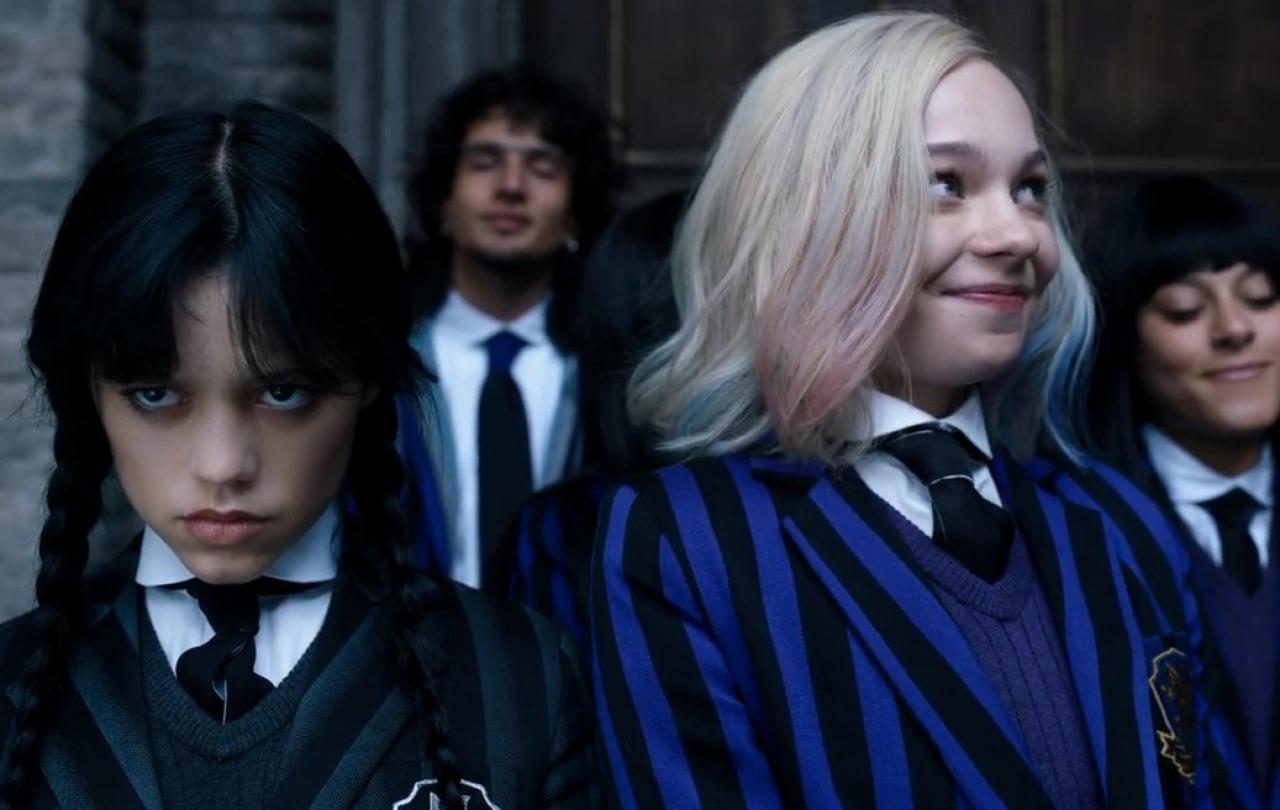
There’s something delightfully ironic about the mainstream success of Wednesday – Netflix’s Addams Family spin-off directed by Tim Burton. With its whimsy gothic aesthetic, star-studded cast and viral TikTok dance to boot, the first season was a highly bingeable hit in 2022. This summer, the split-release of season two scored over 50 million streams in its first five days. But beyond its cult-like reception lies something deeper: a collective reckoning with identity, acceptance and the desire to belong.
Jenna Ortega’s Wednesday Addams is an outsider among outsiders. Upon returning to Nevermore Academy – a supernatural boarding school meant to be a haven for ‘freaks, monsters and outcasts’ – she finds herself more alienated than ever. Don’t feel sorry for her: she’s difficult, destructive and I’m not sure I’d want to share a dorm with her (or her pet disembodied hand, Thing.) But that’s why we love her so much.
Wednesday ‘taps into that sense of not quite fitting in that everyone has,’ praised Marina Hyde on her The Rest is Entertainment podcast. ‘We all feel like we’re the kind of excluded weird mad kid from Burbank, as he [Burton] was growing up.’
