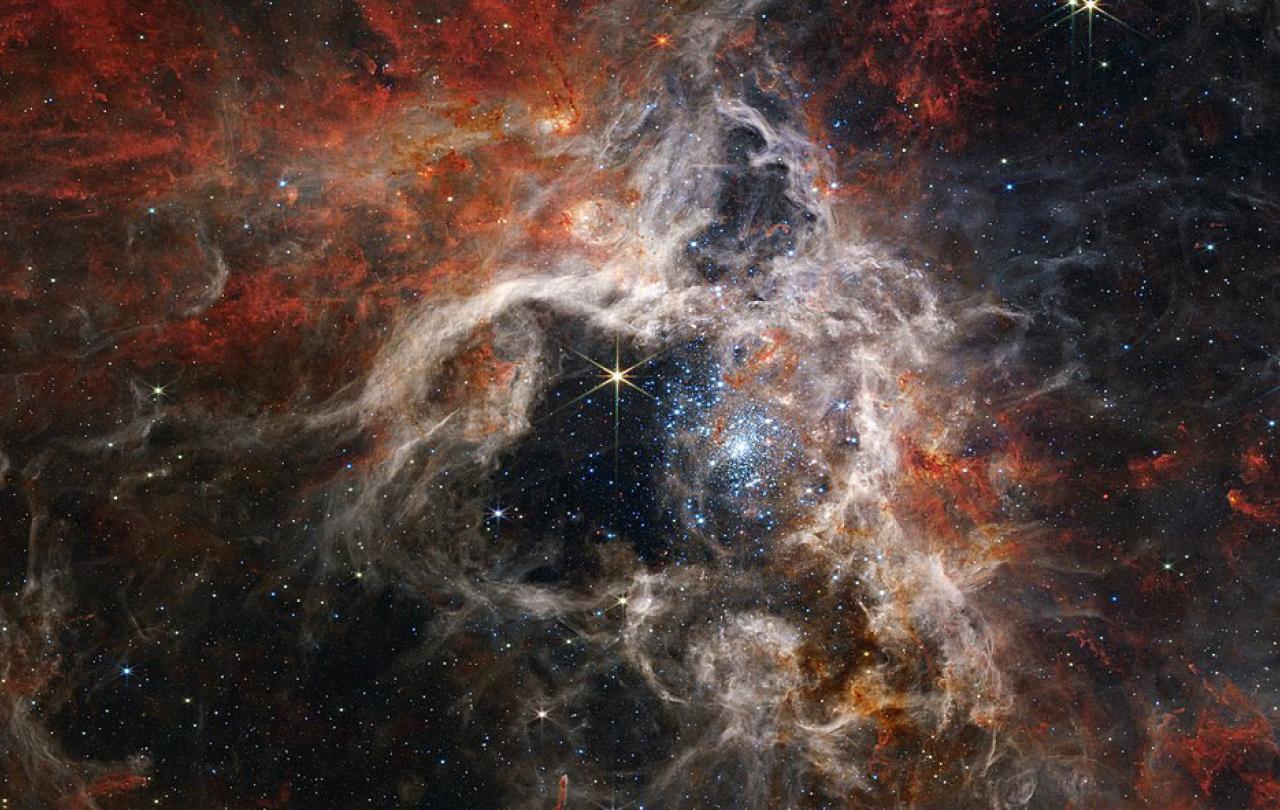
The James Webb Space Telescope was launched on Christmas Day 2021. After hair-raising maneuvers to unfurl its tennis-court-sized mirrors, it has been sending back breathtaking images of the cosmos since July of last year.
Christmas was a good day for the launch, given its astronomical connections. ‘Glory to God in the highest heaven’, the angels sang to the shepherds, ‘and peace to his people on Earth.’ Meanwhile, the wise men were above all diligent observers of the heavens. ‘Where is the child who has been born king of the Jews?’, they ask, ‘For we observed his start at its rising, and have come to pay him homage.’
Quite what that ‘star’ might mean there is open to debate. Comets have been popular with artists. Giotto painted one, for instance, in his Adoration of the Magi in the Scrovegni Chapel in Padua. It is almost certainly Halley’s Comet, which had appeared just a few years before, in October 1301. But why would anything in the heavens be interpreted as a birth in Judea? It would probably involve something in a constellation associated with the nation of the Hebrews. Pisces seems to be favoured, for some reason. A nova of some kind is one possibility: what would look like a temporary new star because, in fact, a previously invisible star was undergoing a spectacular death. Chinese records suggest a nova in 5 BC, which fits the likely date for for Christ’s birth of 7–2 BC.
