Turn on the news and death is all around us. Yet somehow, we think it will never happen to us. In one sense that’s good. We have a child-like innocence that protects us from the harsh realities of life.
A few years ago, as a church minister, I thought I knew about death. I’d been trained to take funerals and had supported families when a loved one had died. But it wasn’t until I was bereaved myself - when my husband died suddenly of a heart attack - that I realised how little even I knew.
Although busy, life had been good until then. My husband had a successful job, my own work was going well and our three children were flying the nest and finding their feet in university. Little did I know that in one, short phone call from a colleague, our lives would change forever.
Simon had been found dead in his hotel in Spain, and I was faced with telling each of the children and his mother, the worst news anyone could convey. Concerned about social media the news was embargoed until all family members knew, then I had to go to Spain to find, as well as identify the body, and bring him home. I had to work out our finances – no one knew what we had to live off – close accounts and put things in my name. I discovered our house wasn’t insured, nor our car for me to drive, that bank accounts were frozen, and that no organisation is geared up to help. Everyone insists on speaking to the account holder or seeing the actual death certificate before being willing to oblige. I had a funeral and thanksgiving to organise – two big occasions in just 3 weeks - and a mountain of admin to deal with, which would be difficult at any time.
Grief is a journey of adjustment of who we are to a new existence – one that takes a long time and never comes at a convenient time.
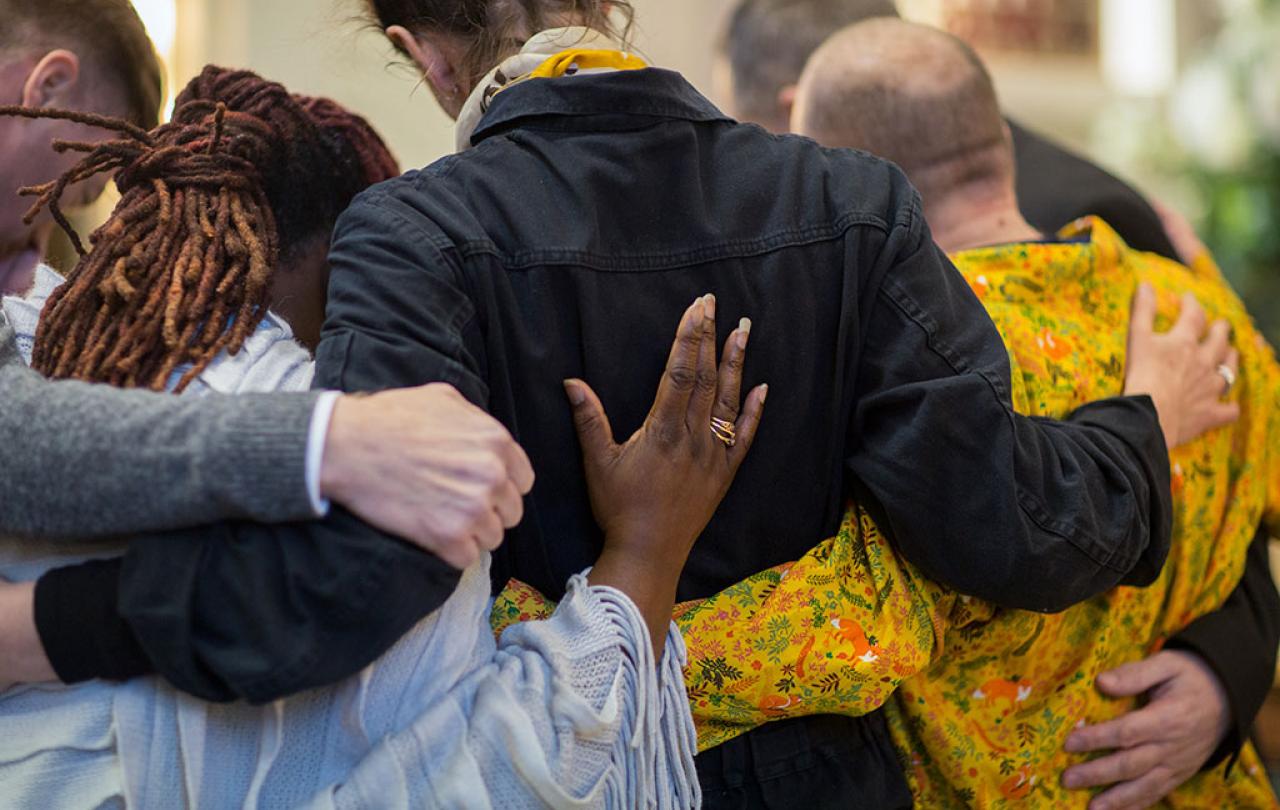
We’ve been a death-denying culture, I now realise, for many years. With death invariably happening in hospices or hospitals, we’ve pushed death away and pretended it doesn’t happen. Consequently, we’ve lost knowledge of bereavement and the art of support. We’ve tended only to think about preparing for funerals and then counselling if the person isn’t doing well. But what about all the other help that’s needed? Understanding and support is necessary in all manner of ways. Bereavement is one of the most stressful times of life, affecting everyone sooner or later and every part of their life. Grief is a journey of adjustment of who we are to a new existence – one that takes a long time and never comes at a convenient time.
At first most of us are shocked or emotionally numb; we run on adrenaline and we’re in survival mode. At the funeral others can think we’re doing well, and we can too. But it’s after, when the real sadness tends to hit, when the future must be faced and by then support has dropped away.
Many of us experience a roller coaster of changing reactions and responses which we don’t recognise as us or don’t associate with grief.
There are the physical reactions, for instance. I couldn’t eat, I couldn’t sleep, I was cold and I shook for months, I had a heavy ‘weight’ in my gut and was taken to hospital three times with suspected heart problems - our bodies are always in tune with our emotions.
And there are the psychological reactions. We can experience anxiety, anger and guilt; we can’t concentrate or remember, or function to do the most basic of tasks. I kept thinking I was seeing Simon and had a psychosis which made me feel separated from the world. We can think we’re going mad.
Grief is a natural response to loss which we need to work through for our future wellbeing.
For me help came from two initiatives I was fortunate to find: Care for the Family’s Widowed Young Support and The Bereavement Journey course run by a church in London. In each of these I discovered others who had been bereaved, who understood what I was going through and who helped me to navigate the alien territory I found myself in. They also helped me to understand my spiritual responses which had been the biggest surprise. I had never doubted my Christian faith but with bereavement, that too was challenged, and God, who had always felt present, suddenly disappeared. I realize now that this is natural. Grieving is a process of deconstruction and reconstruction of meaning, and therefore some of whatever meaning we had before the person died, will deconstruct as we grieve.
Roll on a few years and I’m on the other side, running a charity helping people to understand that in our death-denying society bereavement impacts greatly, and that grief is a natural response to loss which we need to work through for our future wellbeing. Support is needed in various ways which we direct to through our signposting website ataloss.org. And I’m helping people myself through The Bereavement Journey course to find healing and hope, offering also spiritual support for the faith questioning I find most people have. Unfortunately, though, because we’ve neglected death, many haven’t been supported through a bereavement in the past and are carrying loss which is unresolved.