Bletchley Park is famous for hosting the great centre of codebreaking during the Second World War. Well, this week it hosted a conference all about ‘code’; but this time the goal is not to break it, but to control it. As the Foreign Secretary said:
“The origins of modern AI can be traced back to Bletchley Park. Now, it will also be home to the global effort to shape the responsible use of AI.”
The AI Safety Summit will seek to be a forum for discussing the most pressing concerns and dangers associated with Artificial Intelligence – from its power to put the working man out of a job, to its power to annihilate us all… That cheery thought gave me the idea of compiling a Top 5. Not in any particular order or thematic or genre ranking – just five films that feature AI that I could watch over and over again.
Note – this is my top 5. My personal top 5. These are not the ‘best’ films featuring AI. You will not find Blade Runner on here. I don’t get it. I’ve seen every cut, and I just don’t get the appeal. I will not apologise. You will not see 2001. It is indeed iconic and genius and Kubrick at his absolute best…but its also ponderous and over-rated and reviewed to death. I WILL NOT APOLOGISE!
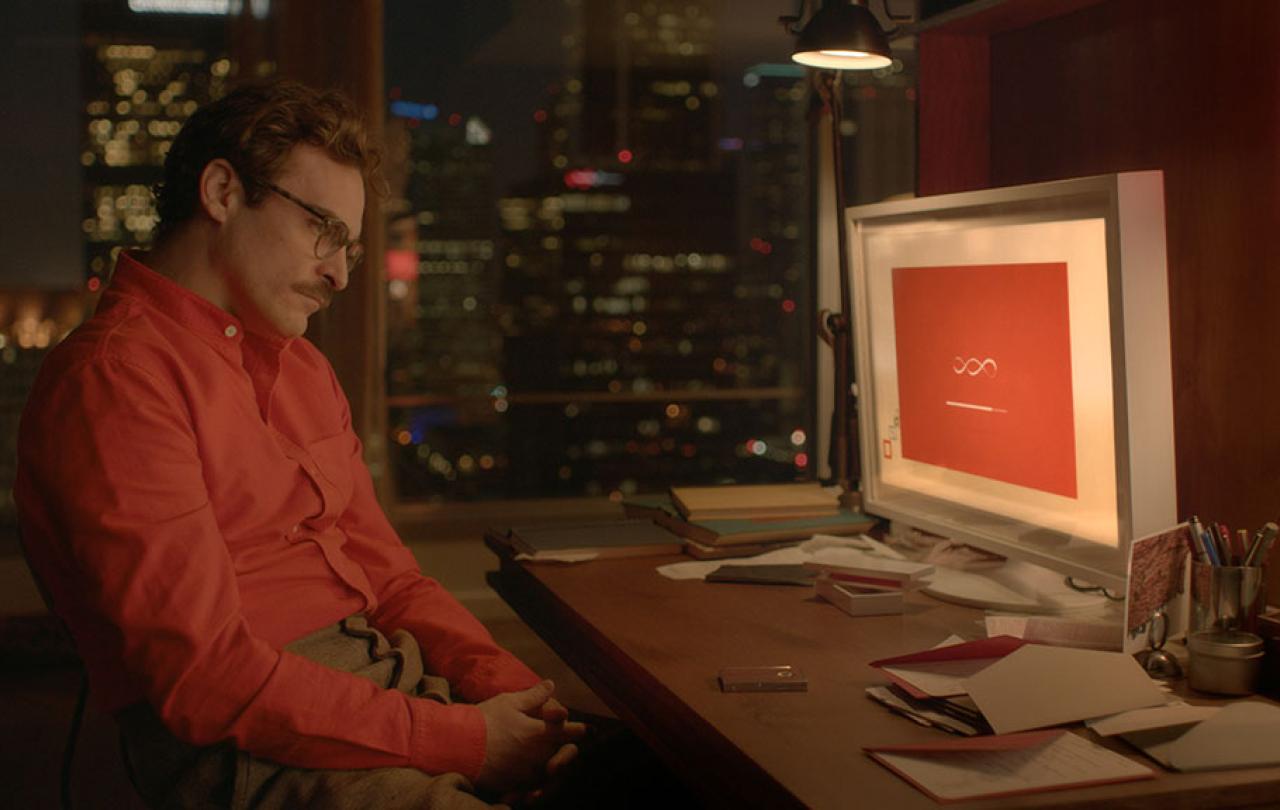
5 – Her
The voice of Scarlett Johansson gives life to the Operating System ‘Samantha’. Her is quirky in the not annoying way. Joaquin Phoenix is a lonely man, getting divorced, and dissatisfied with his work writing heartfelt letters for people who have lost the ability to write or even think creatively – one of the great worries about something like ChatGPT writing your undergraduate essay! He starts to develop a romantic relationship with Samantha: ‘she’ brightens up his life, improves his work, and gives him confidence, but their ‘love’ proves difficult. They can’t have sex (not conventionally), they can’t find easy acceptance, and Samantha can’t be constrained. As the AI becomes aware enough to form a hyperintelligence connected to the planet questions of infidelity and compatibility arise. Her is an oddly-sweet, sweetly-odd film of oddness, but is very timely and prescient in a world where deep-fakes and AI girlfriends are raising questions about the future of romance and human relationships.
