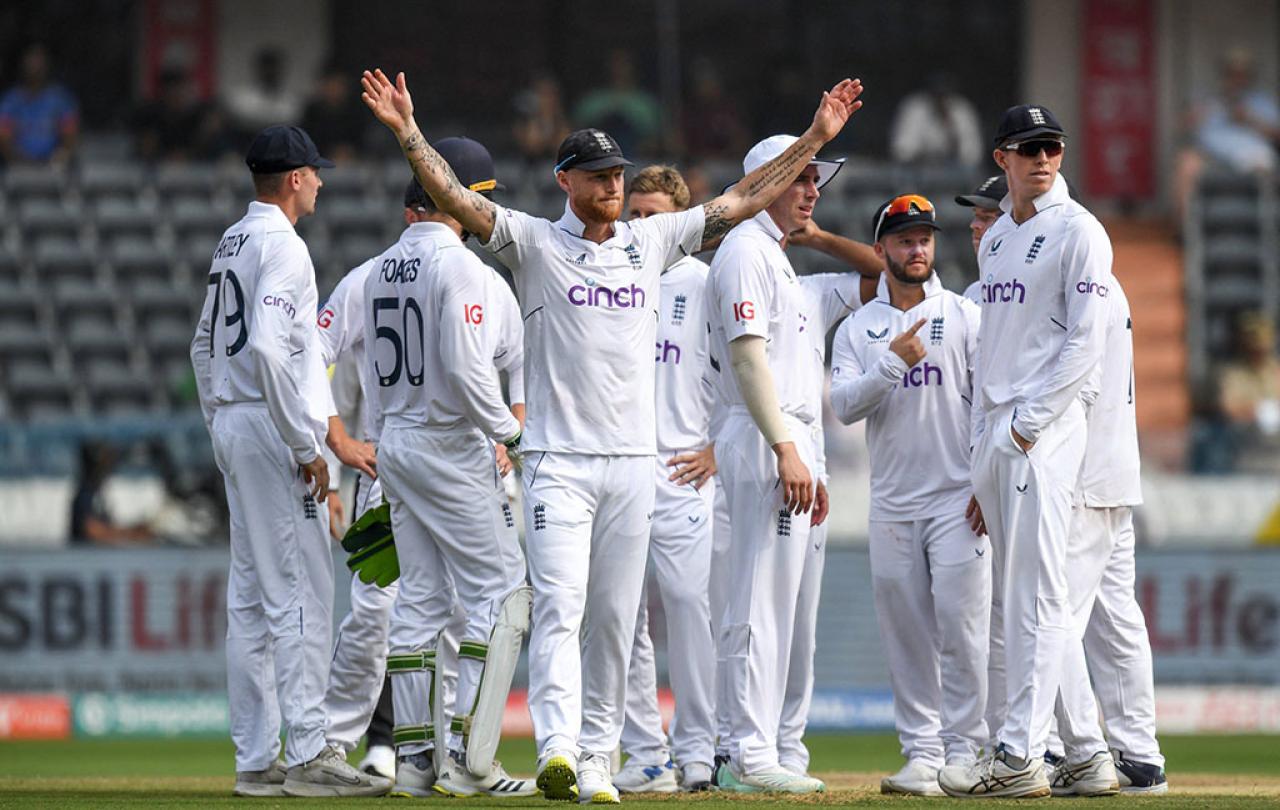
Back in May 2022, the way England played cricket got a new nickname - bazball. Coined by a journalist, it reflected the name and attitude of the pair who lead the team - .Brendon 'Baz' McCullum and captain Ben Stokes. Both had reputations as attacking players. That nickname has proven to be extremely prescient.
The name has accompanied England in the eighteen months since, describing their transformation from a side languishing with a record of one win in seventeen, to perhaps the most feared side in the world because of their aggressive style of play, winning twelve of their first thirteen tests with Stokes in full-time charge. This England team are currently testing their newfound confidence on an away trip to India where no side has won for eleven years, travelling with more optimism than at any point in the last decade, having whitewashed Pakistan last winter 3-0.
Bazball, at its core, is about freedom to fail. Stokes and McCullum realised that fear of failure was suppressing performances, so they took the burden from the players.
What is ‘Bazball’? It’s even made it into the dictionary, with its definition being ‘a style of test cricket in which the batting side attempts to gain the initiative by playing in a highly aggressive manner.’ This doesn’t go far enough.
The approach is not merely about batting but aggression in bowling, fielding, and team selection, encompassing almost a way of life. Recently retired fast bowler Stuart Broad summarising it as choosing ‘running towards the danger.’ Perhaps cricket journalist Ali Martin sums it up best; ‘to soak up pressure when required but also be brave enough to put it back on opponents at the earliest opportunity; to make taking wickets the sole aim in the field; and to strive chiefly for victory across the five days without considering the draw.’
All of this seems a little bit corporate-speak. Bazball has been accused of this fragility often; that it consists merely of good vibes and brash talk, and that the steam will soon run out of this new approach once some better teams are faced. But dig a little deeper and one principle stands out above the rest: freedom. Cricket can be a suffocating sport to play, even on a village green on a Saturday- a team sport, but one in which the bowler and batsman compete alone in a gladiatorial contest repeatedly. Scale this up to test level, with bowlers throwing them down at 90mph, thousands of spectators, the pressure of performing for your country, and the fight to keep your place in the team, and you can soon see how the pressure can become a burden.
