration of the film. The romance of the genre comes from getting to vicariously live the hero’s superseding of the limits of legality, which is legitimated by their superior sense of justice. We are meant to envy Batman’s vigilantism: even when the authorities come after him, he is always too crafty, too physically fit, and too technologically advanced for the bumbling police to handle. This contempt for the law is then assuaged for us by a vision of justice that actually effects the change for which we long. The vigilante movie depends on ends that clearly justify the means.
Philosophical Joker
Released in the summer of 2008, The Dark Knight would have spoken to a generation of youth raised on the cynicism of post-9/11 society and distrust of authority resulting from the interminable war in Iraq. Even as the film was entering theaters, the global financial crash was well underway, even if the majority of the public was as yet unaware of it, spurred on by government deregulation in favor of too-big-to-fail banks and their dubious financial exploitation of the middle class. The resulting economic downturn, amplified for millennials by ballooning student loan debt and the ineffectiveness of university degrees as a stepping-stone to quality employment, would in turn have elevated Batman’s appeal in the years after the film’s release. Unlike other superheroes whose power resides in abilities we can never possess, Batman’s fully human limitations and resourcefulness uniquely channel our anger into seemingly plausible solutions. (The film seems to recognize this, as a theme early on in the movie is Batman’s struggle to control less skilled copycats of his vigilante style.) Batman sanitizes our thirst for vengeance under the aegis of a higher justice.
The effectiveness of the Joker as a philosophical villain, then, comes from the incisiveness with which he accurately diagnoses the inconsistencies in Batman’s arrangement with the law. In an early scene, the Joker attempts to make inroads with the mobsters of Gotham City. When their accountant flees to Hong Kong because it is beyond the jurisdiction of district attorney Harvey Dent, the Joker responds, “Batman has no jurisdiction. He’ll find him and make him squeal.” That Batman then predictably follows through on the Joker’s prediction—kidnapping the accountant with some spectacular escape artistry—is apparently no cause for the audience to question whether the Joker might be onto something.
The Joker’s philosophy in many ways articulates Batman’s actions better than Batman’s own worldview. Batman wants to inspire the public to justice. But what he is in fact doing is undermining the legitimacy of the institutions charged with enforcing justice, implicitly endorsing anarchism as a necessary response to official corruption. Of course, the Joker doesn’t malign Batman for his contempt of corruption but only for his hypocrisy. In what amounts to his philosophical manifesto, toward the end of the film the Joker explains his worldview to a newly scarred and traumatized Dent, attempting to lure him into his orbit:
They’re schemers. Schemers trying to control their little worlds. I’m not a schemer. I try to show the schemers how pathetic they’re attempts to control things really are… It’s the schemers that put you where you are. You were a schemer. You had plans. And look where that got you…
You know what I’ve noticed? Nobody panics when things go ‘according to plan.’ Even if the plan is horrifying. If tomorrow I tell the press that, like, a gang-banger will get shot or a truckload of soldiers will be blown up, nobody panics. Because it’s all ‘part of the plan.’ But when I say that one little, old mayor will die, then everyone loses their minds! Introduce a little anarchy. Upset the established order, and everything becomes chaos. I’m an agent of chaos. Oh, and you know the thing about chaos? It’s fear.
The Joker’s worldview, in a nutshell, is that evil is baked into the state’s attempts at control. No matter how hard they try, official authorities (governments, police, even churches) will never be able to enact real justice but only a mediocre shade of it. The compensation they provide is little more than a narrative to justify our collective misery and, if we’re lucky, a series of spectacles to distract us from our malaise.
Ahead of the curve
The Joker is in many ways a firm believer in existential freedom. Despite his apparent flippancy, he is the most serious character in the film, completely committed to his philosophy. The laughter and joy with which he carries out his heinous crimes is as much evidence of the ecstasies of genuine freedom as it is an indication of psychological disturbance. Contrary to the views of some, the Joker of Nolan and Ledger is not mentally ill. He is completely rational. He knows the human capacity for transcendence and finds civilization wanting as a vehicle for true human flourishing. He recognizes that we all know this to some extent, and he further recognizes that our primary motivation for denying our freedom is fear and convenience.
