A note to our readers: this article includes reports that some readers may find particularly distressing.
On 27th May, the Archbishop of Canterbury, Justin Welby, tweeted about his concern at what has been, and still is, unfolding in Manipur in India. He wrote,
‘I’ve been distressed to hear about the attacks on the indigenous tribal Christians of Manipur, India, and of the churches that have been destroyed in recent weeks.
Kailean Khongsai is training for ordination to the priesthood in the Church of England, and is from Manipur. I join him in praying regional authorities would protect all minority groups, including Christians and their places of worship, and that justice and peace would prevail.’
In doing so, Archbishop Justin pointed the world in the direction of those who are facing extreme pressure, discrimination, and violence in their home of Manipur. Therefore, allow me to paint a fuller picture of what has been happening (largely unnoticed) for weeks now – let’s rewind to May 3rd.
May 3rd
On the streets of Manipur, a state in the northeast of India, indigenous communities protested the (apparent) impending accreditation of Scheduled Tribe status to the Meiti community. Let me provide some context as to why this would be a development to protest about.
Manipur is a self-governed state. A state that is home to the Meiti community, who make up around 53 per cent of the population, and other indigenous communities – the largest of which are the Kuki community, to the south, and the Naga community to the north. There is, and has long been, friction between these neighbouring people groups. The Kuki and Naga communities, being minority groups, have Scheduled Tribal status, thus ensuring that they have a right to protection (particularly regarding the reservations they call home) and representation. The Meiti people, being the state’s majority demographic, do not have such a status… yet.
Despite their legal protection, the Kuki people, in particular, have already faced ongoing evictions from their homes in the hill regions that they have inhabited for hundreds of years. Their expectation is that this is only the beginning. The fear is that, if the Meiti people were to be granted a similar Tribe status, it would result in the Kuki people further losing the right to keep and protect their spaces in both the hills and the forests. It would also pave the way for the Meiti people to assert more societal dominance, as they would be entitled to increased governmental representation; the imbalance would no longer be countered.
And so, on May 3rd, people from both the Kuki and Naga communities took to the streets and marched for ‘tribal solidarity’.
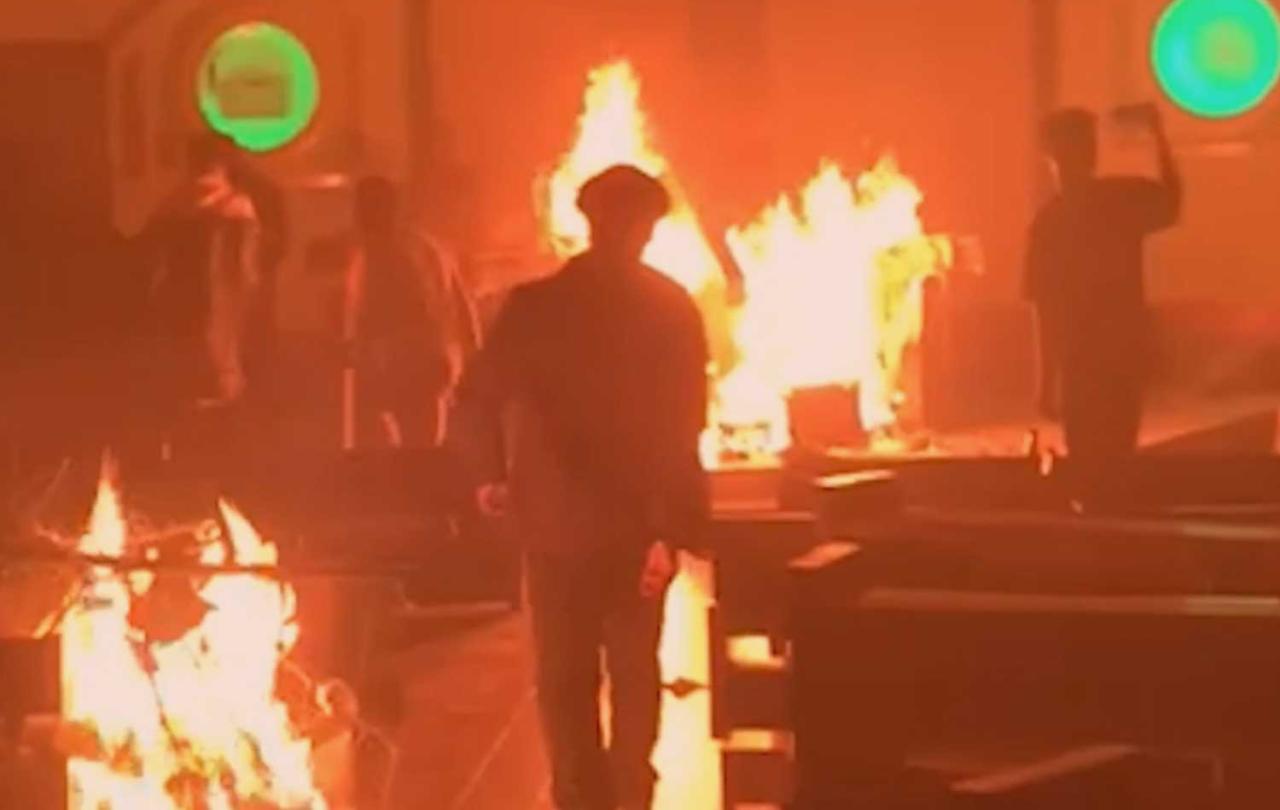
Within a matter of hours, a peaceful protest was transformed into riotous violence as the people marching were met with a wall of resistance. Since that Wednesday afternoon, whole villages have been burnt down, around 15,000 people have been made homeless, hundreds have been injured, the price of essentials has risen to unprecedented levels, schools and public facilities have been closed, internet has been suspended, and although numbers are proving a challenge to confirm, it is thought that anywhere between thirty to seventy people have been killed. Some media outlets are perceiving this violence as the rumblings of an impending civil war; while the Kuki and Naga communities are placing the entirety of the blame upon the Meiti people, The Meiti community are directing all blame toward the tribal communities. And the violence continues to rage on.
