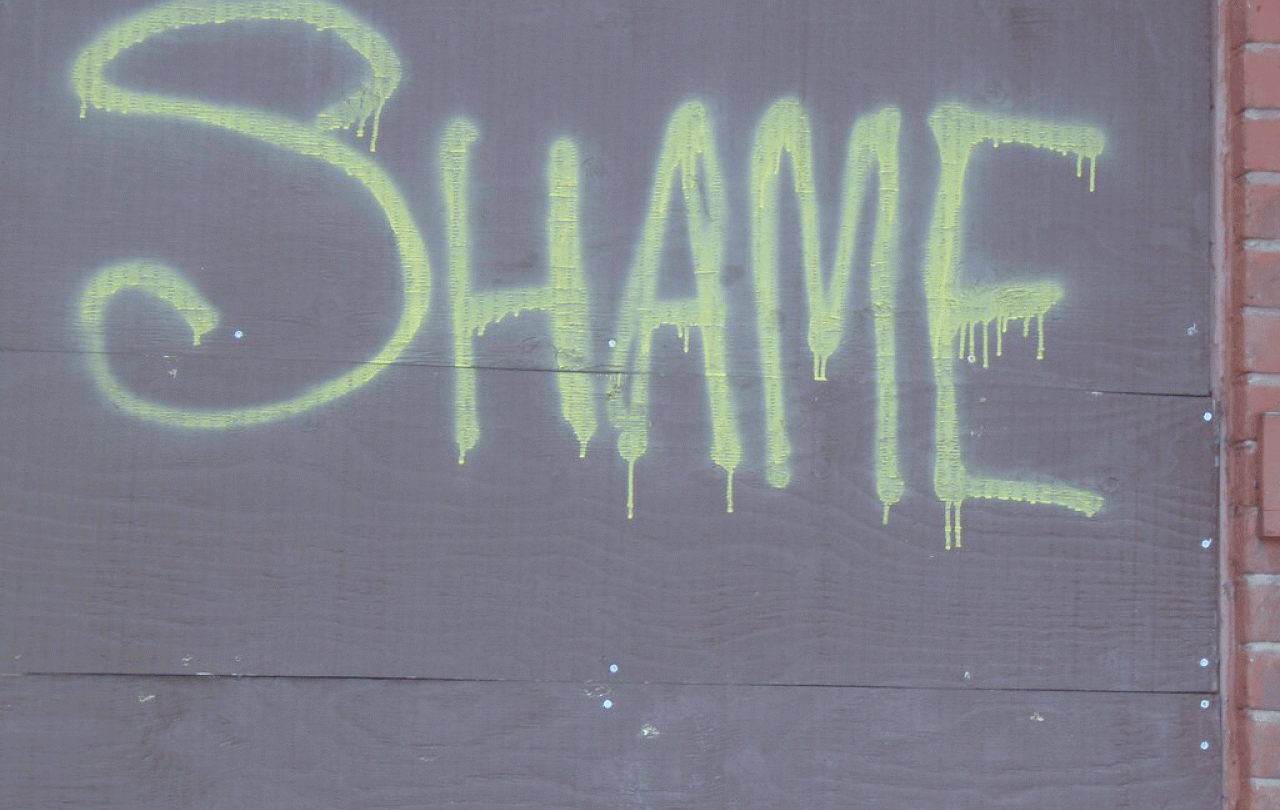
“Put on this dunce’s cap and go and stand in the corner!” cries the teacher, and immediately we are transported to a scene that takes place in a schoolroom of centuries past. Likewise, if nowadays we were to see a woman being led down the street wearing a scold’s bridle, we might assume that there was a very odd sort of party going on; we might even intervene or phone the police. Why? Because these are not the scenes of 21st century Britain. We don’t do public shaming anymore – at least, we like to think we don’t.
But the truth is we very much do; in fact, shame is essential, at least to a certain degree. For a group to survive with any sense of collective identity and purpose, something has to prevent each person within that group from becoming too greedy, or too lazy, or too dishonest. That something is often the fear of being shamed, not even punished – just shamed. It doesn’t feel nice to be judged and found wanting, or to fear that you might be.