During what is probably the film’s philosophical climax, Batman conducts an extrajudicial interrogation of the Joker. In a profound twist, it is the Joker who is the more rational of the two characters in this scene, accurately diagnosing the unacknowledged dark side of Batman’s ideology while the ostensibly self-disciplined hero spirals into ever more erratic violence. Derisively comparing Batman to official law enforcement, often maligned throughout the film as variously corrupt or incompetent, the Joker says:
Don’t talk like one of them—you’re not, even if you’d like to be. To them you’re just a freak. Like me. They need you right now. But when they don’t, they’ll cast you out like a leper. See, their morals, their code: it’s a bad joke. Dropped at the first sign of trouble. They’re only as good as the world allows them to be. I’ll show you. When the chips are down, these ‘civilized’ people, they’ll eat each other. See, I’m not a monster. I’m just ahead of the curve.
In one fell swoop, the Joker has indicted both Batman and the establishment. If we side with the government, then we accept hypocrisy and ineffectiveness as the cost of a milquetoast justice. A grown adult fighting crime in a mask is freakish and absurd, nothing more than fantastical escapism. It is better to fall in line and get over your ideals. But if we instead take the side of Batman, then we have already cleared the greatest hurdle to embracing the Joker’s monstrosity.
The righteous Batman
Batman’s justice is derived from his single principle not to kill. He is constrained by neither ideological mercy nor legal precedent but only his own conscience. Yet as the Joker points out, once a vigilante has decided that their own justice is sufficient to discard the law, there is little to stop them from forsaking rules altogether: “The only sensible way to live in this world is without rules. And tonight you’re gonna break your one rule.” Batman understandably becomes more violent as the dialogue continues, exposing the dark side of his extralegal sense of justice. Pummeling the Joker in the interrogation room, Batman becomes a villain in his own right, enacting the Joker’s plan to perfection. The Joker wants Batman to kill him, if only because then the Joker’s triumph will be complete. One thinks here of Obi-Wan’s statement to Darth Vader in Star Wars (1977): “If you strike me down, I shall become more powerful than you can possibly imagine.” Or the final scene in V for Vendetta (2005): “Behind this mask there is an idea. And ideas are bulletproof.” The Joker’s philosophy is not proved by the superiority of his own strength but by his ability to lure even the most righteous figures into the abyss. Once stated, his diagnosis becomes a self-fulfilling prophecy. In his own words at the film’s finale, “Madness, as you know, is like gravity. All it takes is a little push.” From the first time he donned the mask, Batman had entered the realm of nihilism. The Joker is simply pointing this out and trying to get him to follow through to vigilantism’s natural conclusion.
In his ideological war with Batman, the Joker’s final trick is consequently to turn Gotham City into a madhouse. If the general public caves to fear and begins to tear itself apart, then the Joker’s assessment of human nature will be proved correct. In the film, Batman is justified, first by the civilians and prisoners who collectively choose not to blow up each other’s boats with the Joker’s explosives (perhaps more out of cowardice than idealism) and then by his decision to personally take the blame for Harvey Dent’s murderous rampage in order to preserve Dent’s inspiring figure for the public. Whether or not these constitute real victories is debatable, but the film ends by willing us to believe that Batman’s worldview is not inconceivable for average folks like us. In an obviously Christlike swap, Batman is so righteous that he is even willing to take the consequences of the corrupted sinner on himself in order to redeem both the sinner and the public who needs him as their hero.
But with the contemporary proliferation of illiberal ideology, the dissemination of myriad conspiracy theories, and the surge in political violence in the years since The Dark Knight’s release, we may have cause to reassess the outcome of this ideological battle. Has Batman or the Joker more accurately grasped the modern public’s psyche? Is it the Joker or the film’s optimistic finale that is spinning a fantasy?
