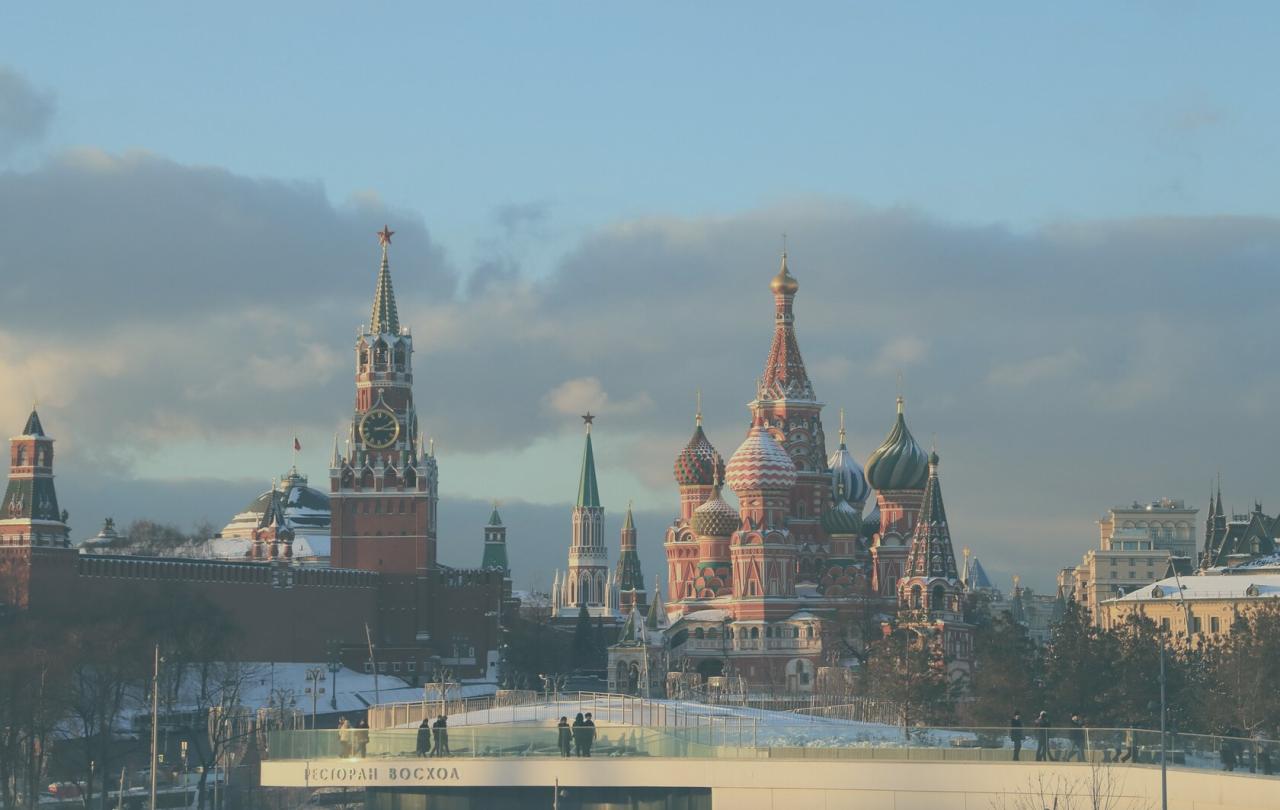
On 24 February 2022, Russian tanks crossed the border of Ukraine. President Putin believed that the ‘special operation’ would be swift, that Ukrainian resistance would crumble and that the Russian soldiers would be welcomed as liberators. It will go down as one of the most catastrophic failures of intelligence in history and, as a result, tens, if not hundreds, of thousands of people have died, and the lives of millions of people have been devastated.
There can be no justification for the invasion of Ukraine. But if there is to be any lasting peace in the future, and if Europe is to live even in an uneasy peace with its eastern neighbour, then we need to hear the Russian critique of the West. We may well not agree with it, but unless we engage with it and try to understand where people are coming from, we are storing up yet more trouble for the future.
Sir Laurie Bristow, the former ambassador in Moscow, was often asked what Putin was thinking. His answer was simple: 'Listen to what he says’. People have mocked the long historical narratives in his speeches, but they are not to be ignored. There is no reason not to assume that Putin speaks what he believes. The conflict, certainly in his mind, is not economic but ideological.
