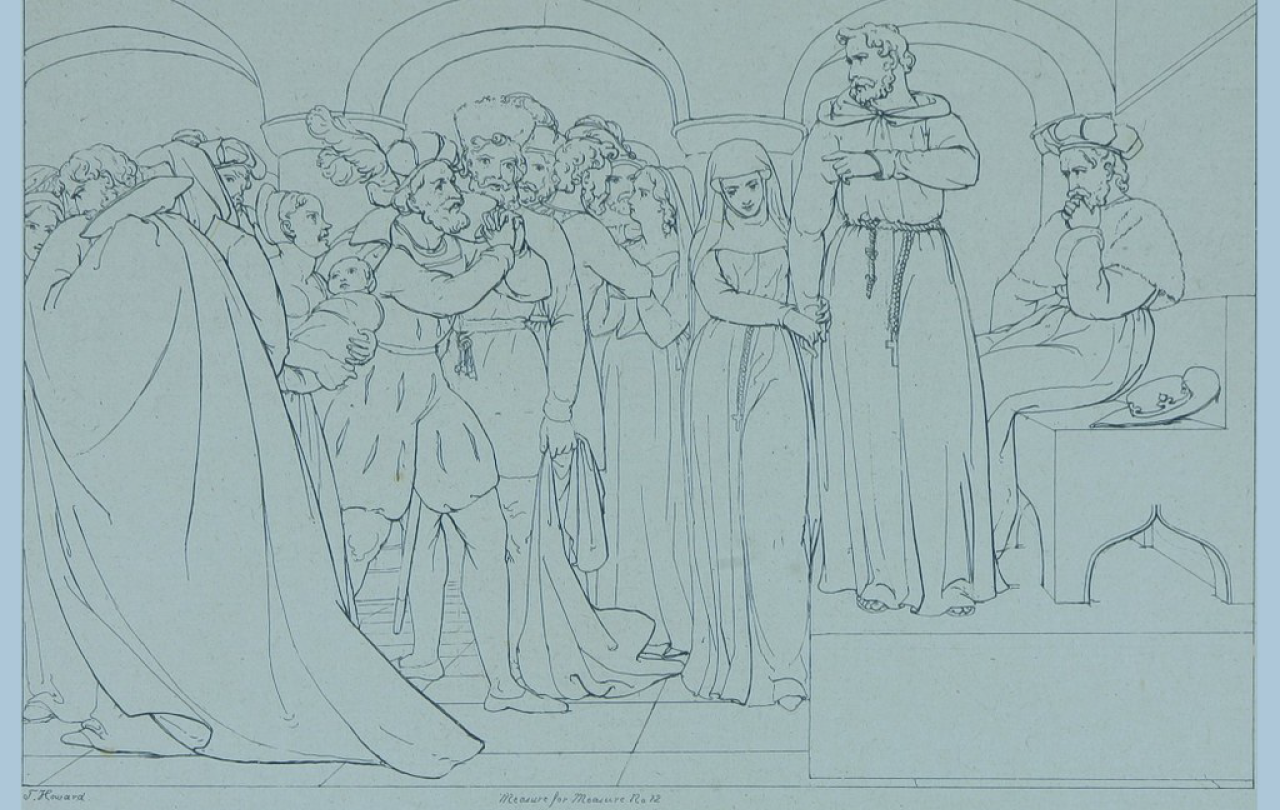
In order to act with mercy toward someone, must I forgo a sense of justice? If I decide to act justly, have I decided to leave mercy behind? These are questions of philosophers and theologians. They also provide some of the thickest philosophical and theological ponderings of William Shakespeare.
A studied contemplation of mercy and justice does not, of course, originate with the Elizabethan playwright. For as long as humans have pondered how to order their civic spaces, they have puzzled over the demands of each. Around 500 B.C.E, Rabbi Yehudah is recorded as having said that God spends three hours a day on a throne of justice before getting up and crossing over to a throne of mercy, on which he spends an equal length of each day. 200 years later, when Plato devoted his most famous dialogue to the question of justice, he gave only the slightest nod to mercy, acknowledging that the just ruler would need a reputation for generosity.
Though many of Shakespeare's plays notice the interaction, or lack of interaction, of these two qualities (The Tempest and nearly all of the history plays, for instance), he penned two for what seems to me the explicit purpose of letting these two ancient enemies fight it out on stage. I'll focus on one of these and return briefly below to the other.
Justice Unbound
The first, Measure for Measure, takes its title from a line from Jesus' sermon on the mount. This is a signature move of the Bard, to take a religiously charged line, doctrine, or even person, and make theater out of them. While some have argued that this was all he was doing with religion or theology, I have suggested that he is doing more. He is mining the depths of faith language to see if he can find gems that we might be missing if we only pay attention to the identity politics of Reformation era England. "Grace is grace despite of all controversy," one character in this play says. That could be the tagline for Shakespeare's theological interventions.
We see Shakespeare having some of his typical fun with religion in Measure for Measure. The Duke of Vienna gives away his power in order to go abroad, as he claims, for a piece of international politics. In fact, he sneaks back into the city immediately, now disguised as a friar (a member of a religious order like the Franciscans). He tells the friar who lends him the robes that he is doing this because he has made an irresponsible practice of letting the city's "strict laws and biting statues slip." He has, that is to say, been more of a merciful father than a just ruler. He doesn't want to unbind this "tied-up justice" himself, since he fears this would cause his people to question his integrity. ("But you've always been so merciful before now!") So, he contrives a plan to deputize one of the nobles, Lord Angelo, to be the hammer of justice in his stead. He also hints that there are other reasons for his disguise. I'll come back to that bit of foreshadowing.
