In the wake of headlines filling our news feed reporting a story, yet again, of a pop culture icon taking advantage of women, be it Russell Brand or “That 70’s Show” star, Danny Masterson, we’re quick to say “enough is enough,” but perhaps the question to ask is “how do we stop it?” What standards are we expecting of men as individuals and as a collective whole? How will they self-edit their interactions with women? What do we expect of men in the workplace, at the gym, at church, or in the public square? We know what we don’t want them to do, leverage their power, privilege, or platform at a woman’s expense, but that’s an undeniably low bar. What could they do to stop each other before their actions get out of hand?
Before heinous stories of sexual violence are aired on the BBC or CNN, we’re holding the communal line of what we’ll accept from men.
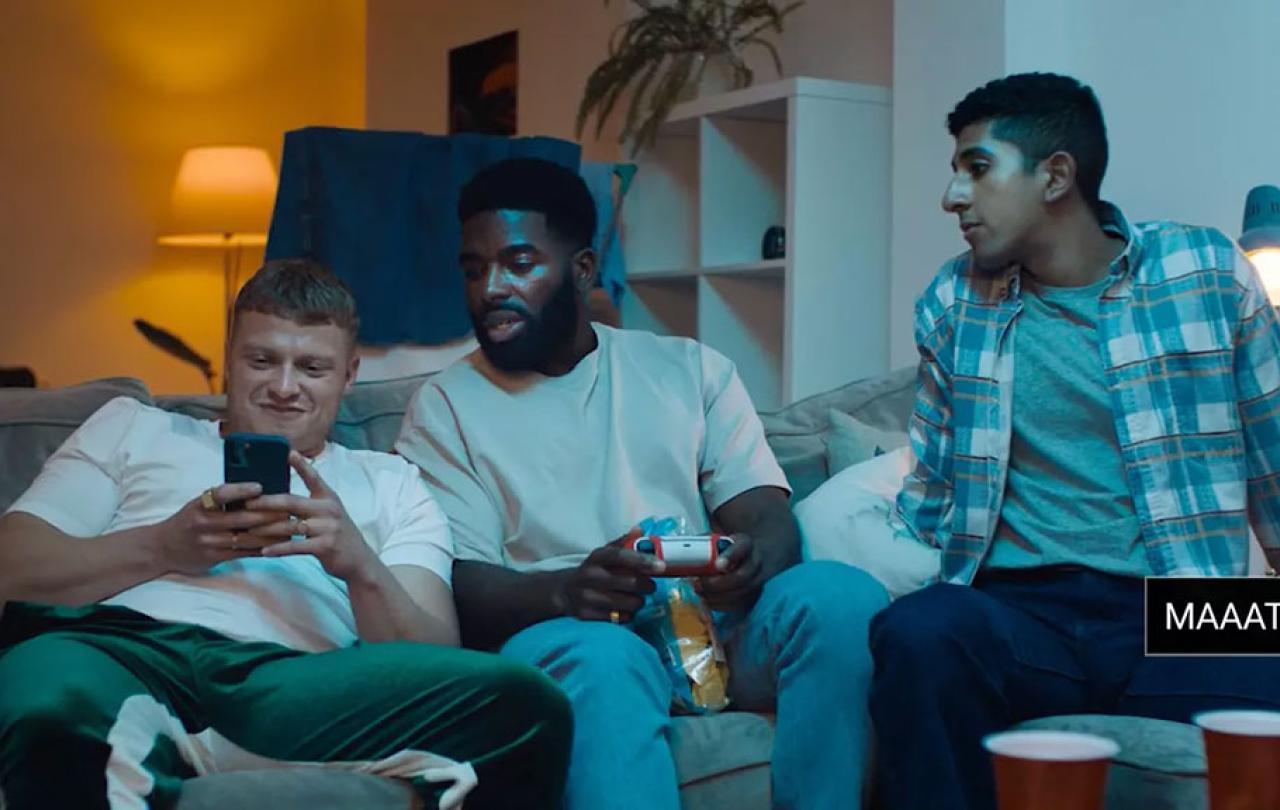
After learning of the ‘Say Maaate’ campaign—a public information campaign inviting male mates to call each other out when they witness misogynistic tendencies toward women without jeopardizing the friendship thus jeopardizing the influence on each other—I recognized its brilliance lies in its interception of misconduct before it gains momentum or is considered high stakes. Before heinous stories of sexual violence are aired on the BBC or CNN, we’re holding the communal line of what we’ll accept from men, be it sexist jokes or public harassment. This endeavor, which includes bystander intervention, where those within eyeshot or earshot will attempt to distract and intervene in a potentially hazardous situation when men assert unsolicited dominance or advances toward women, is so successful that it’s employed by the United States military and countless higher education universities and colleges in the States. It puts the onus not on the woman impacted during the encounter, but on those around her, to step up and intervene at the first sign of a power imbalance, ranging from a man standing too close, to a woman darting her eyes to avoid eye contact, to outright sexual and verbal harassment.
