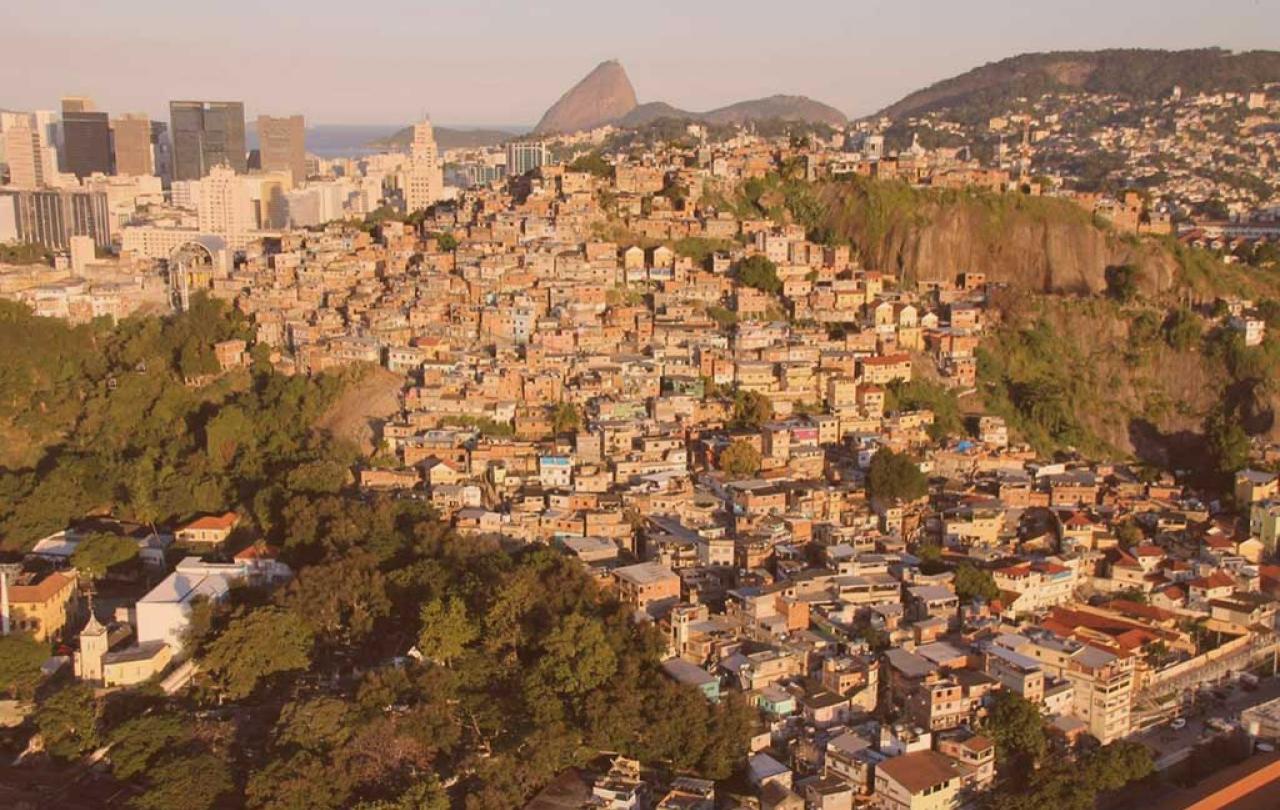
It was a hot and humid evening in 2015 and Luke had just moved into a tiny house in Morro da Providencia, Rio de Janeiro’s oldest favela, a shantytown located in the heart of the city. His new home was near the top of the hill, sandwiched between two loud and rampant drug dens. He could hear the parties and orgies happening above and below him twenty-four hours a day; his neighbours regularly firing bullets out of the windows. The noise was draining and constant. It was dark outside, and Luke sat frozen in fear, staring at a blank laptop screen by his window facing the street… waiting and praying. He had just been informed that the bandidos (drug traffickers from the main drug gang in the favela) were on their way to pay him a visit. Gossip on the street had spread that he was an undercover police officer. Why else would a white British gringo in his thirties choose to buy a house in one of Rio’s poorest and most dangerous communities?
“After about five minutes I saw a glint out of the corner of my eye… I looked around and a number of drug dealers were arriving on the porch.”
Faced with ten heavily armed gang members, they asked who he was and what he was doing in their community. Luke took a breath and explained that God had called him to Brazil from New York, and that he was choosing to live in Providencia because he loved the neighbourhood, and wanted to serve the community and build something for them; for their children and their young people. The gang listened. Then remarkably they lowered their guns, said “ok then”, and walked away. Luke was stunned.