The problem with both comets and novae is that they were more likely seen as harbingers of doom than good news. The better candidate for suggesting something joyful is a planetary conjunction, and there would have been a rather spectacular conjunction of Jupiter, Saturn, and Mars at the right time. None of that, admittedly, explains what it means for the star then to have led the wise men. Coming up against that challenge, we might think that looking into the astronomical detail is the wrong way to approach the story. Nonetheless, Matthew had something in mind when he wrote about a start in his gospel, and it’s worthwhile to ask what that might have been.
It might be fitting for God to deal with other species as intimately as God has dealt with us, so that they might see ‘God made visible’ in their own nature, as we see God made visible in ours.
More recently, the Christmas story has intersected with astronomy in questions about how to think about Christian theology now that we are aware quite how big the universe is, especially if it may contain a great deal of other life. We don’t know whether that’s true, of course, but given we now know that planets common around stars, and there are billions of billions of stars in the universe, the probabilities seem to tilt towards other life, at least as I see it.
Suggestions surfaces from time to time that the world’s religions have arrived late to the party, when it comes to thinking about life beyond Earth. The astronomer and broadcaster Carl Sagan made that claim, for instance, in his best-selling book Pale Blue Dot. In fact, the earliest discussions of life beyond Earth I know about from Christian writers come from the mid-fifteenth century (and they stretch even further back in Judaism and Islam, to give two other examples). Christian writers have written on the subject ever since. If few gave us more than a paragraph here or a page there, that’s usually because the prospect of other life did not worry them enough to warrant more. They noted the prospect cheerfully, and moved on.
Until the twentieth century, the prospect of parallel Nativities on other planets was rarely in view. In a sense, it didn’t need to be. It’s a consistent Christian position to say that God joined his life to all creation in joining it to one species of rational animal on Earth, just as God joined his life to all humanity in being born in a stable, in a wayside town, in a backwater province of the Roman Empire.
One erudite early exploration of multiple Incarnations comes in a poem from the 1920s by the Roman Catholic poet Alice Meynell, entitled ‘Christ in the Universe’. More recently, Meynell’s topic has become perhaps the central theme in thinking theologically about life beyond Earth. My own book (Astrobiology and Christian Doctrine, 2023) looks at the prospect of life beyond Earth from the perspective of all of central topics in Christian doctrine (creation, sin, redemption, revelation, the Trinity, and so on), but the largest section is on Christmas and possible parallels. I am sympathetic to the idea that God would also unite himself to another natures, alongside the human nature he took up in Christ: not because I think that would be necessary, but because it might be fitting. It might be fitting for God to deal with other species as intimately as God has dealt with us, so that they might see ‘God made visible’ in their own nature, as we see God made visible in ours.
Hiding in plain sight in the Nativity stories is another key to Christian thinking about life beyond, namely the angels. It’s not that I think that angels are aliens, or that alien life is angelic. In fact, being a disciple of St Thomas Aquinas, I’m inclined to view angels as entirely immaterial, and so very much not examples of biological life. But angels are useful for thinking about other biological life beyond Earth nonetheless, because of what they mean for the Christian imagination. The angels show that there’s always been space in that imagination for rational creatures other than human beings. They show that Christianity has never imagined that we’re the sole object of God’s love, or even the most glorious of species.
The Christmas story has its cosmic elements: the star, glory in the highest heavens, and the angels, reminding us that wonderful though humanity is, it has no monopoly on rational life. My hunch, as much as my hunch matters, is that if there is other life then they too may see God face-to-face in their own Incarnation. Even if we find evidence of life beyond Earth, however, it’s not going give us much detail. The balance of gases in the atmosphere of a planet around another star might indicate life, but not much else about it. The prospects for interplanetary comparative religion are far off indeed. Alice Meynell had the right idea, when she recognised that one of the joys of the life of the world to come will be learning the stories of God’s dealings elsewhere:
But in the eternities,
Doubtless we shall compare together, hear
A million alien Gospels, in what guise
He trod the Pleiades, the Lyre, the Bear.
O, be prepared, my soul!
To read the inconceivable, to scan
The myriad forms of God those stars unroll
When, in our turn, we show to them a Man.
Alice Meynell