Introduction
For many people, Christianity and India appear as two distinct identities with Christianity being as foreign to India as India is to Christianity. They are surprised to learn that Indigenous Christians have maintained a continual existence in India since the time of the Apostles. And that, for centuries, Christianity has played a tremendous, yet underrecognized role, in shaping India’s artistic and intellectual history.
Examples of this include the vast collection of Christian artworks, produced by Hindu and Muslim court artists, of the Mughal Empire. And the synthesis of Christian social teaching and Gandhi’s political and philosophical views into a field now known as Gandhian economics, initially developed by the Indian-Christian, J.C. Kumarappa, who was an economist an activist for Indian independence.
This centuries old interaction between Christianity and broader Indian society continues into the present day with Indian cinema being a major arena for this. Despite its enormity and tremendous success across the Global South the attitude of many Westerners towards Indian movies lies somewhere between apathy and condescension. With the industry often erroneously perceived as a homogenous genre defined by three-hour run-times, over-the-top dance routines, syrupy dialogue, melodramatic acting, and campy fight scenes.
These stereotypes mask the sheer diversity of Indian cinema which since its inception, more than a century ago, has sought to depict the diversity of India and explore a vast array of ideas, including Christian themes and ideals, through creative storytelling. In many cases these films defy clear cut genres. We typically imagine a Christian film as possessing an explicitly religious message which it aims to impart on an exclusively Christian audience. These films exist in India but coexist with a parallel stream of movies featuring authentically Christian characters and themes targeting a primarily non-Christian audience where the aim is to illustrate Christian ideals to an unfamiliar audience. This creates a sense of subtlety in the film’s messaging that can be hard to find in many Western Christian films.
The goal of this article is to introduce readers to the relatively unknown world of contemporary Indian Christian cinema by highlight five films which depict the lives of Indian Christians and explore the challenge of living by Christian ideals in a chaotic world where right and wrong are not so clear cut. For context, the term Indian cinema refers to all cinema produced in India and encompasses films made in over two dozen languages. Bollywood is a nickname given to India’s Hindi language film industry which coexists alongside several other competing linguistic industries. For example, the 2022 film RRR, which one Best Song for the musical number Naatu Naatu at the 2023 Oscars, is a Telugu language film. This makes it an Indian movie, but not a Bollywood movie.
Kuttram Kadithal

Kuttram Kadithal is an independent Tamil language film which serves as a thought-provoking meditation on the complexities of morality, guilt and blame in an era where the public discourse is dominated by social media and 24/7 news cycles. Directed by Bramma, a newcomer director, and starring newcomer Radhika Prasidhha the film received significant film festival attention going on to receive several awards including the 2014 National Film Award for Best Feature Film in Tamil.
Merlin, a schoolteacher, administers corporal punishment, a practice that remains relatively common and accepted in India, on a student with an undiagnosed health condition. Though the actual punishment itself, a single slap on the cheek, was relatively harmless it causes the child to fall into a coma. The incident quickly erupts into a full-on media circus with Merlin, being advised by her school’s administration, to go into hiding until the situation calms down.
All the while, Merlin must come to terms with the range of emotions. Overcome by tremendous guilt and desperate for redemption she is also keen to avoid falling into the cross hairs of the media who have whipped up the incident with outrageously false allegations. It’s an interesting exploration of how people’s personal notions of right and wrong must be reconciled with society’s own judgement, regardless of how accurate or fair that assessment is. Merlin does feel remorse for her actions, but her assessment of the situation differs drastically from the sensationalist condemnations she was dealt from the media. Ultimately Merlin realizes that the path to forgiveness lies not with the media driven public perception of her by her own relationship with her victim and his grieving mother.
Ave Maria

