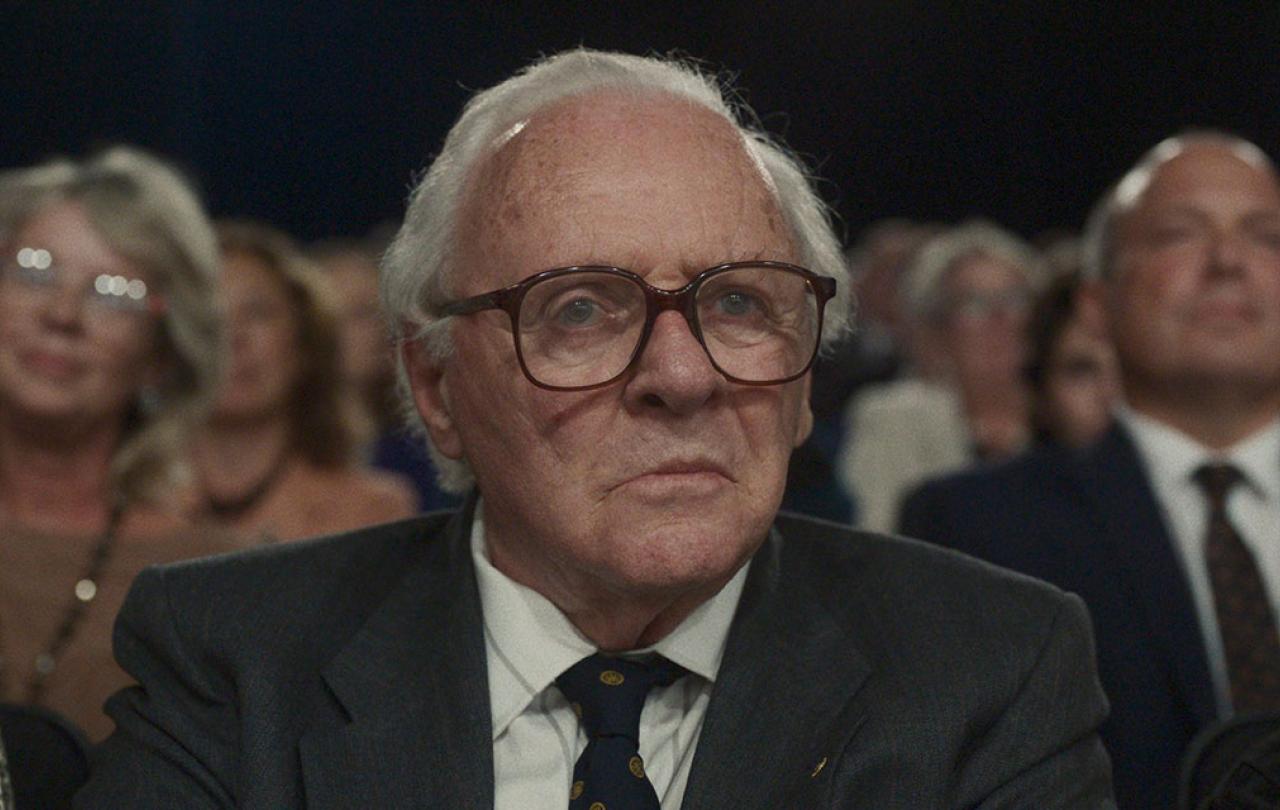
There’s an elderly man with thick-rimmed glasses sitting in the studio audience of a popular 1980s television programme. The camera lingers on him as the presenter on the stage, in her signature blue dress, opens up a scrapbook detailing a hitherto unknown mission at the beginning of the second world war that rescued 639 Jewish children from the Nazi genocide.
The man in the audience was the force behind this rescue mission, and the camera is focussed on him because there’s about to be one of the best television moments in history. Unbeknown to him, he is sitting next to a lady whose life he once saved. As Esther Rantzen reveals the connection, a look of shock, wonder and amazement crosses his face.
The story that was kept secret for nearly a lifetime was broken in front of a live television audience of millions. I’ve watched the recording a hundred times; it never fails to make me tear up. I’ve spoken to people who were on the production team of that show who say that this programme was the highlight of their careers. It was a truly brilliant piece of television.
40 years later and I am sat in the Royal Festival Hall next to another elderly gentleman. We have just watched Anthony Hopkin’s incredible performance as Nicholas Winton, that man in the studio, in the new movie One Life. The director of the movie, James Hawes, makes his way to the front and asks if there is anyone in the audience who is alive today because of Nicholas Winton. The elderly gentleman beside me stands along with hundreds of others. Some of those standing were on the Kindertransport in 1939. Others were their children, grandchildren, and great grandchildren.
It was an immense privilege to spend some time with these survivors. Many had their original identity photographs with them. It was an emotional evening as I heard stories from those who remembered boarding the trains in Czechoslovakia in 1939 and saying goodbye to their parents for the last time.
Many of the Kindertransport descendants had met Nicholas Winton personally before he died and were astounded by Hopkin’s ability to capture his likeness and his story.
I never met him myself, but as I watched One Life, I felt like I was in the room with him. The audience meets him as a young man discovering the terrible situation for Jews in Europe and deciding to take action. We journey through the many obstacles to the rescue mission. At first nobody would take in the Jewish children because of the misconception that migrants would overwhelm local services at a difficult time for the country. Yet through savvy use of media, great administration and pure unrelenting persistence, Winton and his mother (Helena Bonham Carter) were able to get a system running that meant hundreds of temporary foster parents not only came forward but paid for the privilege of helping to save the lives of these children.
As many of the children lost their families to the horrors of the gas chambers and could not be reunited with their families, a large number were adopted by their foster carers and grew up in the UK. Some went on to greatness, others lived quiet lives of service. The 91-year-old man who sat next to me at the premiere had dedicated his life to the church and also to making sure the next generation didn’t forget either the horrors of the holocaust, or the hospitality of ordinary people.
One Life is a deeply inspirational film. As I reflected afterwards, I couldn’t help but draw parallels with the situation in the world I live in now with terrible wars that are in full swing. I wondered what Nicholas Winton would do for the children being slaughtered today. What would a modern equivalent of the Kindertransport look like? Who could step forward to inspire our nation once again to offer sanctuary, protection and hope to our world’s most vulnerable children?
Watch
Kirsh Kandiah reports from the One Life premiere.