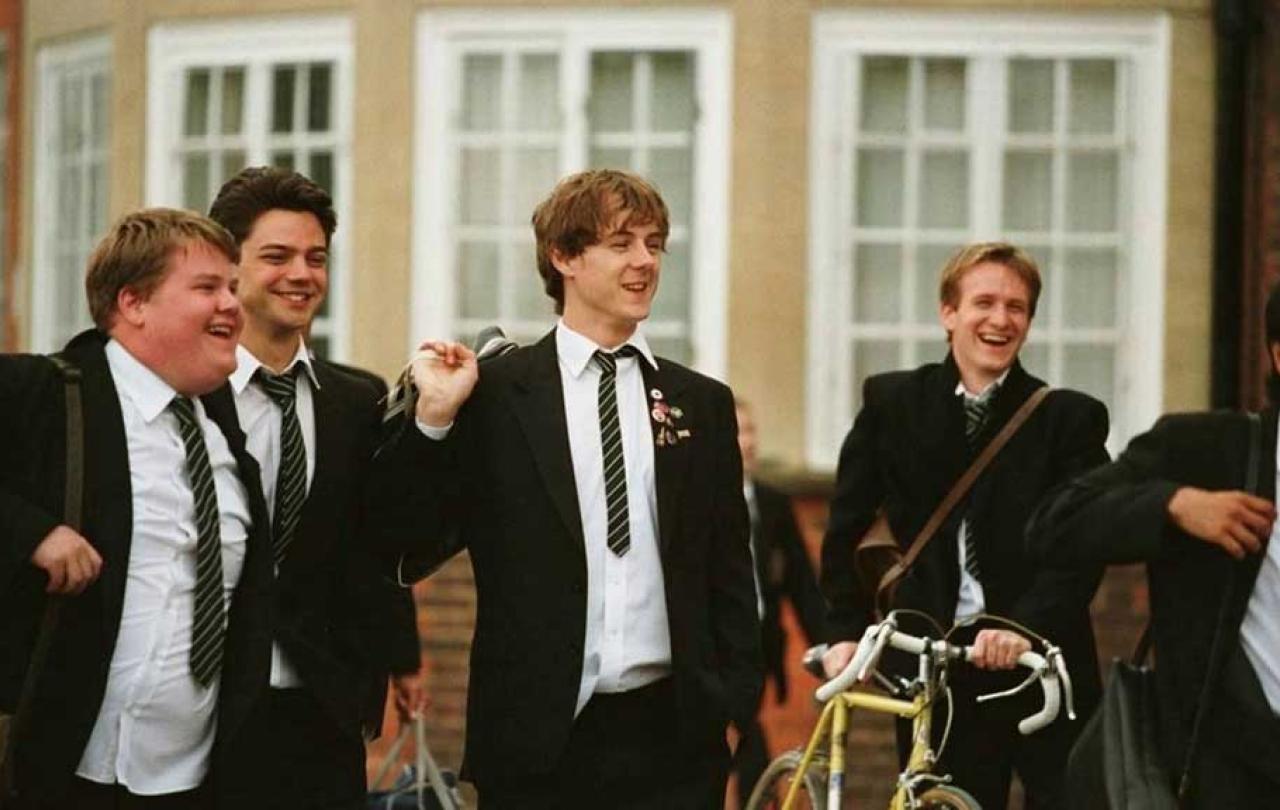
The summer is coming to an end, the last BBQ embers are sputtering to sleep, the weather…appears not to have been told, at least in London! Sweltering! Most importantly of all, our children are back to school, nursery or college. In light of this momentous time of year here are my top five back to school film choices, one each for the last five decades, and some honourable mentions.
