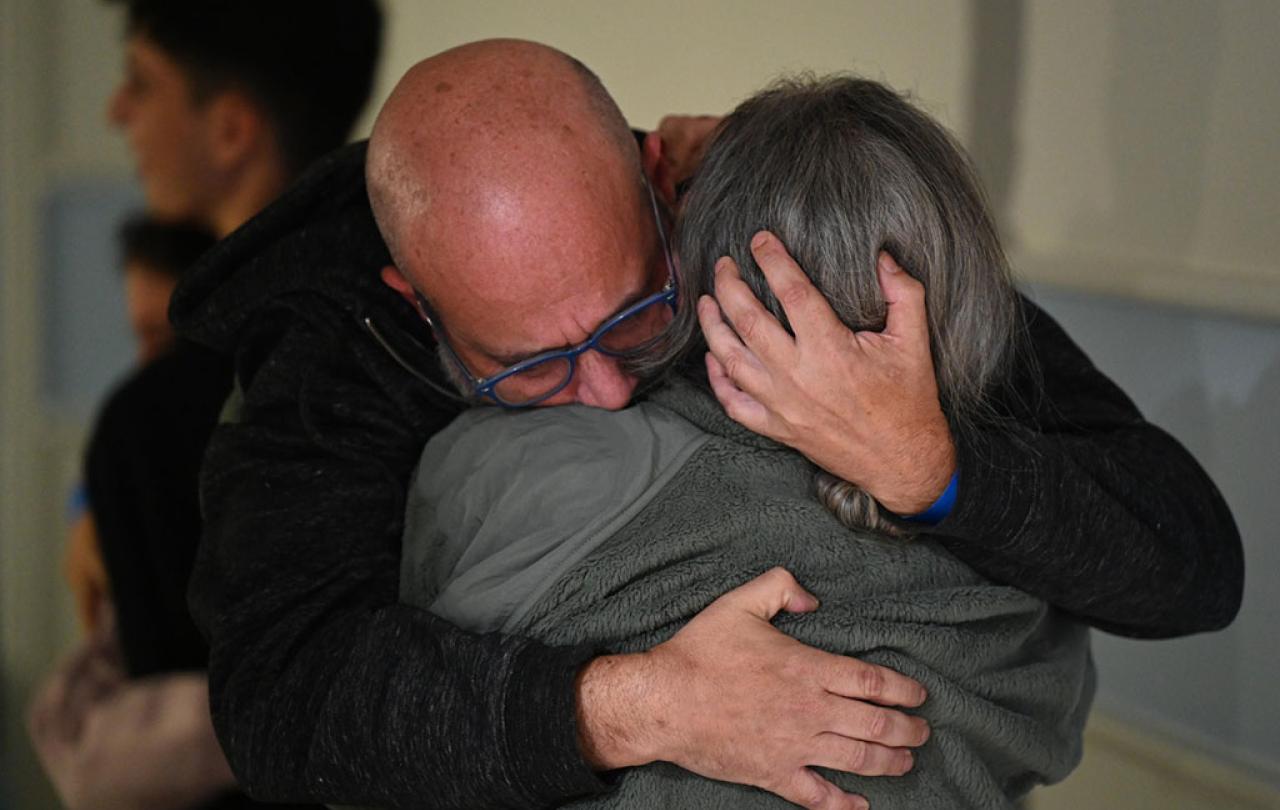
With the drama over temporary ceasefires and limited hostage exchanges, we are fixated at the moment on the day-to-day drama of the Israel - Hamas conflict. Yet, to draw back for a moment, what about the longer-term prospects for peace? Many people in the west, dimly aware of the politics of the region might wonder how on earth some kind of settlement might ever be reached. How does it all end?
Prediction, so we are told, is a mug’s game when it comes to international politics. Or is it? Because the history of Israel/Palestine has taken a depressingly predictable pattern over the past 50 years or so – periods of relative peace, interspersed with occasional Palestinian uprisings of various degrees of violence, followed by Israeli military reactions, of which the current conflict is the most serious for many years.
So, what are the options for the future? This article aims to spell out the main possibilities going forward, their advantages and their problems.
We start with the two extreme scenarios.
