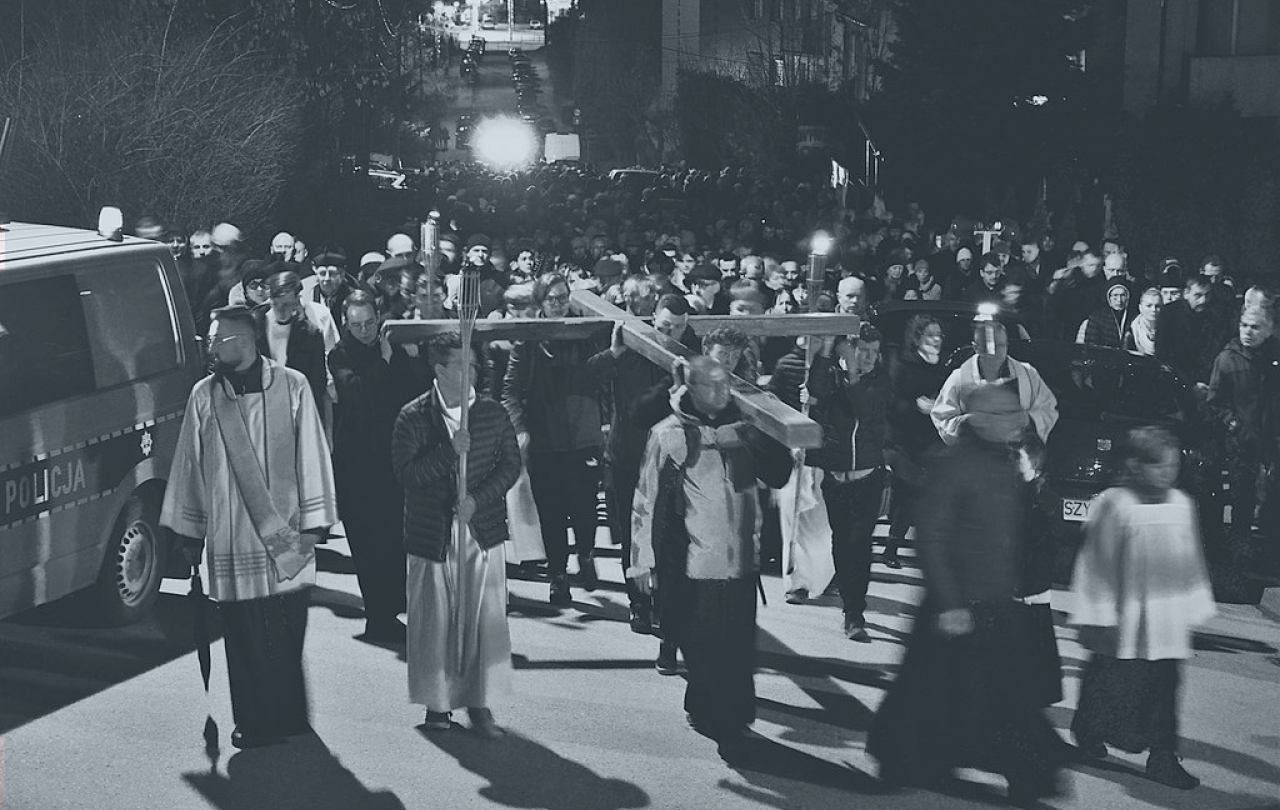
Easter is not about the Easter Bunny. Easter is about the paradox that we all try to skirt: only in death is there life.
But Easter is not just about metaphorical death and rebirth, at least not for Christians. Christians don’t believe that Jesus died for our self-esteem. Nor that he raised an Idea of himself. As Thomas Lynch, undertaker and poet in Midwest America reminds us,
“Do you think they would have changed the calendar for that? Done the Crusades? Burned witches? Easter was a body and blood thing, no symbols, no euphemisms, no half measures.”