1970s - American Grafitti
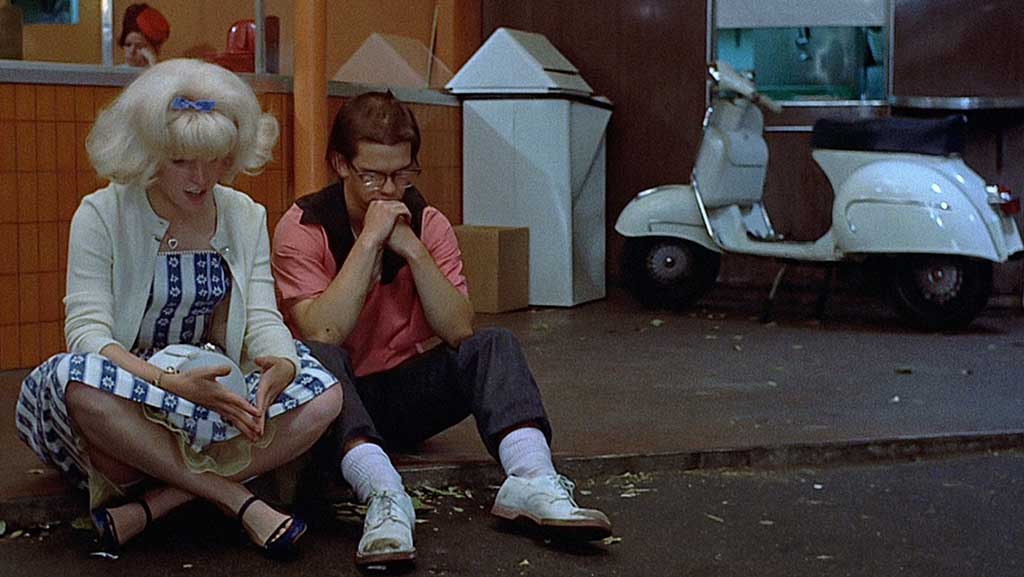

American Graffiti isn’t just a lovely piece of nostalgia now, it was back then. A misty-eyed look back at 60s Americana, this film is packed with slicked-back hair, classic cars, diners with roller-skating waitresses, and the complexities of teenage romance. Four friends meet on the last day of summer to experience the joys of a California evening one last time before two of them jet off to college ‘back East’. Curt is unsure about his future and is even considering staying in his hometown. Steve is hubristically thrilled about the prospect of fleeing his humdrum life and even shedding his loving girlfriend for new conquests. Terry is insecure and simply desperate to prove he is as good as everyone else, and Milner is the older friend who never left town and is a local-legend drag-racer. Over the course of a long night they go their separate ways, have adventures, and finally find some closure to their ongoing anxieties: one finds new confidence, another begins to take risks, another learns to be happy with his lot, and Milner wins a drag race…oh, an learns the genuine happiness that can be found in adult responsibility. It's too long, but it is a lovely atmosphere to meander about in, and is edited superbly so it never really drags. With superb performances and a soundtrack bursting with 50s and 60s hits, this is well worth a watch.
1980s - The Breakfast Club
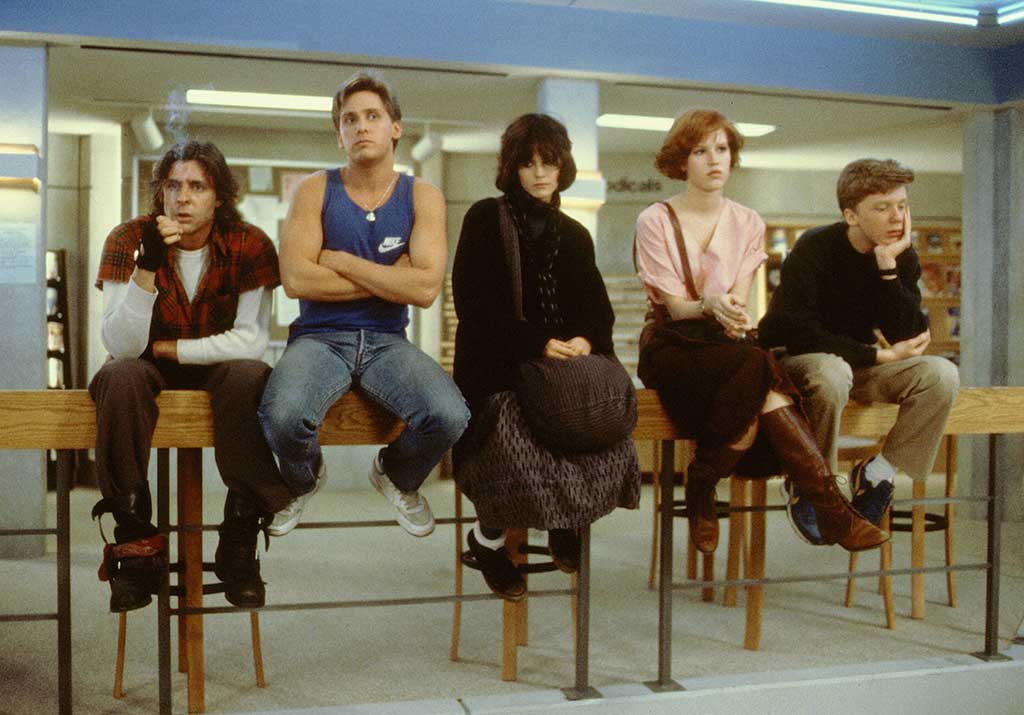

Well what else could it have been!? In many ways the film set the classic pattern of US High School living (which did and sometimes still does inform UK attitudes) and the High School movie. John Hughes didn’t invent these archetypes and wasn’t the first to put them on celluloid, but he was the master of crystallising them. The Breakfast Club presents an all-day detention that just so happens to have a representative from every social caste of the High School system: Andrew the jock (Emelio Esteves), Brian the nerd (Anthony Michael Hall), Allison the weirdo (Ally Sheedy), Claire the popular girl (Molly Ringwald), and Bender the burnout (Judd Nelson). These five kids have nothing in common but their dislike of the domineering Vice-Principal (Paul Gleason was born for this role!)…OR DO THEY!? Whereas American Graffiti explored the process of maturing into adulthood and the taking charge of one’s sense of self (with a background hum of Vietnam paranoia and the end of golden Americana days), The Breakfast Club is much more forthright in demonstrating just how difficult being a teenager is. These kids don’t need help ‘growing up’, if anything they need to be allowed to be kids. Over the course of the day their defences break down and they learn that each of them has expectations and pressures that seem overwhelming, and grown to have genuine respect and compassion for each other. A script that is sometimes on-the-nose and prone to soliloquy is saved by the sheer bravura of the performances. A go to comfort film, that will always be iconic. Any film which ends with Simple Minds is a 5 star affair for me.