The points below are a summary of some of the criticisms of the West that have been expressed in his speeches, in the Patriarch’s addresses and views published in Russian state-controlled mass media. It is possible that these views are now held, at least tacitly, by about 70% of the Russian population.
Putin’s defensiveness
Putin’s first criticism of the West is that NATO was planning to expand into Ukraine and place nuclear missiles there.
NATO, it is claimed, is an anti-Russian alliance, whose ultimate goal is the fragmentation of Russia. Russia, with its size, natural resources, military might and influence is too much of a threat to Western (US) hegemony.
NATO went back on an agreement given to Gorbachev in 1990 that it would not expand beyond its current borders. Since then, it has grown from 17 to 30 countries, and has steadily expanded East, incorporating the Baltic States, and offering promises – although vague – to Ukraine and Georgia that they would one day be able to join NATO.
How we tell history matters. The story deep within Russian consciousness tells of how Russia, as a nation, was held together by the Orthodox faith and by the ‘heroic’ defence of the land against invaders. In the centre of the new main Cathedral of the Armed Forces (consecrated in June 2020, and a powerful symbol of the union of army and Orthodoxy) there is an icon of Christ the Saviour. Around it are four scenes depicting the defence of Russia against the Mongols, Swedes and Poles, Napoleon and Hitler. It must not be forgotten that 26 million people from the Soviet Union died in the second world war and Hitler intended to turn the Slav peoples into a slave people.
The current conflict has become part of this narrative. Ukraine has become the Western Trojan horse. Many Russians have never thought of it as an independent country; for many Kyiv is their physical and spiritual mother. But after Maidan in 2014, which it is claimed was facilitated by western money and information, it is considered to have become a western puppet. As a result of the revolution, a democratically elected pro-Russian president (Yanukovych) was replaced by a pro-western president (Poroshenko), and it has followed an increasingly anti-Russian and pro-Western line. It was therefore only a question of time before, whether openly or in secret, nuclear weapons directed at Russia would have been placed there.
In September 2022 the Patriarch spoke of how Russia, in her history, has only engaged in defensive wars: the ‘special operations’ are perceived by the leadership as defensive. This was a conflict, it is claimed, that needed to be fought now, in order to prevent a bigger war in the future. They are necessary to secure the future of Russia against an aggressive NATO, who have always wanted to break up Russia, and are now showing their true colours by fighting a proxy war against Russia in Ukraine. There is a current poster on billboards which shows a Russian soldier superimposed on the image of Alexander Nevsky, who defeated the invading Swedes (1221-1263). Underneath is the slogan, “A time for heroes.”
A cultural conflict
Putin’s second position is that Russia is standing up against an arrogant, even satanic, West which wishes to impose its economic, cultural and moral values on Russia and on other nations.
In his speech to the Federal Assembly on 21 February 2023, Putin spoke of how the West has lost touch with its moral and spiritual roots, has rejected ‘traditional spiritual and moral values’. It has replaced Christian tradition with what is called totalitarian liberal individualism. There is bemusement about gender debates (it is not illegal in Russia to practise homosexuality, but it is illegal to promote it), and a perception that in the West the rights of small minorities have come to dominate public debate and set the public agenda. Western Churches are accused of having sold out to the agenda of liberal individualism, and of losing their spiritual foundations. It is said that, having sown the wind the West will, in time, reap the whirlwind.
Nevertheless, it is claimed, because of its economic power, the West has been successful in exporting liberal individualism and has trampled over other cultures and value systems. Globalisation is perceived as Americanisation. Putin regularly speaks of wishing to create a multipolar world, not dominated by the hegemony of the United States and the dollar.
This is an argument which is persuasive in many parts of Asia, Africa and Latin America. It is noteworthy that of the 180 nations who were eligible to vote in the UN resolution on 23 February 2023, 141 nations demanded that Russia should immediately leave Ukrainian territory, but 39 countries either abstained or voted against the resolution, including China and India. There has been no change since a similar resolution in March 2022. About 40 countries have introduced sanctions against Russia, representing only 16% of the world’s population (Wilson Center). It is difficult to imagine, given the virtually universal opposition to the invasion in the West, that there is a deep global divide which is growing. As Russia’s doors to the West close, they are opening to the East and South. At St Andrew’s Anglican Church in Moscow, our western members have left the country, but they are being replaced by increasing numbers of people from India and Indonesia.