Bystander intervention invites the bystander to disrupt the moment, and after the moment has passed, confront the antagonist with either the benefit of the doubt, “maaate,” if deserving, or a “Man, she didn’t like that, read the room.” Lastly, it beckons the bystander to check on the woman who was the recipient of unwanted harassment. Bystander intervention provides much-needed boundary reminders of what we will and won’t accept in a society where the moral arc of the universe desperately needs to bend toward justice. This practice refuses to normalize women’s subjugation or sexualization, it offers a lifeline where there hasn’t been one before, with women left to their own defences against men with no intention of respecting them.
I feared the ramifications of speaking up against a man with more clout than I.
Interestingly, men with power—financial, organizational, political, celebrity—perceive themselves to be more attractive, assume women want them, and sexualize interactions with women. In a world where women are often playing by men’s rules, this makes for disastrous outcomes. Far too many women fear they’ll lose access to their place of perceived or actualized power if they speak up for themselves, or other women, who’ve been maligned, even slightly, by men with power and poor intentions. In my own experience, I feared the ramifications of speaking up against a man with more clout than I. How would this affect my social and professional standing in my community? Would others perceive that I have an axe to grind when that wasn’t the case? Would they frame me as prudish? Would they assume I asked for it? Would they assume I’m trying to unnecessarily take down a “good guy.” Instead of speaking up when the stakes were small, after an off-handed comment, sexist joke, or a lingering hug, I assumed this is just how it is, boys will be boys. If I want to get by in this world, I must put up with it.
If only the men listening would have thrown him a “maaate.”
Research shows that this pompous approach men exhibit toward women starts on the playground in primary school, gains steam in the locker room in secondary school, cements itself in university culture, (what Americans refer to as “frat culture”) and before we know it, twentysomething men are carrying this toxic idea of what it means to engage women into adult life, and further, it’s celebrated, as was the case of Brand’s public persona. Too often harassment and misogynistic tendencies of any sort equate to validation of masculinity. In this line of thinking, the subtext is that women exist to be dominated, harassed, or taken advantage of for the sheer pleasure of men. This is the genius of bystander intervention; it swiftly reckons with the subtext of a culture hellbent on letting men get away with whatever they want and whoever they want.
He addresses her harassers, beckoning them to examine their own lives rather than fixate on hers.
While the Christian church is no stranger to sexual trysts or infractions by men of the cloth, the ethos of Jesus regards women as worthy not of subjugation nor sexual harassment, but respect and dignified engagement. He modeled this respect and casts a vision for women to find solace and safety in men, never harm.
A great example of bystander intervention in history starts with pious religious leaders attempting to trap the counter-cultural rabbi Jesus by throwing a woman at his feet, alleging she engaged in adultery, a crime, at the time, worthy of public stoning. A clear imbalance of power, with a woman’s life as collateral for trapping Jesus, the religious leaders wondered if he might keep allegiance to the law or break from it. They made the encounter about Jesus; Jesus centered the encounter on protecting the woman who’d been dragged to the public square. Jesus first intervenes by writing in the sand as his answer to the question posed by the leaders. Her physical safety is of utmost importance as evidenced by his actions. Then, he addresses her harassers, beckoning them to examine their own lives rather than fixate on hers. Finally, he checks in with the undoubtedly traumatized woman, a mere prop in an attempt to trap a man who modeled equality and respect between the sexes.
If bystander intervention was effective 2,000 years ago to protect and uphold women’s dignity and safety, and has modern success in the military and on university campuses, maybe there’s room for the men in our community to prevent harm before it happens? Maybe we can right cultural wrongs? Maybe before learning of Brand’s misconduct, we’ll learn of a bystander who stepped in before a sexist slur was accepted in everyday conversation or intervened when a woman was uncomfortable. Since the issue is not weak femininity but toxic masculinity, maybe men can learn to say, “Enough is enough.”