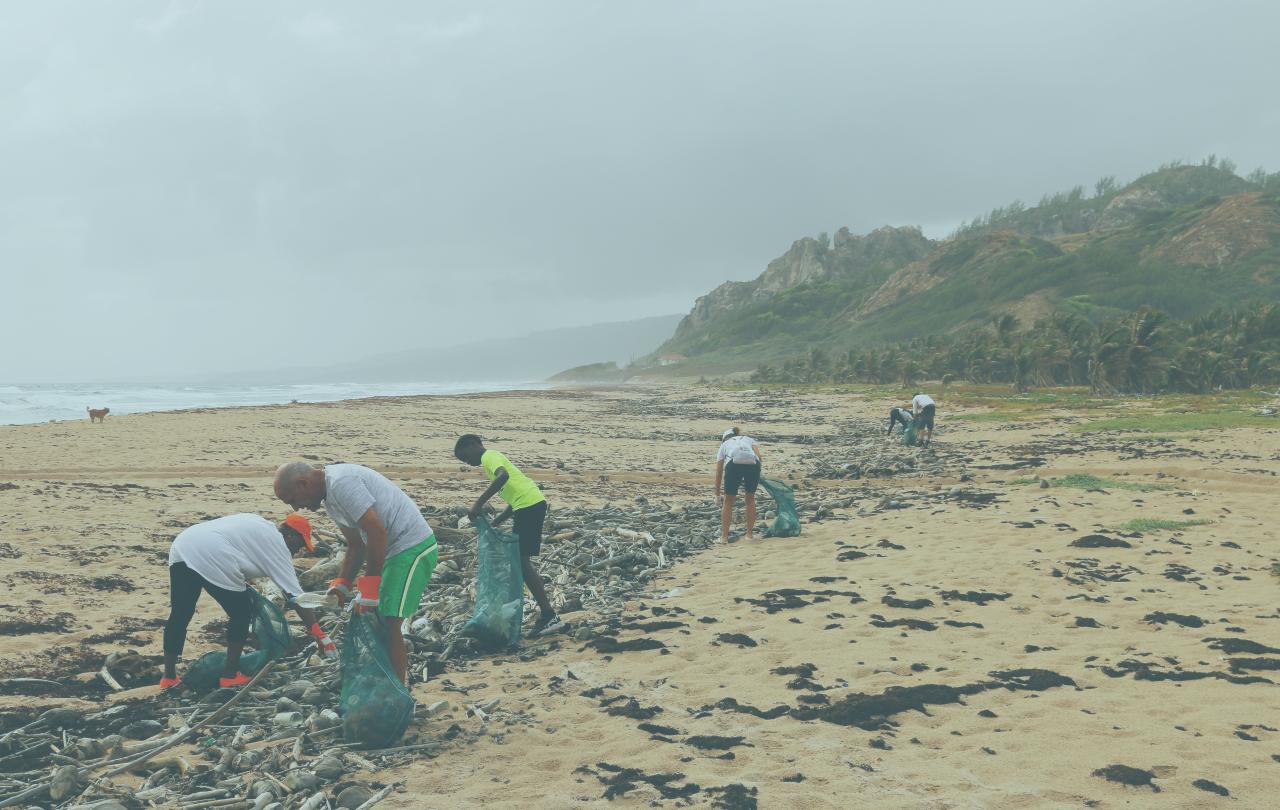
What on earth might the Easter story have to say about our climate catastrophe? What does this ancient story mean to us today, who know that the universe is fourteen billion years old and that, according to the best predictions, one day entropy will have its way with our world, leading to the universe either cooling down as it expands or rushing back together as gravity reasserts itself: the big chill or the big crunch? And what more urgently, might it mean in a world where we have woken up not only to man-made climate change but also to frightening levels of toxic pollution, in our seas, in the atmosphere?
John’s gospel is one of the sources of that ancient story. And the way the author tells it, gives us an answer.
A new story reflects an old story
Like Shakespeare, John does nothing by accident. The way the author introduces the story of Easter reaches far beyond the central fact of Jesus rising again from the dead. John’s point is that with that extraordinary event a new creation is launched. And that means hope – not just for individual humans, but for all creation.
On the first day of the week, very early, while it was still dark. That’s how John begins the story. Twenty chapters earlier, at the start of his book, he deliberately echoed the start of the book of Genesis: ‘In the beginning was the Word’. He has told his story in a great sequence of seven ‘signs’, representing as it were the ‘week’ of creation itself. Now, with Jesus’ resurrection, a new week is beginning: the eighth day of creation, if you like.