Christians believe that Jesus’ body died. Ceased breathing. Flatlined for three days. And then (in myth-like fashion of the dying and rising god) this human being who lived at certain GPS coordinates, and had DNA from his mother, was given his life back. Not resuscitated. But resurrected. Yes, reader, Christians believe this.
Our culture is body-obsessed when we are living, and body-denying when we die.
Who are we without our bodies? When people die, Christians insist that their body isn’t just a “shell” of the real person. No, their body still is the person. That’s why cremation didn’t catch on in the Christian west until recently, and even so, your local priest might turn up their nose if you want to distribute the ashes into jars to be divided between the grandkids. Often, as soon as a person dies, our impulse is to insist, “she’s not there.” This is because our culture is body-obsessed when we are living, and body-denying when we die. As Prof John Behr, a University of Aberdeen specialist in thinking about death, observes, we want to live like hedonists and to die like Platonists. Easter presents a counter-narrative here. Our bodies have meaning. Jesus’ body has meaning.
In re-living the events of Holy Week, all eyes are on Jesus’ body. And Jesus’ body is doing some very physical actions – like healing bodies, raising bodies, touching unclean bodies, washing feet. And then it is his turn to have his body ravaged by arrest, torture, sleeplessness, betrayal, and execution. All eyes are not on the idea but on the body of Jesus. So much so, that they put guards at the tomb so that there could be no more monkey business about this man’s body.
It might seem peculiar to us that Christianity, infamous for its historically mixed relationship to the body, is centered on one man’s body. Ancient Christians spoke poetically that the tomb that held Jesus’ body became a womb. In his death, in the absolute silence of death, Jesus chose to share dead-ness with us. That this was the essence of his “work.” That his work could only be accomplished by surrendering, doing nothing – and that in doing nothing, he undoes the great “nothing” that threatens each one of us. Almost everything we fear, big and small, is somehow connected to a fear of death in one form or another. It is not death, per se, but the “fear of death” that enslaves us (says an early Christian preacher in Rome. And so, Easter stands at that pivot point between fear of death and life. Christians celebrate Easter as the day the world tilted. Where death no longer has the final say, but is something we can now use to our advantage. In fact, life begins to break in precisely through death. This is only because, as James Alison once said in an Easter sermon, “He entered into death and made it untoxic.”
The question is not “is there life after death” but is there life before death?
And so, strangely, Christians embrace death. We parade it on crosses through the streets. We paint it on our tombs, over our meeting houses, wear it on our chests. Because in embracing death (and the even more enslaving fear-of-death), we defeat it. Because of this belief, ancient Christians flung themselves at lions. They endured the agony of torture. They sanctified suffering. They also practiced small unnoticed “little deaths” of that great overlord, the ego. Not because suffering or death is good, or to be sought. But because death and suffering have been transformed into portals. Even in baptism, with oblivious babies being christened in frilly white dresses, we are dipping them defiantly into the waters of death and waging war on death. This is the mystery of Easter. This is why every Sunday is called a “little Easter” because even as we shuffle into that old stone church, something outlandish is being proclaimed. Death is not a friend, but neither is it to be feared. The worst has already happened. Now we can get on with living. The question is not “is there life after death” but is there life before death?
And here is the final kicker: Christian orthodoxy proclaims that Jesus still has his body. (Not every Christian would insist on this, but it has been central to the tradition for two millennia). Easter isn’t just a mythical story of the paradigmatic victory of life over death. Paul talked about it as a complete reversal: that instead of death swallowing life, Jesus’ embodied life swallows up all death. Christians believe that he is alive and well, in some kind of body (“transfigured” in Christian slang), pouring out blessing on all embodiment. This isn’t a body that is somewhere floating above us in the clouds, but is an embodied person raised as their whole life narrative into eternity – as one recognizable life. Resurrection is not the hope of our joining Jesus in the clouds, but of this same raising of our whole lives into Life itself. This is called “putting on immortality” like a coat – where everything from our past (even scars, like Jesus still had) is integrated into one recognizable life.
This is the Christian hope of Easter, as we live in the interim, no longer fearing but using death for dear life.