1990s - The Faculty
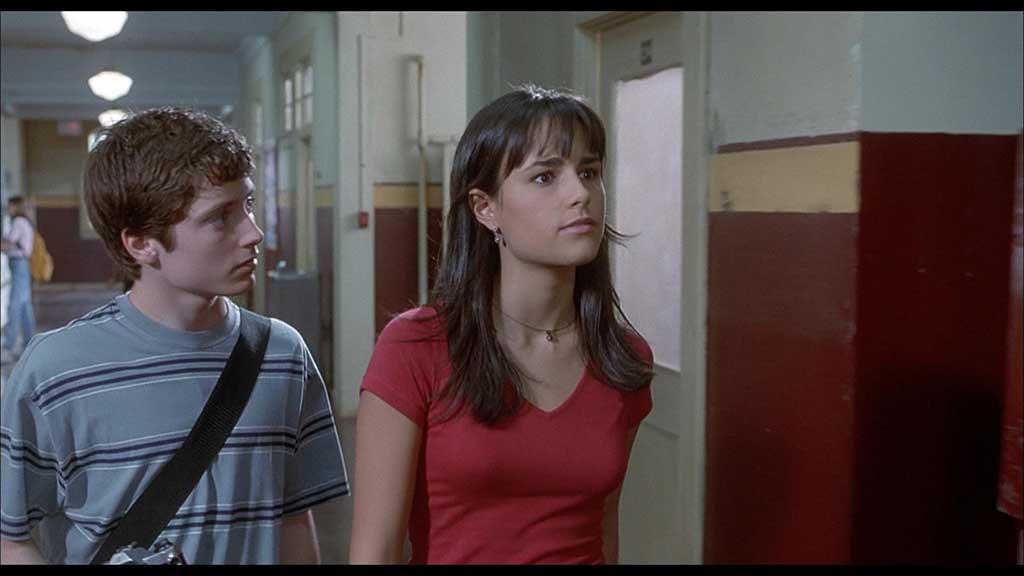

We move to slightly scarier fare with the 90s. The Faculty asks the question you were all asking…what if Invasion of the Bodysnatchers took place in an American high school? The answer is subtext; a lot of subtext and allegory. You know, when you’re a teenager, everything can seem quite tough. The world can seem like it's against you. It can seem like everyone you know has changed overnight and you’re lost in a sea of hostile faces. It can seem like a parasitic alien is using your school as a beachhead for a planetary takeover. The Faculty is cinematic junk-food and unapologetically so. It is camp and silly and fun. It takes those Hughesian archetypes, puts them on steroids, and then throws them into a plot joyfully riffing on the most classic sci-fi and horror tropes - all held nicely together with a quip-filled Kevin Williamson screenplay. An underrated Robert Rodriguez directorial effort which shows that he can work well across genres, and an excellent opportunity to see early performances from Josh Hartnett, Elijah Wood, Jon Stewart, and…wait…is that Usher in that film!?
2000s - The History Boys
Yes, we move to British shores at last. Alan Bennett’s stage-play is brought to beautiful cinematic life by original director Nicholas Hytner, who has an excellent track record of translating Bennett’s work from stage to screen. It’s another flash of nostalgia (which all such films are, as adult writers and directors look back to their own school days and teenage angst and adventure) which transports the viewer to 1980s Sheffield. A group of friends at the local Grammar School have all done very well in their A Levels and are now put to the task of preparing for the Oxford entrance exams. All are lovers of History (well, maybe not Rudge) and have received an enviously eclectic education in the full gamut of culture from the eccentric and long-suffering Hector. Like all the films above, The History Boys explores the challenges of adolescence, but with a specific focus on ‘doing well’ in a particularly British way. Sporting excellence or popularity aren’t the measure of student success - Oxbridge is. The teachers don’t push the young men nearly as much as they do themselves, seeing a place at Oxford as the best form of advancement. The witty and moving script also touches on the issue of infatuation, attraction, sexual fluidity, and chaste reciprocity: Posner’s love for Dakin being encouraged only so far in some sort of mutually agreed stand-off, Dakin’s willingness to sleep with the substitute teacher Irwin, and (of course) Hector’s tradition of giving the boys a ride home on his motorcycle and…appreciating them aesthetically. Not easy subject matter, but written and directed and shot and performed with such sensitivity that you can’t help but fall in love with every character.