It takes everyone by surprise. At the time, many Jewish people had longed and prayed for God’s new day to dawn, but nobody had imagined it would look like this – a young Jewish prophet announcing that it was time for God to become king at last, being brutally executed by the ruling authorities, and then rising again from the dead. The hope of ‘resurrection’, cherished by many Jews at the time, was the hope for all God’s people to be given new bodies to share in God’s new world, the world in which heaven and earth would at last become one. Nobody imagined that this might happen, in advance as it were, to one person ahead of time. But by the time John writes his gospel he has reflected long and hard on what it all means. When he says ‘On the first day of the week’ – which he repeats a little later, in case we missed it – he is pointing to the truth that Paul expressed when he wrote that ‘if anyone belongs to the Messiah, there is a new creation.’ With Jesus, and then with his followers, we see in microcosm that the new creation has been launched.
Back on earth
This truth, central to the early Christians, has long been obscured by the influx of Greek philosophy into Christian thinking. For Plato, and those Christians who looked to him to help explain their faith, the point of it all was not to renew the present creation but to leave it behind. They supposed, as many Christians do to this day, that the aim of the their faith was to go to ‘heaven’ after they died, where they would at last see God. But the central story of the Bible, stretching back into Israel’s scriptures but focused now on the story of Jesus, is that ‘heaven’ was supposed to come to earth. That, after all, is what Jesus himself taught his followers to pray. The point was not that we – or our ‘souls’ – would go and live with God. The point was that God would come and live with us. The ‘God’ in question is the creator God. His aim, emphasized repeatedly in the Bible, is to renew his good creation, flooding it with his presence ‘as the waters cover the sea’. That is the biblical hope, quite different from that of Plato and his followers.
St Paul insists, at the climax of his greatest letter, that this will happen through a powerful, convulsive, fresh action of God. All creation, he says, is groaning like a woman going into labour, awaiting the new world which is to be born. And he sees Jesus’ followers as themselves ‘groaning’ in their present suffering; a majority of Christians in Paul’s world, just like a significant number in our own day, were being persecuted for their faith, and Paul encourages them to see that suffering as part of the larger cosmic labour-pains. But then, he says, God’s own spirit is also groaning within us, so that the new world which is to be born will come by the same divine agency that raised Jesus from the dead. In fact, Paul’s claim could be summarized that way: God will do for the whole creation, at the last, what he did for Jesus at Easter. The message of the resurrection isn’t just about God rewarding Jesus for his own terrible suffering. Nor is it simply about there being hope beyond death for his followers. It is about new creation – a new world in which we are all invited to share, not just eventually but already in the present.
Looking at the evidence, at the present state of the world, it might indeed seem that the promise of new creation is just a fantasy. But the message of Jesus’ resurrection was never designed to fit into the expectations people already had. Everybody knew perfectly well that dead people don’t rise. The Jews believed that one day all God’s people would be raised because they believed in two things about God: first, that he had made creation and made it good; second, that he was committed to putting right everything that had gone wrong. Creation and justice converge at this point: resurrection and new creation.
But Jesus’ resurrection, bursting into the world unexpectedly, like an important guest arriving several hours early when the family is all still asleep, adds another dimension to this. In Jesus, God himself has come forward in time to meet his tired and groaning world halfway. When the early Christians tell the story, they indicate that this is above all else an act of love: of rescuing, re-creating love. And that love invites an answering love, which takes the form both of faith itself and of allegiance, personal commitment. It takes basically the same faith to believe that God will one day renew the whole creation, flooding it with his glorious presence, as it takes to believe that Jesus rose from the dead. And that faith is awakened, again and again, as people hear the news about Jesus and realise that it is a message of love, the love of the creator God for his wounded and weary world.
A community of care
With that faith, and that love, there comes as well a new vocation. If Jesus represents the long-term hope of God’s people arriving unexpectedly in advance, in the present time, then part of the point is to equip people who follow him with his own spirit so that they can be agents of new creation even in the present time. That means a vocation to be small working models of new creation: to engage in advance in the tasks of creation care and renewal, and to encourage those working to address the major challenges of global warming and pollution. We are meant to bring into the world such a measure of justice and beauty as we can, to model in communal and personal life what the creator God always intended and what will come to pass in the ultimate new creation. We are meant to be people of hope: not just people who are motivated by the personal hope of sharing God’s new world, but people through whom that hope comes true in the present time in a thousand living ways, all of them anticipations of, and hence signposts towards, that final new creation.