The Hamas solution
The original charter of Hamas, published in 1988, called “The Covenant of the Islamic Resistance Movement” is uncompromising. Article 1 reads:
“The Movement's programme is Islam. From it, it draws its ideas, ways of thinking and understanding of the universe, life and man. It resorts to it for judgement in all its conduct, and it is inspired by it for guidance of its steps.”
Hamas is an explicitly Islamic renewal movement and aims at the creation of an Islamic state across the land of what is now Israel, the West Bank and Gaza. The covenant was updated in 2017 with (mostly) more moderate language, but still the aim is clear:
“Palestine is a land that was seized by a racist, anti-human and colonial Zionist project that was founded on a false promise (the Balfour Declaration), on recognition of a usurping entity and on imposing a fait accompli by force.”
Now, it states:
“Hamas’ is a Palestinian Islamic national liberation and resistance movement. Its goal is to liberate Palestine and confront the Zionist project. Its frame of reference is Islam, which determines its principles, objectives and means."
It claims to oppose, not Jews as such, but what it calls ‘The Zionist entity’, in other words the state of Israel.
The Hamas solution is an Islamic state within which Christians and Jews would be allowed to live, but definitely under Muslim rule. It has no truck with a shared land: “Hamas rejects any alternative to the full and complete ‘liberation’ of Palestine, from the river to the sea.” As the 1988 version puts it:
“The day that enemies usurp part of Moslem land, Jihad becomes the individual duty of every Moslem. In face of the Jews' usurpation of Palestine, it is compulsory that the banner of Jihad be raised.”
It’s hard to see this in any other terms than a project which would mean ethnic cleansing of the majority of Jews from the land of Israel.
The settler solution
Israel's political voting system is Proportional Representation. Historically the two main parties, Labour and Likud have struggled to gain enough votes to have an absolute majority. PR means that numerous marginal political parties have small groups of members of the Knesset, the Israeli parliament. It also means that they wield disproportionate power as they can make or break governments by joining one or the other of the two main parties. At the most recent elections, Benjamin Netanyahu, the Likud leader, generally the more right-wing of the parties, established a coalition which brought some of these more extreme right-wing parties into government.
For example, Israeli Heritage Minister Amichai Eliyahu, a member of the Otzma Yehudit party, recently suggested that one way to resolve the war would be to drop a nuclear bomb on Gaza. For him, the people of Gaza “could go to Ireland or deserts [and] should find a solution by themselves.” He was immediately suspended for his comments by Netanyahu, but it illustrates the problem the Israeli Prime Minister has. Eliyahu is at the extreme end of the spectrum, but many of these small parties are strong advocates of the building of Israeli settlements on Palestinian land, taking more and more of that land under Jewish control and effectively freezing out the Palestinian population. Their solution is somewhat of a mirror image to the Hamas solution. It is effectively to push as many Palestinians out of the land as possible, ideally relocating them in other Arab countries or throughout the west – another form of ethnic cleansing.
The two-state solution
This has been the favoured end-game of many on both sides of the dispute and the wider international community until relatively recently. Going back to the UN partition plan of 1947 which proposed two contiguous states, one Jewish, one Arab, various versions of this solution have been proposed over the years including the Oslo accords of 1993. This has also been the cornerstone of US foreign policy and its preferred pathway. Its attractions are obvious - two independent states living happily alongside with another without the ongoing tension of the Israeli occupation or Palestinian hostility. There are however a number of problems with it.
First, political solutions that involve partition are rarely stable. Northern Ireland embraced a version of partition in 1921 with the island of Ireland split between largely Protestant Northern Ireland and a largely Catholic Republic in the south. However, this did not resolve tensions between the two communities and led to the troubles of the 1970s and 1980s which left thousands of people dead. Secondly, it is not clear what kind of state the Palestinian entity would be. As outlined above, Hamas envisages this as very definitely an Islamic state under which Christians and Jews would have to submit to a form of Islamic law, whereas Christians (for example) have in the past been a major presence in Palestinian society. Third, and most importantly, the West Bank would clearly be an obvious location for a Palestinian state, yet Israeli government policy over the past few decades has seen a huge increase the building of Israeli settlements on Palestinian land, especially within the West Bank. With its numerous scattered Jewish settlements, it is really no longer viable to envisage an independent Palestinian state as so much of the West Bank is now occupied by settlers who have no intention to leave.
