A couple of years ago I had a conversation with some friends that has stuck with me. One of them is a palliative care doctor, and we were discussing medical trends which seek the extension of life at all costs. My friends are Jewish, and we as were comparing religious notes, it was unsurprising that they asked me: "well what do Christians think about death?"
I replied, without really thinking: "Well, death is the enemy that is defeated." Somewhat to my surprise, their response was quite negative. "Oh, I don't like that idea. That pushes us towards denying our mortality, and trans-humanism, and the inability to let aged relatives go. We need to become better at welcoming death, at recognising it as part of our humanity."
And as I groped to try and explain why that wasn't quite what I meant, the best analogy I could find for articulating what Christians think about death came from Harry Potter. And in the years since that conversation, it is still the best analogy that I can find to talk about mortality.
So, here is the version of what I wish I had said.
The Harry Potter books have many themes, but above all they are about death. That may sound unlikely for a series of books apparently aimed at children, but the evidence stacks up...
The main character is an orphan, and the majority of people he comes close to will die across the seven books. (Now seems as good a time as any to mention that the rest of this article will basically all be spoilers, so maybe stop now if you've been putting off reading the books for the last 20 years. I'm also going to assume you are at least reasonably familiar with the plot).
Harry's life is defined by the death of his parents and his own close shave with mortality as a baby, and as the books continue the body count gets almost ludicrously high.
Indeed, the author J.K. Rowling has said that Harry is "the prism through which I view death in its many forms."
Unsurprisingly, given how central the theme is, there is a certain amount of explicit reflection on death, even if it is somewhat vague. Thus, we find that: "to the well organised mind, death is but the next great adventure." Dying hurts not at all, but is "quicker and easier than falling asleep." Those who die can "go on," perhaps by "boarding a train."
If all of this sounds a touch sentimental and the sort of thing that might appear in bad funeral sermons, it is paired with descriptions of grief that are visceral and deeply moving. (I may have cried more than once whilst doing the "research" for this article).
But where the discussion of death gets really interesting, at least to me, is in the plot, and the metaphysics that underpins it. By metaphysics I just mean the whole picture of the structure of reality that makes the world of Harry Potter work.
And in this metaphysics we find that death is indeed an enemy. This becomes clear partly through the sheer excruciating depiction of loss that runs through the books - how could something that causes this much pain be anything but an enemy? - but in book seven it is also made explicit.
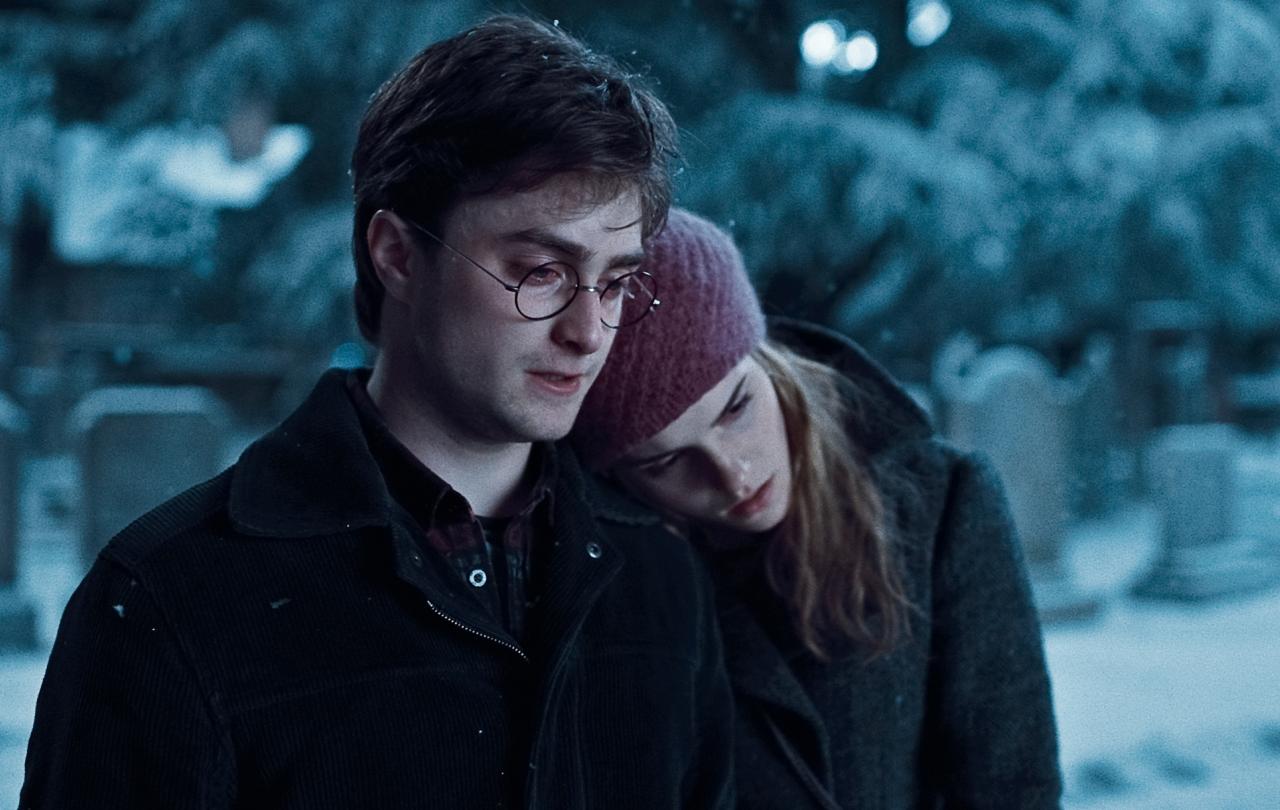
In one of my favourite moments of the whole series, Harry stands before his parents' gravestone, and reads the epitaph:
'"The last enemy that shall be destroyed is death"... A horrible thought came to him, and with it a kind of panic. "Isn't that a death Eater idea? Why is that there?"
"It doesn't mean defeating death in the way the Death Eaters mean it, Harry," said Hermione, her voice gentle. "It means... you know... living beyond death. Living after death."'
In Harry and Hermione's reaction to the quote on his parent's tombstone we find that there are multiple ways for death to be an enemy.
The Deathly Hallows sounds eerily like a current technological advancement: the rising trend of griefbots.
Book seven, in fact, presents three ways to defeat death, and they are highly illuminating.
Firstly, there are Horcruxes. This is Voldemort's project for immortality: the division of his soul via murder and the darkest magic, and the implantation of those parts of the soul into objects which guarantee that, even should he die, he will live on.
This is, I think it's fair to say, not a vision of the death's vanquishing which the books present as appealing - Voldemort is the darkest wizard of living memory, and the creation of his Horcruxes takes him deeper into evil than anyone has ever gone. Yet it has strange parallels to various current attempts at death defiance. Dividing your soul up and placing it in objects sounds pretty similar to me to uploading your consciousness into a computer.
Now I'm not saying that all transhumanists are evil wizards whose projects rely on murder, but I do wonder if the same impulse lies behind Horcruxes and downloaded consciousness.
There is, in both, the same fear of death, the same refusal to accept that my life might end. And there is the same default assumption that the body doesn't really matter - that the centre of my being is somewhere else, and that I can separate it from this inconvenient vessel which is so subject to injury and decay. The inevitability of bodily death is acknowledged, but life can go on even if my body fails, because I can place myself into objects. What matters is my consciousness, and that can be made eternal.
The second option is a little more complex: the Deathly Hallows. These are three strange, mysterious objects, possession of which promises to make the bearer "master of death." The wand that gives murderous power. The stone that brings back the dead. The cloak that conceals.
The Hallows dress up their promise in esoteric garb - they offer a quest for the initiated that requires a certain embrace of mystery, and they certainly seem friendlier than Horcruxes, since no one has to die to make them.
But in the end, as Dumbledore admits, they are not really that different from the Horcruxes, for those who seek them also respond to the temptation to defy death, just like Voldemort. And if Horcruxes are about preserving the soul in the face of the inevitability of bodily death, the Hallows tease the possibility of avoiding death altogether, through the exercise of power.
The wand gives the power of invincibility and conquest: the avoidance of death through the murder of all who might threaten to kill.
The cloak gives the power to hide, to keep out of trouble, to evade death by escape.