Ave Maria is a 2018 Malayalam language film, not to be confused with a 2015 Palestinian short film with the same name. Set in Velankanni, a famous Roman Catholic pilgrimage site in South India, which attracts millions of pilgrims annually the film, follows the unlikely friendship of two very different people.
Maria Gomez, a young woman and devout Catholic from a well-off background, is now contemplating an abortion due to exceptional, and highly unique, circumstances. Believing it to be a sin, she decides to pre-emptively seek forgiveness and atone for the planned abortion by making a pilgrimage trip to the Catholic Shrines of Velankanni where she also plans to use her money to help transform the lives of a select few individuals in poverty or crisis. To do this, she enlists the help of Rex, a taxi driver and lapsed Christian, and the two set off to achieve Maria’s plan for atonement which goes disastrously and forces Maria to reevaluate her faith more closely.
At its core the film is an exploration on whether you can offset the harm of one sin, as Maria believes abortion is a sin even though she intends to have one, by committing good deeds elsewhere? Theologians will likely have a lot to say on this topic but the movie is more interested in the perspective devout but theologically uninformed believer. Her objective is further complicated by the messy reality of life. In one instance, Maria makes a sizable donation to a charitable old age home in exchange for housing an elderly beggar who has spent years on the streets of Velankanni. She is dumbfounded when she discovers the elderly woman back on the streets a little while later. When questioned, the old lady apologetically confesses that after years on the streets she simply cannot adjust to the regimented life of the old age home. Maria is now unsure as to whether this development undoes her previous good deed.
Kunju Daivam

Kunju Daivam is a 2018 Malayalam language children’s film. The film begins with a young boy, named Ouseppachan, who believes his prayers to postpone a math exam by any means necessary led to the death of his beloved grandfather, whose demise gets him pulled out of class right before the math exam begins. Upset by this, the boy takes to reading Bible scripture which leads him down the path of trying to find a kidney donor for a terminally ill neighbor, something most would agree is beyond the capacity of a young child. Along the way he eventually learns to make peace with his previous conviction that he was responsible for his grandfather’s sudden demise.
The film is an interesting exploration of the parable of the Good Samaritan, as understood by an innocent child. We all agree it’s good to help others, but society has also conditioned us to believe there are unspoken practical limits to helping others. Ouseppachan encounters this time and again in his quest, which the adults in his life look upon with admiration that turns to irritation when he refuses to give up. In one scene a priest, losing patience with his antics, admonishes the boy’s fixation on finding a kidney donor and directs him to more age-appropriate concerns like doing well in school. Ultimately Ouseppachan’s childlike dedication, forces us to reconsider our own attitude towards charity and helping others.
The Sky is Pink

This 2019 Hindi language film retells the love story between a married couple from the perspective of their daughter who is living with terminal pulmonary fibrosis and a severe immunodeficiency. The film is based on the true story of Aisha Chaudhary (1996 – 2015), whose memoir My Little Epiphanies was released just one day before her death.
The film is a depiction the struggles that families and children living with severe chronic illnesses and also a meditation on the inherent value of human life, even in the face of severe illness and hardship. These beliefs are most strongly held by Aisha’s mother, Aditi, whose conversion to Christianity allowed her to embrace the perspective that all human life is inherently valuable. This allows Aditi to come to terms with Aisha’s health issues and the death of a previous child who died shortly after birth. Aisha herself credits this belief as being the reason for her own existence.
I was also personally impressed by the decision of director Shonali Bose to depict Aisha’s mother’s conversion to Christianity and how these Christian beliefs impacted her parenting and perspective on life. Religious conversions, particularly to Christianity, had always been a contentious topic in India and at the time of this movie’s release the issue had transformed into an all-out moral panic with conspiracy theories claiming foreign funded churches had converted hundreds of millions with the intent of fueling social discord and separatist violence. Bose isn’t Christian and The Sky is Pink was never intended to be a Christian film. Bose was likely aware that by including the Christian aspect of this true story in her film she was opening herself up to the possibility of public outrage, boycotts and even political censorship, which have all grown increasingly common since India’s post-2010 majoritarian turn. Despite these risks, she opted to incorporate Aditi’s Christian beliefs into the film which aside from ensuring the film’s authenticity introduced many non-Christian viewers to an alternative perspective on Christian conversion.
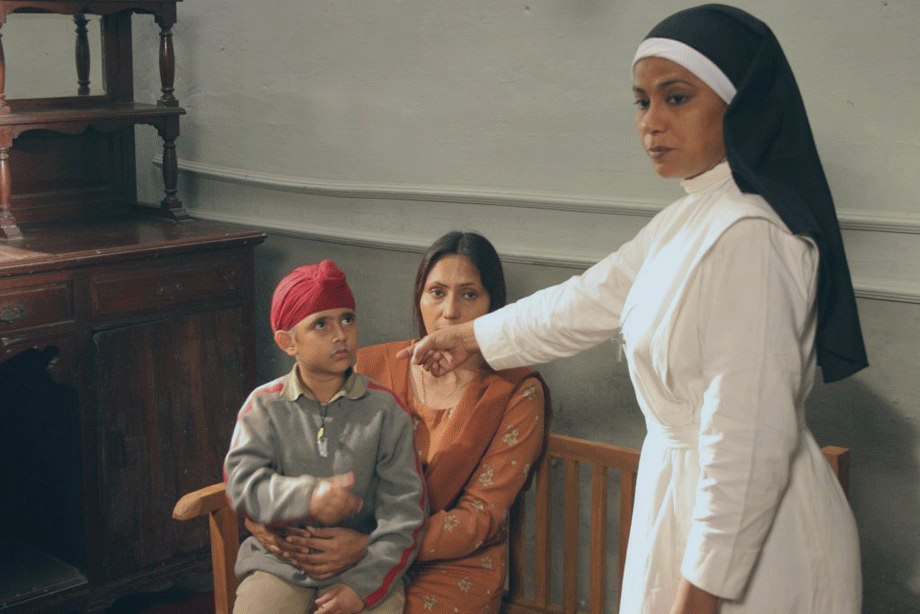
Kaya Taran