The one state solution
This is the solution increasingly favoured by many Palestinians, whether in the West Bank, or Israeli Arabs who live within Israel itself. It is the idea of a fully democratic state where Jews, Christians and Muslims could live alongside with another with equal rights and responsibilities, where Israelis and Arabs were equally recognised as full members of society with no need for rockets fired, suicide bombers, checkpoints, house demolitions, security walls, freedom of movement and so on. The attractions of this to those living in western liberal democracies will be obvious.
The problem, however, is that Israel has always been seen from the beginning of the Zionist movement as a safe haven for Jews in particular, and in 2018, a law was passed to make Israel an exclusively Jewish state. It is not hard to see the anxiety that a one-state solution would create amongst Israeli Jews, with the memory of the Holocaust behind them. What if the Palestinian population were to grow such that Jews were in a minority? Would Israel then be a safe place for Jewish people? Also with the history of tension and trauma in the past, it's hard to see Jews and Palestinians, especially those who have been through the traumas of the past living peacefully alongside each other anytime soon.
The status quo
Israeli government policy in recent years has effectively been to keep the lid on a relatively unstable situation by the gradual increase of settlements to make a Palestinian state impossible. It may be hard to imagine under current circumstances, but the Israelis have until recently thought that Hamas’ control of Gaza was a good thing for their purposes, as it split the Palestinian population between the Hamas-controlled Gaza and the Fatah-controlled West Bank, the two parties being at loggerheads with each other. Combined with the policy of what is sometimes called ‘mowing the lawn’, striking back with some force at Palestinian uprisings when they occur, keeping resistance in check, this is represented to many within Israel as the only and best way of ensuring some kind of security in the long term. The problem is that it perpetuates the conditions that sustain Palestinian resentment, leading to the regular intifadas, uprisings and rebellions that we have seen over the past decades.
What is clear is that the international community has not always helped to find solutions, either supporting extreme parties on both sides to protect their own interests, or funding for military purposes that ensure these constant uprisings and responses, rather than advocating for the genuine long-term benefit of the people who live in the land itself.
What do we make of all this? And what does Christian faith have to offer such a bleak prognosis? For one thing, it doesn't offer a neat solution. The important business of politics is to work out the intricacies of ways of living together in peace and harmony. What seems clear, and as Christian faith insists, with its unlikely and radical call to love the enemy, is that there is no way to kill your way to peace and security. What Hamas did on October 7th and, however it may be justified in the short term, what the Israeli government is doing at the moment - neither will lead to peace and security. The Israeli bombardment of Gaza is a tragedy not just for the Palestinian people but also for the Israelis as well. Unless it succeeds in driving the Palestinians from the land entirely, in the kind of ethnic cleansing that few seriously contemplate, it will simply lead to another generation of young Palestinians who hate Israel and all it stands for, and who are dedicated to attack it again in a decade's time. Recent polls among Palestinians suggest that Israel’s action in Gaza, however understandable, is already having that effect. It is very hard to see any way in which it can lead to the security and peace that most Israelis want and so badly need.
What would Jesus do?
The first century in Judaea faced similar issues. The ownership of the land was disputed – did it belong to the Jews or the Gentile Romans? And how do you relate to those on the other side? Is the only way to either avoid them or try to kill them?
The result of the coming of Jesus was the creation of an entirely new kind of community: the Church. Here was a gathering (which is what the word 'Church' or ‘ecclesia’ really meant) where the main distinctions that ran through normal social life no longer mattered – here there was to be “neither Jew nor Greek, male nor female, slave nor free”. It was not that these distinctions were done away with entirely - but they made no difference within this new community. The unity between people was based not on any ethnic, class or national commonality, but on each of them belonging separately to God in Christ. Their relationships were not two-way, but three way – each relating to the other because they both relate to the God revealed in Jesus.
This was a new kind of politics. The church has, to be fair, struggled ever since to live up to this vision. It is as if a beautiful song was given to the church to sing, yet it so often sings it out of tune. Yet the church, for all its faults, is the vision that Christianity offers the world. A way needs to be found for this land with such a complex heritage, where both Jew and Arab have strong claims for it as a historic homeland, to be shared in some way. Whether that is a form of the one-state solution or a two-state solution - or an entirely new scenario as yet unimagined - that cannot be decided from outside but has to be decided by those who live there. What it will need is a newly imagined form of politics, both within Israel and outside - a new way of living together with difference in the polis, one towards which the Church, with all its faults, and in its own stumbling way, points.