May 4th
Recent footage has emerged of a particularly heinous incident taking place on 4th May, one that has re-caught the world's attention and thus prompted Prime Minister Narendra Modi to break his silence, declaring that the attack has 'shamed India'.
Two women, both of whom belonging to the Kuki community, were taken from a police van, stripped, publicly paraded and sexually assaulted in broad daylight. Two men, the younger woman's brother and father, were killed while trying to protect them. It is now being reported that this attack was carried out by armed Meiti men, none of which were arrested until astonishingly recently, more than two months after the attack took place.
Manipur is imploding, and the violent ramifications are devastating.
But there is just one more piece of context that undergirds the Archbishop’s tweet, one more thing to note about the societal dynamics at play in Manipur: while the Meiti community are a majority Hindu people group, the various indigenous groups are almost entirely Christian. As such, Open Doors have reported that the women who were subjected to to the afore-mentioned attack were Christian women.
A complex ethno-religious conflict
The goings-on in Manipur are anything but simple; and so, it is not my intention to reduce the geographic, political, and historic complexities of this conflict, nor to wholly define it as a war between religions. Following Archbishop Justin’s lead, it is with particular caution that I speak of violence being inflicted particularly on Christians in Manipur, acknowledging that it is not the only identity marker that is proving to be targetable.
Nevertheless, it is being widely reported that Christians are being singled out; their Christianity used as a target to aim at, their identity wielded as a weapon against them. Whether it be as the means or the end, as the goal or merely the tactic: it is happening.
According to further Open Doors’ reports, derived from their partners in Manipur, around three hundred churches have been burnt down thus far, one of which still had people in it when it was set alight. A further one hundred public Christian buildings have been destroyed, while one thousand homes which were owned/inhabited by Christian people were ruined, while neighbouring properties remained untouched.
And it isn’t only the Kuki Christians who are facing such discrimination, the (very few) Meiti Christians are also facing particular difficulties as a result of their unusual ethno-religious identity. Noticing this, one Indian news publication is reporting that from the perspective of the Meiti Hindus, Meiti Christians are somewhat of an oxymoron, personified. It is believed that to be Christian is to have converted to a tribal way of living (assimilating the Kuki and Naga people), and therefore comes with assumptions of deep betrayal. And yet, the publication also observes that ‘if their [Christian] faith is making them feel insecure in the valley, it has not come to their rescue in the hills either. The Kukis have made no distinction between them and other Meiteis’. They are, subsequently, a community that are ‘sandwiched’ in conflict.
While the conflict is undoubtedly spilling over ethnic and religious lines, Manipur has just become one of the most dangerous places on earth to be a Christian. In yet another part of the world, it is now a hazardous faith.
And so, back to Archbishop Justin’s tweet.
The need to be seen
One only needs to spend thirty or so seconds tracking the comments generated by this particular tweet to get a sense of how powerful it is to be seen. To be noticed when in distress, to be acknowledged when in chaos, to be advocated for when in danger.
In many ways, social media is a genie that we wish we were able to squeeze back into the bottle. And as justified as such feelings often are, in this case, as in many others in our recent history, it has proved to be a way in which our eyes are opened to what is happening in the most remote corners of our world. Archbishop Justin has publically called for protection, justice, and peace, and in doing so, has made it difficult for the conflict to continue to rumble on unnoticed.
It is now on all of us to refuse to look away. The people of Manipur, Christian and otherwise, need us to continue to look in their direction.