Meanwhile the conflict is spoken of in church circles in increasingly apocalyptic language, as Armageddon, or pre-Armageddon, a ‘war of the army of the Archangel Michael against the devil’, a Holy War for the defence of Orthodoxy and traditional values against ‘liberalism, globalism, secularism and post-humanism’ (Alexander Dugin, 27 Oct 2022). Both President Putin and Medvedev have at times used this apocalyptic language, declaring that Russia is engaged in a war against satanic forces.
Understanding Russophobia
Putin’s third criticism is the West is Russophobic, and has neglected the fate of Russians – particularly those in the Donbas, and is guilty of double standards.
In his book on the origins of the first Crimea war, 1853-6, Orlando Figes writes that the immediate cause of the conflict was a dispute between church wardens over some keys (to the Holy Sepulchre in Jerusalem). Of such things, history is made! But he also partly blames Russophobia in both England and France for stoking the conflict. He writes of tracts and articles written at the time, “The stereotype of Russia that emerged from these fanciful writings was that of a savage power, aggressive and expansionist by nature, yet also sufficiently cunning and deceptive to plot with ‘unseen forces’ against the West and infiltrate societies”. That could have been written today. For many years, long before the current war, the stereotype of the bad guy in films has either been a Russian or eastern Slav.
Russia’s foreign policy has done nothing to counter Russophobia. There is an understandable huge fear of Russia in Eastern Europe, and Moscow has never recognised or acknowledged any of the atrocities committed in the Soviet era (although, to be fair, it has taken the UK about 100 years to begin to recognise some of the harm that the British empire inflicted on its colonies). And certainly some, at least on the surface, relish in the Russophobia. A man I met in the supermarket (this was just after the Salisbury poisonings) said to me, ‘You don’t need to be afraid of me. I’ve tied my bear up outside.’
The accusation of Russophobia is often levelled at any criticism of the Moscow regime, but among other things, Russophobia is blamed for what is perceived as the neglect of the role played by the people of the Soviet Union in defeating Nazi Germany. That may sound strange to us, but it is a huge thing in Russia. For the last ten years, on Victory Day, after the tanks have rolled through Red Square in the morning, there has been a far more significant event in the afternoon, usually neglected by western media. Up to 2 million people have gathered in Moscow, and similar numbers in other Russian cities, for the march of the ‘Immortal Regiment’, to commemorate those who died in the second world war.
Russophobia is also blamed for the fact that, after the collapse of the Soviet Union, Russia was treated as a defeated enemy, and never given sufficient respect. It is blamed for the neglect of the fate of Russians left behind on the wrong side of the border after the collapse of the Soviet empire. That was particularly true after 2014 in Ukraine, when it is claimed that Russian majority areas such as the Donbas and Crimea were discriminated against. Kyiv refused to implement the Minsk agreement, which would have allowed elections of self-determination and which would almost certainly have been pro-Russia (Kyiv’s response is that Moscow had invaded Crimea, destabilised the Donbas and did not implement its part of the Minsk agreement). Certain incidents in which Russian speakers were targeted by Ukrainian nationalists were widely reported, as were the anti-Russian views of some of the right-wing nationalist groups in Ukraine, such as the Azov Brigade - which has led to Putin declaring that this is a war against Nazis. Putin has said that he will stand up for persecuted Russian minorities.
There is also the accusation of double standards. While the West has condemned Russia’s special military operations, which Russia claims is to guarantee its security, de-nazify and de-militarise Ukraine and protect the predominantly Russian population in the Donbas, the West has embarked on its own military expeditions, most notably in Iraq, Libya and Syria, justifying them in terms of either guaranteeing its own security or extending democracy.
On the edge
Perhaps the Russian critique of the West can be best summarized by Sahid, a taxi driver from Dagestan. We’d arrived in Moscow, a couple of weeks ago, after one of our epic journeys from the UK back to Russia and were exhausted. But he was very talkative! He defended the ‘special operations’: ‘Imagine that you are a peaceful guy, wanting to live a peaceful life. You are sitting on a bench. Someone comes and sits next to you. And then they start to push you to the edge of the bench. At some point, however peaceful you are, you are going to have to do something. You are going to have to either push back or be pushed off the end of the bench’. In other words, Sahid was saying what many Russians are saying to the West, you have pushed us so far, and we are not going to take any more. The tragedy is that, once again, the Ukrainian people – the border, edge people – are paying the price.