C.S. Lewis termed the phenomena of not quite fitting in as the ‘Inner Ring’ – the unwritten systems of belonging that permeate all areas of life, from early youth into old age. It can neither be fully defined nor totally avoided. Lewis suggests that all people, at some point or another, experience this ‘desire to be inside the local Ring and the terror of being left outside.’ Ultimately, he warns, this pursuit of surface-level or self-furthering belonging ‘will break your hearts unless you break it.’
Lewis, one of Christianity’s most profound cultural influencers, was stirring a deeper call among his fellows Christians: to remember that the gospel is not just good news for those sitting comfortably in the pews – it’s good news for those outside. It’s good news for those searching for belonging in a world that prizes conformity and feasts on exclusivity.
Tim Burton’s genius lies in his ability to reach out, subverting the mainstream and dismantling the Inner Ring, seemingly with ease. Everyone’s an outsider, so no one is an outsider. As in Edward Scissorhands or Jack Skellington from The Nightmare before Christmas, Burton’s decision to not only tolerate but to celebrate the outcast bridges the gap between the socially excluded and socially accepted.
The sense of belonging that Burton creates doesn’t feel twee, manufactured or forced. It isn’t the sort of embrace that comes under strait-laced conditions, either. He cultivates spaces where the strange, the sad and the misunderstood become protagonists, empowered to tell their own story. He boldly platforms that which is different, unwilling to conform or compromise. Even the visual language of his work is distinct and unashamed, and his trademark scribbled twists and turns that creep into set designs, costumes and title sequences.
In Wednesday, this contrast is emphasised by a window that is half-spiderweb, half-kaleidoscope, dividing the room that Wednesday shares with Enid, the optimistic and bubbly roommate. They’re an extreme black-cat, golden-retriever pairing who have little in common, except for feeling that they don’t fit in.
Their desire for belonging and acceptance looks different. Enid cares very much about how others view her, whereas Wednesday’s cold defiance masks her vulnerability to be seen, known and accepted. This symbolic shared space, and the friendship that is imposed upon Wednesday by Enid, signals a deeper truth: belonging is not found in sameness, but in recognising what connects us and how we can honour one another in spite and because of our differences.
The subversive nature of Burton’s imagined universe holds a dim mirror to the liberating reality of God’s Kingdom.
While Burton elevates the outsider, his worlds often remain solitary and cut-off. But the Church, at its best, offers not just visibility but the embrace of fellowship. Jesus consistently chose people on the margins – lepers, tax collectors, women – and invite them into relationship. The gospel accounts for him taking less efficient travelling routes seemingly to encounter the lonely, the sick and the despised, to share news of their belonging to God, whose love for them was so strong that he would dwell not only among them, but within them through his Spirit.
The culture of the early church was informed by Jesus’ example, and their meetings were a mosaic of cultural, ethnic and social diversity, brimming with unlikely partnerships and clashes of custom. Paul reaffirmed the concept that all are ‘one in Jesus Christ’ in his letter to the church in Galatia, declaring that ‘there is neither Jew nor Gentile, neither slave nor free, nor is there male and female.’ This is not a call to erasure, but to radical inclusion. Rather than everyone being an outsider, as in Burton’s world, everyone is an insider in the Kingdom of God.
Perhaps it isn’t about whether Tim Burton or the Church has done more for outsiders, outliers and outcasts, but to invite personal challenge: Am I willing to get used to different? To disturb my norms, routines and expectations in the name of mutual inconvenience? To embrace a little mess and chaos for the sake of greater unity?
The subversive nature of Burton’s imagined universe holds a dim mirror to the liberating reality of God’s Kingdom, where the last are first, the poor receive a rich inheritance, and the margins become the centre. Where Burton’s audience may find solace in shared strangeness, the gospel offers something greater: a home not built on similarities and commonalities, but on divine welcome and spacious grace. And an unlimited set of keys to welcome others to their room, too.
Support Seen & Unseen
Since Spring 2023, our readers have enjoyed over 1,500 articles. All for free.
This is made possible through the generosity of our amazing community of supporters.
If you enjoy Seen & Unseen, would you consider making a gift towards our work?
Do so by joining Behind The Seen. Alongside other benefits, you’ll receive an extra fortnightly email from me sharing my reading and reflections on the ideas that are shaping our times.
Graham Tomlin
Editor-in-Chief





