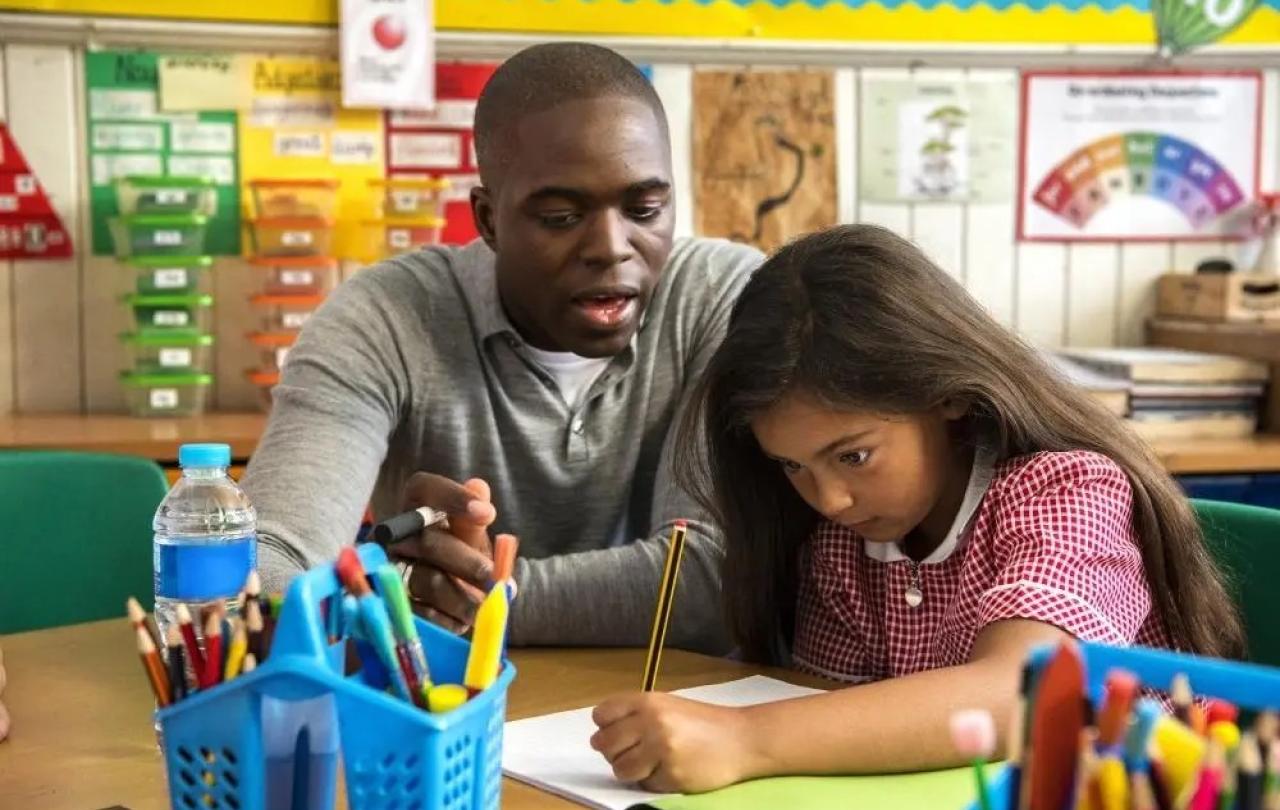
In the coming weeks, those little critters will start to emerge, easily identified by their autumn plumage of coloured sweatshirts and oversized backpacks. Anxious parents and caregivers can be spotted, shepherding their young along paths and pavements, casting worried glances left and right at the pelican crossings. Listen carefully and you may hear the squeak of uncomfortable new shoes and juveniles complaining about the wearing of a coat, as adults of the species re-establish social bonds with cries of, “Back to school already, I can’t believe how fast it’s gone!”
As they congregate upon the tarmac staging ground, some will be taking part in this ritual for the very first time. Neophytes who have maintained social bonds throughout the pre-school years might be seen to greet their fellows cordially, “Did you have a good summer? Can Flo make it to Izzy’s party?” Others will stand alone, scanning the playground for a half-remembered face from the bygone days of antenatal classes. That was only five years ago, but it feels like a millennium. The faces are changed; everyone looks more…tired.