“I know what happens to people… It was a very violent time. I thought I was going to die and it was terrifying. But God turned it around...”
The relief that he was alive quickly turned into disappointment; a realisation that despite all the sacrifices he had made to be there, he wasn’t wanted by the people he had given up everything to serve.
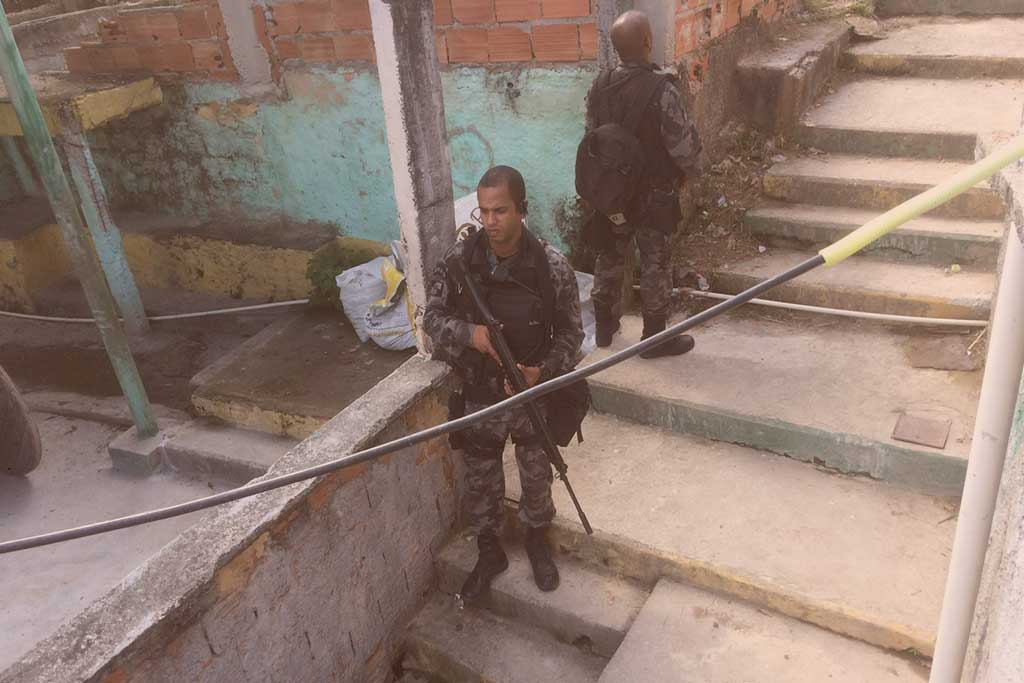
Armed police patrol the favela.

Five years previously Luke was living in New York working as a finance lawyer with a corporate law firm. He was single, his firm paid for his Manhattan apartment, and he had so much disposable income that he saved half his pay each month. Originally from the UK, he grew up going to a local church in Surrey with his family, but he’d fallen far away from God.
“I was in a favourable position to go off the rails. And I did go off the rails.” he says.
In 2009, the financial crash hit and having spent five years living and working in New York, Luke began to question the premise and direction of his life. Through a family member, he was put in touch with a Christian association working with street children in São Paulo in Brazil, providing living accommodation to homeless children, who were disenfranchised from their families and/or victims of abuse and neglect. The aim was to reintegrate the children where possible with their families. During a weekend visit to São Paulo, within fifteen minutes of being shown around one of the shelters, Luke had a deep conviction that this was where he was meant to be.
“It was not this Damascus Road moment,” he says. “It was a familiar voice. Not someone who was needing to twist my arm or convince me. I felt I was in good hands. Even though change was going to mean going from a six-figure bonus to zero salary…. I was suddenly ready to risk everything knowing I was in these safe hands.”
A few months later Luke moved from New York to Brazil and went on to live and work in one of the shelters for street children for several years. He talks about a particularly bleak time when one of the boys in the shelter took a dislike to him, the relationship becoming so acrimonious that Luke even began fearing for his life. Emotionally and mentally drained, feeling rejected by the children he was trying to care for, he went away for a couple of days to regroup and called his sister. He recalls,
“She said to me, ‘Just come home Luke. Just come home.’”