Jesus and The Joker
From the Christian perspective, the question is nuanced but not necessarily answered. The Jesus of the gospels is by turns vigilantist, nihilistic, and neither. He is at some moments indifferent to the state—as when he endorses paying taxes to Caesar while unambiguously discounting money as having any real value—and at other times openly hostile, as when he challenges King Herod as a schemer in the mode of the Joker’s own critique. He self-consciously transcends the law without abolishing it. The entire Sermon on the Mount endorses a view of justice that goes beyond what could ever be meted out by law or reasonably enforced by institutions. Jesus is even willing to engage in some raging guerilla theatre to expose corrupt institutional authorities, and he frequently lambasts legalist hypocrites for preaching an ideology inconsistent with their practice.
If I had to stake my own interpretation, I would aver that the Jesus portrayed in the New Testament is closer to the Joker’s nihilism than to Batman’s vigilantism, both in his own behavior and the model he endorses for others. Of course, Jesus’ pacifism differs immensely from the murderous Joker. The Joker wants to make a point through the expense of human life. For Jesus, abundant human life is itself the point. Jesus forgives his persecutors from the cross and condemns violence as a response to injustice. But what Jesus and the Joker both fundamentally agree upon is the inadequacy of institutional channels for true justice. Batman might agree in principle, but his view of justice is plagued by internal contradictions: He abandons the law while seeking to uphold it; he forsakes legal constraint while encoding justice in specific principles.
What the Joker gets right from the Christian perspective, even if he never says so, is that genuine flourishing is incompatible with legal framing. Spontaneity, play, and delight are essential to human freedom. The Joker exemplifies this, even if his joy is perversely tethered to violence. What the Joker desires is evil, but he effectively illustrates how law devoid of desire cannot amount to justice.
For Jesus, true justice consistently comes down to love, which is nothing if not rooted in desire. The only motivation to turn the other cheek, pray for your enemies, or give all your possessions to the poor is because you truly desire to do so. Such extreme acts of charity are absurd by the standards of the social contract. Transcending social and legal expectations can have no motivation other than desire. Gratuity, in the sense of both an unmerited gift and ridiculous excess, is the defining feature of Jesus’ ethic. This comes through most profoundly in Jesus’ metaphors for the Kingdom of God: a weed that grows like crazy, a pound of yeast in fifty pounds of flour, an economy where everyone gets paid the same regardless of merit. We need to remember that Jesus attracted the kind of followers who walked off good-paying jobs and abandoned their boats on a whim. The Joker has just the right amount of insanity to be a Christian, even if he misses the key ingredient of love.
This sketch of a classic film and the character of Jesus is not enough to provide a coherent ethical program. But that is precisely not the point. The attempt to narrowly codify justice is what Jesus and the Joker both call out for hypocrisy, and it’s the thing that sends Batman spiraling through contradictions. If we are to properly respond to the nihilism that surrounds us online and in our politics today, then we first need to appreciate the credibility of the nihilistic diagnosis of contemporary life. This does not mean conceding to the despair that leads to hatred and violence. If anything, the life and teachings of Jesus illustrate something akin to a post-nihilistic doctrine of love. Just as resurrection requires death, so answering nihilism might require passing through it rather than ignoring its existence. Like Batman, Jesus insists that true justice is realizable for all of us. Like the Joker, though, Jesus understands that this requires a leap into the absurd. We cannot love until we can play, when we burst the bounds of cultural norms and the status quo. We will be truly just only when we find the freedom to go beyond what is required and chart a new frontier, when we learn to jump out of the boat and wager our sanity on the absurd.
Since Spring 2023, our readers have enjoyed over 1,500 articles. All for free.
This is made possible through the generosity of our amazing community of supporters.
If you enjoy Seen & Unseen, would you consider making a gift towards our work?
Do so by joining Behind The Seen. Alongside other benefits, you’ll receive an extra fortnightly email from me sharing my reading and reflections on the ideas that are shaping our times.
Graham Tomlin
Editor-in-Chief