Bazball, at its core, is about freedom to fail. Stokes and McCullum realised that fear of failure was suppressing performances, so they took the burden from the players- the talk of aggression, of running to danger, of attacking, is the permission to fail. By being prepared to lose, if the loss is a result of a determination to win, the fear of defeat is removed. Of course, without the intense pressure of defeat looming over them, players revel in this freedom and performances and results have dramatically improved. Almost all the batsmen have improved their average runs per innings and the bowlers have taken every wicket available except in one instance. Stokes has explained the freedom given in this way to the media:
‘[Bazball] has taken away all the external pressures of playing international sport. There's enough on individuals and as a team as it is but taking all the other stuff away is why everything is so relaxed, calm and enjoyable at the moment.’
Despite Bazball’s wider impact, with England football, rugby, and hockey all admitting to being inspired, does Bazball have anything to say to us outside of elite sport? It could be perceived as simply a method of getting performances out of cossetted professionals weighed down by expectation through a bit of team building and positive messaging. Instead of practicing cricket Stokes’ team practice golf. Players can now set their own bedtimes. How does this relate? However, it’s the stories of McCullum and Stokes that give bedrock to the ethereality of the Bazball concept.
Perhaps this is all Bazball is: cricket-with-context. It’s easy to give freedom from fear of failure when you’ve come close to losing everything.
In November 2014, promising Australian cricketer Phillip Hughes was killed by a bouncer in an Australian domestic game, shocking the cricketing world. Brendon McCullum at the time captained New Zealand’s test team, and Hughes’ death awoke something in him; a realisation that cricket didn’t matter all that much, and was best enjoyed as entertainment, both for the players and spectators. Already an aggressive player and captain, McCullum went into overdrive, playing aggressive but joyful cricket all over the world, freed from consequences and simply enjoying playing. His New Zealand team reached the World Cup final the following year and McCullum signed off with the fastest Test hundred of all time- 54 balls(!)- in his final test.
Stokes himself has walked in his own darkness; arrested in 2017 just as his performances were rocketing for England for violently defending a gay couple on a night out after a win in Bristol, he lost the vice-captaincy and a place on an away Ashes tour despite eventually being acquitted. In 2021, after sustaining an injury to his finger that would not heal, and amidst the death of his father, he wrestled with panic attacks and anxiety, ultimately taking a six-month break from the sport completely. It’s easy to see because of these stories why losing a game of cricket has come to matter less than enjoyment of the sport and playing in an entertaining and relaxed style. Perhaps this is all Bazball is: cricket-with-context. It’s easy to give freedom from fear of failure when you’ve come close to losing everything.
This is something Christians have known for centuries. The knowledge that your darkest sins and most crass mistakes aren’t fatal, but can be forgiven and wiped clean can give a freedom that transforms life. Rather than the anxious striving for perfection that can come in both religious and in secular forms, there is freedom to fail. After all, performance anxiety is a problem for social media influencers, hedge fund traders and teachers as well as cricketers.
Of course forgiveness can be abused as a kind of license to do what you want, knowing you'll get pardoned in the end anyway. But that only reveals a heart that acts out of self-interest, not love. Just as Bazball arises out of a sheer love for the game, as even more important than winning, so Christian behaviour arises, not from a desire to get away with as much as you can can, but out of love for God and your neighbour. And paradoxically - both approaches end up 'winning' more often than not - either successful cricket, or a healthy spiritual and moral life.
This is the graced existence: knowing that we are all free to fail because of the love of God who forgives. In an infinitely truer way than that Bazball is context-making for cricket, so this grace is context-making for life; held by this God in friendship, despite our petty sins and moral confusion. Just as Bazball allows cricketers to play with freedom, ignoring the pressure of expectation and simply enjoying the game, so humans can live with freedom, winning the battle against the limitations and pressure we put on ourselves, and simply enjoy being alive.
After all, if we offend, make awkward, or receive rejection, grace holds us. And if these things go well, our lives will be much richer.
The freedom to fail has released these cricketers to play the most exciting, aggressive, entertaining cricket they can. They have used their self-made context for good. How can we use our God-given context for good? In the same way: remembering that we are held by grace and able to live without fear, able to conquer our own pressures and expectations, the narratives of self-criticism that restrain us in our same old ways. If our actions had no consequences, what risks might we take? Perhaps we would tend towards the destructive like the scenes played out in The Purge. Or perhaps, held by grace, we could tend towards the constructive. Breaking the habits we know have held us back. Conversing with people outside of our comfort zone, seeking out their stories. Phoning the friend or family member with whom our relationship has broken down. After all, if we offend, make awkward, or receive rejection, grace holds us. And if these things go well, our lives will be much richer.
Sometimes Bazball is revered as a novel method to relieve pressure and extract performances from tense athletes, but the Christian faith demonstrates this is nothing new. Bazball might have revolutionised Test cricket, but Stokes and McCullum have simply rediscovered the freedom that comes from God’s gift of grace.