Her words made him realise that he had life choices the street kids simply didn’t have. He could choose to leave them and “go home” at any moment; home to people who loved and cared for him. The children he was working with were born without options or choices. So, Luke decided to stay, and by making that decision, hoped to model a love and commitment to those who perhaps had never experienced it. A love that doesn’t diminish or disappear, even when we turn our backs.
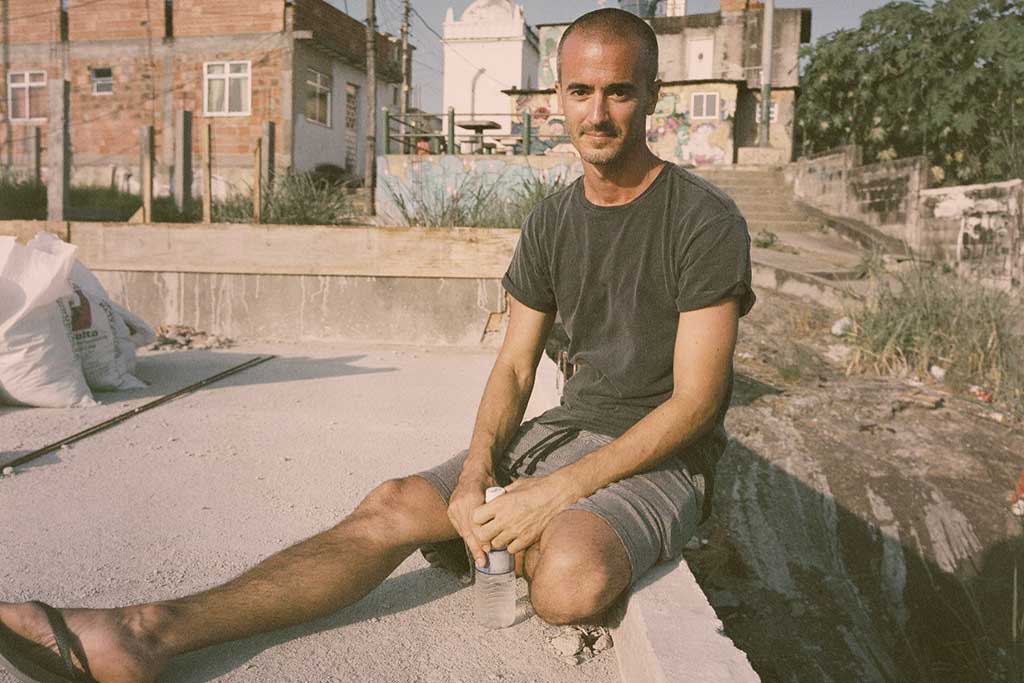
Luke Simone.

What is intriguing about Luke’s story is not the desire to “re-purpose” his life. So many of us feel at times in our lives that we are drifting without purpose or meaning but when we look for more purpose, it tends to be either seeking fulfilment in our work - towards more wealth or influence or social legacy - or through our relationships. What is intriguing is that Luke chose to follow God’s purpose, rather than his own.
Luke’s story is one of sacrificing comfort, wealth and status to simply do life alongside the people that society in general has given up on, and, at times, in return getting hostility and death threats from the very people he is walking with. The story is a little reminiscent of the gospel story of Jesus Christ. Although, of course, Luke will be the first to say that he’s certainly not Jesus - “unqualified”, “unprepared” and “broken” are words he uses to describe himself – but perhaps this self-awareness of his own flaws has given him the ability to rely entirely on God rather than himself, in a place where he simply has to.
Missionaries, like Luke, are perceived by many to be the outworking of a colonial interpretation of the “Great Commission.” This refers to a number of passages in the gospel of Matthew where Jesus tells his apostles to “make disciples of all nations.” People assume this means going to far flung places and preaching about Jesus. But when I asked Luke about his work in Providencia, for him, mission is far more integral and encompassing than “straight evangelism.”
As theologian Christopher Wright points out, Jesus was concerned with responding to the needs of people - both materially and spiritually - in the power of the Holy Spirit. The two go together and are integrated. The Book of Acts and letters of the apostle Paul in the Bible show a commitment of the followers of Jesus to preach the good news and bring others to faith, but also to live with compassion as a loving community seeking to address the social and material needs of those around them. In fact, Paul’s first of many missionary journeys was to provide famine relief to prevent starvation of the people in Judea.
So where is Luke now thirteen years after he first left New York? He still lives in Providencia and together with his team of volunteers and a local church in Rio, he has built and runs a community house, Casa Cruzeiro (House of the Cross) and adjoining educational annex at the highest point of the favela.