The world has been turned upside down in those past five years. It’s been said so often that it is almost trite, but nonetheless true: nothing prepares you for becoming a parent. In the UK, new parents increasingly raise their children without the immediate support of extended family, coupled with the tyrannous expectation that one will retain one’s employment rank and contribution to the labour market alongside this new and 24/7 full time job of looking after baby. The Key Performance Indicators of parenting are ambitious. Deliverables for the first five years include toilet training, instilling speech and language skills, establishing basic recognition of 26 alphabetical characters (including the child’s ability to recognise the alphabetical sequence that spells their own name) and ensuring the recognition of and (ideally) ability to correctly sequence numbers 1 to 20. If your child can do all of this by the age of 5, whilst also learning not to punch, kick or bite other children, not to eat food off the ground, and not to stick rocks up their nose, then congratulations! Your child is school ready!
It may comfort some readers to know that very few 5-year-olds manage to hit absolutely all of these milestones. As the education secretary, Bridget Phillipson, commented recently – parenting is too hard. She is working to establish a new iteration of Labour’s ‘Sure Start’ programme (rebranded as ‘Family Hubs’) to offer parents more support in the community. As part of her rationale she states, “When one in four children are leaving primary school without having reached a good level of reading, then something’s gone seriously wrong in those early years that has to go beyond the school gate.”
Whilst I’m keen to see more support for new families – I’m intrigued by this particular rationale for it. Ability to read well by a certain age seems an unlikely metric by which to measure whether a child has had a positive experience of childhood; it appears indicative of what autism-researcher Anne McGuire calls “The normative time of childhood,” in which the success is measured against an imagined future of economically productive years. By this metric, if a child learns to read at a prodigiously young age this is taken as an indicator that they will enter the workforce with greater velocity than their peers, essentially that they will have “more future-yet-to-be-realized” than those around them. McGuire writes, “In a neoliberal regime where ‘time is money’, the child is figured as ‘time-rich’ and so represents a good investment opportunity indeed.”
McGuire’s analysis is piercingly accurate of how we often talk about our children, despite knowing all too well that it represents a fallacy. There are multitudinous stories of adults who have gone on to make staggering contributions to human flourishing, despite being placed (literally or figuratively) under the dunce’s cap at school. But even without focusing on those who go on to excel, those who attract fame, fortune, or both, we don’t have to look far to find cause to re-evaluate what it means for a child to be school ready.
My son’s year group recently finished their own primary school journey, and a quick glance through some of the leavers’ books reveals that children are very good at valuing each other for what is here in the present, without recourse to an imagined economic future. As children wrote goodbye messages for each other they said things like,
“Thank you for always having such good ideas for games to play.”
“You helped me on my first day when I got lost.”
“You’re a great house captain and you always help the teacher.”
No one was particularly keen to predict fame and fortune for the future of their friends, and there was an understandable indifference towards academic milestones. As a literary corpus, the leavers’ books were testament to the old adage that people will not remember you for what you say or do but will remember you for how you make them feel.
One the subject of childhood, Jesus once said something that defies easy explanation. He was out, teaching in the open air, surrounded by crowds of adults including important religious leaders and wealthy individuals who wanted to ask complex and deep theological questions, but in the midst of it all there were parents bringing their children, elbowing their way to the front of the crowd to ask Jesus to pray for their little ones. When some of Jesus’ followers tried to usher the children away, Jesus said, “Let the little children come to me, and do not hinder them, for the kingdom of heaven belongs to such as these.” The precise meaning of this utterance has eluded thinkers and theologians for centuries – what exactly is it about childhood that Jesus was alluding to?
I wonder if it is something about the capacity of children to live in the immediate, and therefore to value what really matters – justice, kindness and friendship. In primary school, yes it helps in some ways for children to arrive aged 5 with a certain command of the alphabet and the ability to finish the day wearing the same set of underwear that they arrived in. But perhaps what matters more is children arriving ready to enter the fray of friendships – being kind, being helpers, having the self-confidence to know that they have something to give to the learning community that they are joining, whatever their learning speed might be. Such things are gloriously untethered to economic potential or a future-yet-to-be-realized, but they are closely tethered to a child’s understanding of themselves as a valuable and important person. If Labour’s intention to offer new parents more help in the community goes some way towards communicating to our pre-school children that they have that have – and will always have – value, regardless of what they will or won’t attain to academically or economically, then it will help many more children reach the milestone of being school ready.
Support Seen & Unseen
Since Spring 2023, our readers have enjoyed over 1,500 articles. All for free.
This is made possible through the generosity of our amazing community of supporters.
If you enjoy Seen & Unseen, would you consider making a gift towards our work?
Do so by joining Behind The Seen. Alongside other benefits, you’ll receive an extra fortnightly email from me sharing my reading and reflections on the ideas that are shaping our times.
Graham Tomlin
Editor-in-Chief