And the stone? The stone overcomes the loss of death by bringing its victims back, by refusing to accept that those we love might leave us.
Again, the Deathly Hallows sounds eerily like a current technological advancement: the rising trend of griefbots. There is the same attempt to respond to grief by clinging to simulations of those whom we mourn, and the same despair at the end of the line. For the dead do not belong with the living, we are told, and legend has it the first owner of the stone was driven to suicide.
The Hallows attempt to deny death through power, and this is why Dumbledore found them so alluring, and so destructive: they promised to wind back his own loss while giving him the victory he thought would give his life meaning.
And yet, in reality, even when Harry unites them all, they don't give what they promise. Indeed, they only work to their full power when they are used for humbler ambitions: to hide friends from danger, to perform wondrous magic without boasting in the glory of the wand, or to face death with the comforting presence of those who have gone before.
For the stone only becomes available to Harry when he finally embraces the third way to defeat the death. The way his parents believed in.
Death, in the Potter books, is defeated by dying. Or perhaps more specifically, by dying for love - love of children, love of friends, love of a world gone tragically wrong.
Harry's mother protected her son from dying multiple times, through the power of her sacrificially loving surrender. Dumbledore, in a complex way, protects Malfoy and saves the Elder Wand from Voldemort, thereby protecting the whole wizarding world, through his voluntary death. Even Snape, in the bitterest and most twisted story of them all, ends up giving Harry what he needs to win and finding a measure of redemption, in and through his own murder.
And, in the climax of this long, convoluted story, Harry avoids death by going willingly to die. Because he loves his friends. Because he hates others dying for him. Because he recognises the terrible duty he faces, the terrible path Dumbledore has laid out for him, and he loves too much to run.
Voldemort is wrong. Love does conquer death.
The parallels to the Christian vision of death are stark. The quote on the tombstone which sparks these reflections for Harry (and for me) is in fact from the Bible. "The last enemy that shall be defeated is death" is a profoundly Christian idea.
Yet my friends were right to react negatively to what they thought I meant by death being an enemy.
For, just like the good guys in Harry Potter, Christians have traditionally been suspicious of attempts at immortality on our own terms. The Bible, I would suggest, knows nothing of a technological defeat of death, whether through downloading our consciences, or radical life extension, or technologies of power. Death cannot be staved off by any of our own work.
But this does not mean that death is a good thing, simply a part of human existence which we would do well to welcome and learn to get along with (though I do think we would do better to think about death more, and be more honest about its existence).
Death is an enemy. It is the final enemy. We are right to rage against it. To grieve those whom we lose. To feel its existential weight.
Yet, perhaps paradoxically, we should not fear it. For death is an enemy that has been vanquished, but vanquished through Jesus' death.
Immortality is not, for Christians, something we achieve, but something that is given to us. We believe in the Saviour who dies, and who rises again, and in whose resurrection, as strange as it may sound, we also will be raised. Death is defeated by love, but it is not our love, it is God's love for us.
This gift, according to the early Christian writers, can only be received by going through death, not by avoiding death. Indeed, Paul's letters, which make up most of the New Testament, are full of the insistence that the pattern of Christian life is always death first, then life. Death in baptism, to new life in Christ. Death to sin, to life in freedom. Bodily death, to bodily resurrection.
And so, what I should have said to my friend, is that Hermione is right. Death is the final enemy to be defeated, but this does not mean the ways of the Death Eaters. It does not mean projects of immortality, whether rooted in science, or a mystery cult, or power over others.
Rather it means it life after death - a life that is given to us, by our saviour who has been through death and defeated it.
Death is the enemy but it is not our enemy to defeat. That victory was won for us, on Easter Sunday 2000 years ago, in a cemetery near Jerusalem, when Jesus rose again.
Celebrate our 2nd birthday!
Since Spring 2023, our readers have enjoyed over 1,000 articles. All for free. This is made possible through the generosity of our amazing community of supporters.
If you enjoy Seen & Unseen, would you consider making a gift towards our work?
Do so by joining Behind The Seen. Alongside other benefits, you’ll receive an extra fortnightly email from me sharing my reading and reflections on the ideas that are shaping our times.
Graham Tomlin
Editor-in-Chief