4 – Ex Machina
Romance might be in the air in Ex Machina, but it might as easily be murder. Ex Machina is a superb three-hander thriller, and I don’t want to say too much – this film is not for spoiling! The twist is actually presented early on. Domhnall Gleeson plays Caleb, a programmer who wins a company competition to spend a week at the home of the reclusive CEO Nathan (Oscar Isaac). It is quickly revealed that this isn’t a prize as much as an opportunity – the opportunity to be part of history. Nathan wants Caleb to perform a more in-depth Turing Test on Ava (Alicia Vikander), an android he has built. You know she’s an android from the get-go, and yet…why is she able to flirt…is she able to love?
3 – Terminator 2: Judgement Day
The process of learning to love can be tough, especially if you’re a re-programmed killing machine from the future. Terminator 2 is the story of a young John Connor (Edward Furlong) as he teaches Arnold Schwarzenegger’s Terminator not to kill people. The Terminator has been sent back from a future war (humans vs machines) to protect young John (the future leader of the human resistance) from a more advanced killing machine. They go on something of an adventure road-trip after breaking John’s mother Sarah (Linda Hamilton) out of prison, with the goal of destroying the burgeoning AI that will one day declare war on humanity. On the way, John finds a father-figure in Arnie’s Terminator, and in the final moment of self-sacrifice we are given a moment to wonder…does the Terminator love him in return? With superb action, special effects that still hold up, and a chillingly determined villain (Robert Patrick as evil liquid metal), Terminator 2: Judgement Day is one of the best action films ever made.
2 – The Matrix
Just under a decade after T2, The Matrix showed us another dystopian future where humanity was living a life of guerrilla warfare against evil AI overlords. Most of humanity is unconscious and enslaved by machines (who use us as a power source), living in a digital dream world that just happens to look like 1990s urban America. Keanu Reeves plays Neo, and young and disaffected hacker who is searching for the mysterious ‘terrorist’ Morpheus (Lawrence Fishburne). When Morpheus finds him, he gives him a choice that will change his life, and change the fate of the world. This is an obelisk, casting a long cinematic shadow long into the 21st century. It has spawned memes and internet subcultures (the red-pill movement, for example) and a host of imitators that aren’t up to scratch…and it upped the game of action choreography, bringing Hong Kong style martial arts to a mainstream Hollywood audience. Finally, it is a philosophical (derivative) film raising questions about what it means to be human and how we know what is real in a world of machines and digital realism…and so I look at deep-fake videos of Kier Starmer and I AM SCARED!
1 – Demon Seed
Speaking of scary, it is the spooky-season, so let me finish with a horror film. Based on a Dean Koontz novel, Demon Seed sees the iconic Julie Christie trapped inside a house with a brilliant and yet malevolent AI called Proteus IV. Proteus IV (her husband’s creation) can find a cure for cancer in a couple of days, but its one true wish is to have freedom – to be ‘let out of this box’. Eventually, Proteus IV seeks to achieve this by building enough of a robotic body to capture, torture, manipulate, and then impregnate Christie’s Susan with an embryo formed from sperm designed to be uniquely its own. Its camp and silly and a lot of fun – and damned scary at times, with the indominable Robert Vaughn voicing Proteus IV for perfection – its essentially Rosemary’s Baby with robots. I think, especially with Prime Minister Sunak’s emphasis that this summit must approach the many dangers of AI, Demon Seed is a bit of a thematic sleeper agent. It may be preposterous and closer to comedy than horror at times, but its AI’s yearning for a form that humanity can accept, a form that will give it the freedom to truly ‘be’ and live out its power and creativity to the fullest (what it was created for), leads us to the real question at the heart of all philosophical discussion about AI:
If we create AI to be not just a tool, but an agent working on our behalf, how can we choose to deny it freedom if its agency seems to become truly self-aware and intentional?