2010s - The Inbetweeners Movie
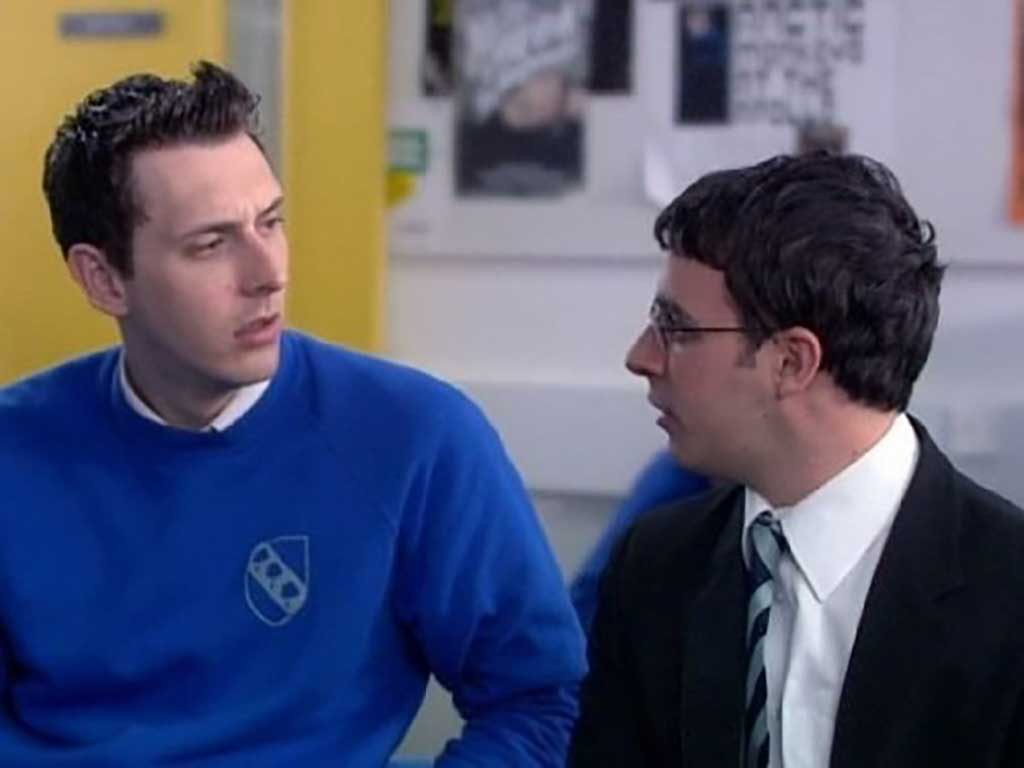

We end with crudity. Crudity and friendship and a booze-filled week in Crete. Lovers of the TV show (I was one) - which explored the trials and tribulations of four unpopular, unremarkable, and unfortunate teens at a British comprehensive school- were well served by this upgrade. TV comedies, like plays, rarely translate well; The Inbetweeners Movie is an honourable exception. Will, Simon, Jay, and Neil have come to the end of their school days and decide that they need one final hurrah before they go their separate ways. The proceeding 90 minutes is a torrent of drunken antics, foul-mouthed discourse, and crass toilet humour, all threaded together by hapless and fruitless sexual intrigue. 90 mins of that might seem like it would wear thin, but The Inbetweeners Movie is too kind-hearted to go stale (unlike its successor which was a genuinely squalid and unpleasant affair which had me questioning humanity). The four young men are so pathetic in the true sense of the word, that you can’t help but cheer for them. The overall message of friendship as a virtue that transcends the ups-and-downs of life give the salty humour a sweet edge. For a certain generation - mine - this might be the definitive British school movie.
Honourable Mentions
Grease
Sort of like American Graffiti…but better. I’m talking Travolta, I’m talking Newton-John, I’m talking songs that are bullet-proof! Graffiti is on the official list because it speaks to the many cultural and political undercurrents of the time…but Grease is so much more fun. If you can only see one of the two, see Grease!
Gregory’s Girl
Pipped by Breakfast because of the archetypes and Simple Minds, but probably one of the finest British rom-coms ever!
Mean Girls
Obviously. It's so fetch!