Angelo immediately finds an episode in need of his firm hand. A gentleman named Claudio has got his girlfriend, Julietta, pregnant. There are in fact circumstances that seem worth considering: the two are engaged and are only waiting for her to receive her dowry - arranged before they go to church. But Angelo will not hear of clemency. He is severe, one noble remarks. This is as it should be, a wise old Lord responds. "Mercy is not mercy that oft looks so," he says, perhaps angling gently at a critique of the Duke's mode of operation.
Justice only deals with what it can see, in other words. We pick up a jewel on the ground only when it catches the light; buried or soiled, we walk right past it or even trample it.
Merciless Secrets
At this point in the play we have our two adversarial qualities in neat, separate containers. One container, called The Duke, is only merciful. But this container must be removed from the state so the other, called Angelo, can display its contents of merciless justice.
But, as this is Shakespeare, things quickly begin to get messy. Angelo turns out to be hiding secrets. The old Lord, having hinted that the Duke is over-merciful, now suggests that Angelo is being a bit hard on Claudio. He cautiously suggests that, had time and place given opportunity, Angelo himself might have come to the wrong side of the law. Angelo's response says more, perhaps, than he means to:
"What's open made to justice,/ That justice seizes."
Justice only deals with what it can see, in other words. We pick up a jewel on the ground only when it catches the light; buried or soiled, we walk right past it or even trample it.
This is our first hint of Shakespeare's subversion of the polarized containers. Listening to Antonio's speech, we've begun to wonder if, lacking the slightest trace of mercy, justice doesn't in fact begin to look a little unfair.
And then we see Angelo acting on his theory. Claudio's sister comes to him to beg for her brother's life. Angelo is quickly captivated by her beauty, and soon offers her a deal. If she will meet him for sex in the garden—secretly of course, so that the crime cannot be "unjust"— he will let Claudio free.
This offer obviously shows the rot in his theory of justice, as he is forming a contract, a just bond, around blackmail and rape. But it also ruins mercy, since his proposed pardon of Claudio is not merciful at all, but simply the meeting one end of a "just" bargain.
The Kiss
Our neat containers have nearly dissolved around their contents. "Mercy is not mercy that oft looks so," but justice is not justice that only looks so. Justice as merciless as Angelo's turns out to be unjust, in the same way that mercy without justice turns up bereft of mercy. This is why the Duke left, and it's why Angelo fails as his deputy.
But the Duke has returned, and now we begin to see what his secret purposes are. He goes to visit Claudio for confession and counsel, and also goes to Claudio's sister for comfort and advice. Here is one of the delightful places where Shakespeare plays with religious stereotypes. The "controversy" of grace that I mentioned above, is for Shakespeare's audience an all-too familiar one, over whether God saves us through our works, and so through a contractual justice, or through grace, which is to say through an act of unearned mercy. The Catholic Church was generally (though not often accurately) associated with the former, the Protestants with the latter. But here it's a Catholic friar (or at least a disguised one!) who enters as the personified mercy.
The Duke/friar devises a plan, and it nearly goes as awry as the more famous friar's plan in Romeo and Juliet. Which is to say that our comedy nearly becomes a tragedy. I won't give away the ending, if you've forgotten or never made it through. But I'll offer a hint: the Duke, on his return, is no longer an embodiment of unjust mercy as he was before. Now he sees clearly that true mercy is just, and true justice is mercy. The two must kiss, as the Psalm puts it. His clever idea for a resolution is all about allowing mercy and justice to exchange a kiss.
When Mercy Seasons Justice
The more familiar play in which Shakespeare lets us watch the battle of justice and mercy is The Merchant of Venice. Here we find the story of maybe the strangest contract made since the dawn of commerce: if a merchant defaults on his loan, the moneylender will claim an entitlement to "a pound of flesh." Is this mutually agreed-upon contract unjust, or simply merciless?
The religious fun is rampant in this play as well. The lender is a Jew and the merchant is a Christian. But the Jew's strict call for commercial exactitude gets tempered by his excessive love for his daughter, and the Christian's supposed reputation for grace is in fact an excuse to practice favoritism. Eventually we have on stage such a confusion of religious stereotypes that someone asks which character is which.
Well, the poor merchant can't pay, as we knew already at the moment he made the foolish contract. And so, Portia, this play's mercy persona, comes—also in disguise—from the fairytale land of Belmont with a clever trick to save her beloved merchant. While her solution involves a highly questionable interpretation of the law, she manages to persuade the ruling authority.
As Portia is making her case, she offers one of the most explicitly theological speeches in all of Shakespeare's works. Earth's rulers might think they are most godlike when they enact the law with authority, she says. But "mercy is above this sceptered sway." In fact, mercy is "an attribute of God himself." She concludes, much as the Duke concludes, that "earthly power doth then show likest God's/ When mercy seasons justice."
In plays like these we see displayed one of his most enduring gifts to us: the ability to play with the familiar and make it strange and new.
Shakespeare, had he indeed been "for all time" as a contemporary put it, would be celebrating his own 459th birthday this week. In plays like these we see displayed one of his most enduring gifts to us: the ability to play with the familiar and make it strange and new. He gives us philosophical and religious figures and themes, and then just as we assume we know who and what they are, he surprises us by showing what sort of dish you can make if you but swirl the ingredients.
Our best efforts at justice, whether of the personal or political sort, must be seasoned by mercy. Our acts of mercy, if not ultimately just acts, will turn out to be merciless. Would we have noticed this if no one had had let it happen on stage in front of us?