Explorations of religious violence and interreligious harmony are nothing new to Indian cinema. Even Western films set in India, like the 2008 British blockbuster, Slumdog Millionaire, feature depictions of the brutal violence that interreligious riots periodically unleash 1992. But the majority of these films tend to focus solely on the experiences of Hindus and Muslims during these riots.
The 2004 Hindi language film Kaya Taran takes an alternative approach. Set in a Catholic convent during the 1984 anti-Sikh riots which led to the deaths of hundreds of innocent Sikhs at the hands of rioters seeking revenge over the assassination of then Prime Minister Indira Gandhi by her Sikh bodyguards. It follows the lives of a group of nuns who offer shelter to a Sikh woman and her eight year old son seeking refuge from the riots and killings outside.
The film explores the growing relationship between the Sikh mother, her son Jaggi, and the nuns who especially grow to adore Jaggi and the shared sense of vulnerability they all face as religious minorities in a country where discriminatory violence is a very real threat. This is especially true for those who wear outward identifiers of their faith. For the nuns, it’s their religious habits, and for Jaggi it’s his long uncut hair and turban which the nuns initially cut to conceal his Sikh identity. The film concludes with a nun helping the young boy retie his turban, the boy no longer willing to hide his religious identity in the face of majoritarian intimidation and discrimination. His convictions serve as an inspiration for the viewers, many of whom have never experienced a situation where we were made to choose between our religious beliefs and our personal safety.
Conclusion
In this article we explored five Indian movies and their engagement with Christian themes. However, I should also mention that not all Indian cinema’s depictions of Indian Christians have been positive ones. For example, the long-standing trend of depicting Indian Christian women as hypersexual hedonists, whose behaviour is usually contrasted negatively against a more virtuous Hindu woman.
There is also the tendency to reverse exoticize Indian Christian society as White people in brown bodies for an audience that has had little personal contact with Indian Christians and tends to view the religion as a foreign import. One trope is to have Indian Christian characters speaking Indian languages in an inexplicably foreign sounding accents despite having grown up entirely within India.
The Indian audience is unique for its willingness to watch movies that present deeply spiritual messages from faith traditions which they themselves do not adhere to.
But, in an era where the Indian Christian community finds itself increasingly maligned in the public discourse, movies like the ones discussed above can play an important role in helping to present an alternative narrative. One rooted in the authentic, diverse experiences of Indian Christians themselves. The Indian audience is unique for its willingness to watch movies that present deeply spiritual messages from faith traditions which they themselves do not adhere too. A quirk which speaks to the inherently multicultural nature of Indian society where which has always consisted of diverse communities living side-by-side one another.