Think back to the last windy day when your recycling bin blew over – did you experience a passing moment of concern about the public pavement acrobatics of your wine-bottles, cake boxes and ready-meal trays? No need to blush – your neighbours probably rushed out ahead of you to hide their own multifarious sins. Studies have long shown that installing self-checkouts at supermarkets dramatically increases the purchase rates of “stigma items” such as alcohol and unhealthy foods. Oh, the things we do when we think no one is watching…
So, shame is, on one level, a functional tool which does the essential job of guarding the life and boundaries of a community. Perhaps one or two of us still eats a little too much and drinks a little too much, but shame is one of the things that keeps most of us from going too far, too often – or at least the threat of shame tends to discourage. As Graham Tomlin has recently explored – we still live in a society that equates over-indulgence with a lack of virtue.
It’s one thing for shame to guard certain moral boundaries (as long as we can all agree what they are) but we’re in a troubling place with the social ones.
However, when an individual does step out of line, then the shaming process has two modes of presentation: exposure or exclusion, sometimes both. This is most clearly seen in a court of law, where an offender is first ceremonially declared to be guilty (exposure) and then is subsequently sentenced (exclusion) – often “removed” from society, at least for a while, via a custodial sentence or a curfew. In this very clear way, shaming plays a functional role for the well-being of society as a whole.
But these two prongs of the shaming process can also happen in rather dysfunctional ways, some of which are dangerously subtle. We fear the recycling bin disgorging its contents because there is a certain social shame in being seen to consume too much junk. Fine. But what about the teenager who is compelled into a cycle of disordered eating because a schoolfellow has pointed the finger and said the dreaded word, “fat”? Likewise, many people love a chit-chat, and the fear of being excluded from a social group usefully prevents most of us from being too fixed on one topic, or from appearing inattentive or impolite. But in my research with autistic people, some have shared that they feel shamed out of social groups entirely simply because “chit-chat” is not right for them. Some have a language processing delay, others find “small talk” a bit confusing and inane and would rather talk about something specific. It’s one thing for shame to guard certain moral boundaries (as long as we can all agree what they are) but we’re in a troubling place with the social ones. Some of this shaming doesn’t sound very functional, not if the wellbeing of society is supposedly the goal.
The inverse of shame is empathy. Where shame excludes, empathy shows attentiveness.
Perhaps the saltiest example of this problem is the now infamous “cancel culture”. I know – even I can’t believe I would risk bringing that up as a writer, that’s how charged this debate has become. But de-platforming, boycotting, or publicly castigating someone for the views that they express – these are shaming activities, an attempt to render an individual exposed and excluded. It can be a very tricky argument as to whether this counts as functional shame, guarding the wellbeing of society, or dysfunctional shame, guarding little more than social norms.
We ought to try and take it on a case-by-case basis, but even then, sometimes what one person takes as a moral absolute another person sees as a social choice. At the same time, those who hold dearly to certain moral absolutes sometimes lose sight of the societal impact of what they say. The result can be a strange kind of war, one where there is virtually no engagement between two opposing factions, and the only weapons are a string of press releases and a whole lot of contempt. Eventually, often regardless of there being no engagement and no progress, both sides vigorously declare themselves to be the winner.
Jesus once said a strange thing when he was talking to a crowd. He said: “Settle matters quickly with your adversary who is taking you to court. Do it while you are still together on the way.” In other words, “Just have a chat first,” says Jesus, “and see if you can’t come to terms.” It was part of a much longer discourse where he also told the crowd to “love your enemies” – and this with the kind of love called agape, a love which favourably discriminates and chooses someone – very much the opposite of shaming them.
For my own research I have looked in depth at the shaming experience, and one of the conclusions that I come to is that the inverse of shame is empathy. Where shame excludes, empathy shows attentiveness. Where shame exposes an individual, empathy draws them into discussion. To empathise with someone is not to agree with them, but it is to recognise they are human just the same, and that through openness and dialogue it is possible for people, even those who have very different experiences of the world, to explore each other’s perspectives. The end point of that exploration may not be agreement – it might still be everyone back to their corners. But in the process no one has been shamed, no one exposed or excluded, no-one othered or dehumanised.
Of course, it is far easier to point the finger, to expose someone to the court of public opinion, and then to turn one’s face away, nose in the air, mouth clamped shut in an apparently dignified silence. On the surface this seems like the elegant response – live and let live – but in fact it is not: to designate someone as not worthy of attention is to very publicly inflict shame. We might as well clamp them into a scold’s bridle and lead them down the street. And, as we do so, let’s hope it’s not a windy day – or if it is, let’s be sure that we have firmly tied down the lids of our recycling bins.