Casa Cruzeiro.
On entering Casa Cruzeiro during my visit to Rio a few months ago, I was struck by the sense of peace. The community around the house is far from calm. It’s poverty at its crudest and, as Luke will say, at times depicting humanity at its darkest. Murder, rape, incest, drugs, extortion, prostitution, abuse, neglect… the list goes on. Life at the margins doesn’t get more marginalised than this. Casa Cruzeiro is a light in the darkness, a stillness in the chaos. It operates an open-door policy where anyone is welcome, drug traffickers included (as long as they behave), for a meal, to hang out, to talk, even to stay if someone needs a roof over their head. About 200 children, adolescents and adults pass through their doors each week, and some of the activities include an afterschool programme, adult literacy support, a communal vegetable garden, career counselling, guitar lessons, bible studies and prayer groups. Material and spiritual needs met seamlessly and uncomplicatedly together as part of a whole.
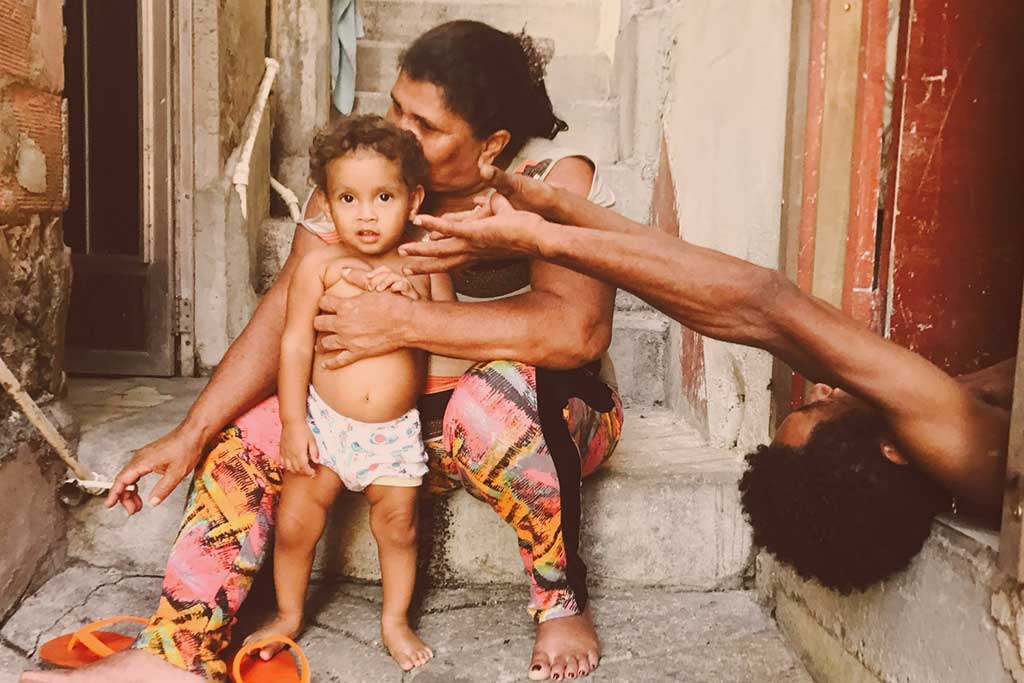
A Providencia family.

If you could rewind the clock by thirteen years, and make a different choice, would you? I ask Luke. He pauses, and says no, but is clear that it hasn’t always felt like an easy choice. He’s often pondered over the comfort and wealth that he left behind. But at the moment he has no plans to leave.
And what has he learnt about God over these years in Brazil?
When he relies on God he feels a deep sense of peace, and a conviction of God’s love in a way he hadn’t known before.
“When God called me to Brazil, he was saying, ‘You need to know me again. I want to reintroduce myself to you. This is who I am. And this is how much I love you.”
Jesus said to His father, “Let thy Kingdom come, on Earth as it is in Heaven.” And as I walk around the safe, clean space of Casa Cruzeiro… chat with Iam over lunch, who became a Christian five years ago when reading a passage of scripture with Luke… hear about Monique, who with the team’s help, has been accepted onto a youth apprenticeship programme… look out from the roof top past the carefully nurtured community vegetable garden to the dark winding alleys and mish mash of favela shacks sprawling down the hill and into the city beyond….and watch Luke’s eyes lighten as he tells me about the young people that he and his team look after and walk through life with…
I realise this is what Jesus meant.